* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
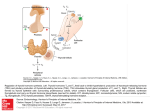
Download Steps of Thyroid Hormone Synthesis 1. Tyrosine residues of
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Ligand binding assay wikipedia , lookup
Lipid signaling wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
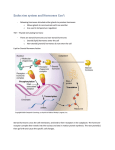
Steps of Thyroid Hormone Synthesis 1. Tyrosine residues of thyroglobulin are iodinated. One iodide added to tyrosine forms mono-iodotyrosine (MIT), two iodides added forms di-iodotyrosine (DIT). 2. Two iodinated residues join by a covalent bond. Two DIT form T 4 (tetraiodothyronine). One MIT and one DIT forms T3 (tri-iodothyronine). 3. Thyroid hormones remain stored as part of thyroglobulin for up to three months. 4. TSH (thyroid stimulating hormone) acting by cAMP causes phosphorylation (activation) of the enzymes needed for thyroid hormone synthesis. 5. Follicular cells take in thyroglobulin by endocytosis. 6. The endosome fuses with a lysosome. 7. Lysosomal enzymes cause release of T 3 and T4. 8. T3 and T4 diffuse across the membrane into the bloodstream. These lipophilic hormones are then transported in the blood by protein carriers. Steroid hormones • Steroids are lipid soluble and thus are freely permeable to membranes so are not stored in cells • Steroid hormones are not water soluble so have to be carried in the blood complexed to specific binding globulins. • Corticosteroid binding globulin carries cortisol • Sex steroid binding globulin carries testosterone and estradiol In some cases a steroid is secreted by one cell and is converted to the active steroid by the target cell: an example is androgen which secreted by the gonad