* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide 1 - AccessMedicine
Bioidentical hormone replacement therapy wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (male-to-female) wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (menopause) wikipedia , lookup
Signs and symptoms of Graves' disease wikipedia , lookup
Hypothalamus wikipedia , lookup
Growth hormone therapy wikipedia , lookup
Hypopituitarism wikipedia , lookup
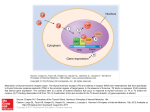
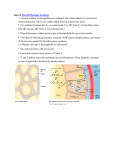
Regulation of thyroid hormone synthesis. Left. Thyroid hormones T4 and T3 feed back to inhibit hypothalamic production of thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) and pituitary production of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). TSH stimulates thyroid gland production of T4 and T3. Right. Thyroid follicles are formed by thyroid epithelial cells surrounding proteinaceous colloid, which contains thyroglobulin. Follicular cells, which are polarized, synthesize thyroglobulin and carry out thyroid hormone biosynthesis (see text for details). DIT, diiodotyrosine; MIT, monoiodotyrosine; NIS, sodium iodide symporter; Tg, thyroglobulin; TPO, thyroid peroxidase; TSH-R, thyroid-stimulating hormone receptor. Source: Endocrinology, Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine, 19e Citation: Kasper D, Fauci A, Hauser S, Longo D, Jameson J, Loscalzo J. Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine, 19e; 2015 Available at: http://mhmedical.com/ Accessed: May 03, 2017 Copyright © 2017 McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved