* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CHM 105 - Test 3 Review
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Catalytic triad wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
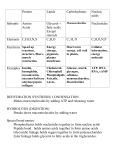
CHM 105 - Test 3 Review (Chapters 16-18) 1. What is a peptide linkage? CO 22. A tetrapeptide contains ____(#) amino acids. NH +3 H 3. The amino acid at right is in its _____ configuration. 4. An ion having both a positive and negative charge is a ________________. CH 3 5. To which of the four classes of amino acid does cysteine belong? 6. Draw the tripeptide: alanine–lysine–aspartic acid. What type of bond links the amino acids? Draw an arrow to this bond. 7. What are the four levels of protein structure? What level is given for the tripeptide above? 8. What is denaturation of protein? What can cause this to happen? Is it permanent? 9. What is the function of a transport protein? Give an example. 10. Which of the following are macromolecules? proteins, lipids, carbohydrates 11. What is the net charge on cysteine, pI=5.1, when the pH=6.3? Which way will it move during electrophoresis? 12. The names of enzymes often identify the substrate and then end with -________ (suffix). 13. An enzyme that will catalyze the reaction of only one molecule has _____________ specificity. 14. The sit on the enzyme where reaction occurs is known as the ___________ site. 15. These substances bind to the enzyme and interfere with the reaction. _______________ 16. Two main categories of nucleic acids. (full names) ________________________________________ ______________________________________ O Name the three subcategories of one of the nucleic acids above. Be sure that you know the purpose of each. 17. What are the building blocks of nucleosides? N HN 18. Give the name and type of base shown at right. H2N N N 19. What is the anticodon for the codon UUC? For what amino acid does this code? H 20. DNA is sometimes made from RNA by ________ viruses. This process is called _____________________? 21. Nucleic acids are synthesized from their ____ end to their ____ end. 22. Define: antiparallel, termination code, frame shift mutation. 23. Give two other names for the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle. 24. Glycolysis begins with the molecule _____________ and ends with the molecule ______________. 25. What organelle produces most of the cell’s ATP? By what pathway? 26. The conversion of glucose to CO2 yields approximately ____ ATP. 27. Each FADH 2 yields approximately ____ ATP in oxidative phosphorylation. 28. During fasting (starvation) our bodies produce glucose for the _____(organ) by a process called _____. 29. Proteins are synthesized at the __________________(organelle) from the ______________ end to the ________________ end. 30. Write the complimentary strand for dA-C-G-C-A-A-G. 31. Give an example of the strand above with a point mutation. 32. What are most likely outcomes for the cell if an uncorrected mutation occurs in the DNA? 33. During glycolysis fructose-1,6-diphosphate is broken into these two 3 carbon phosphates _____________________________ and _____________________________ which are then converted to pyruvate. Without oxygen (anaerobic), the pyruvate is converted into ______________ to recycle the reduced coenzyme ________ back into the oxidized coenzyme ________ so that glycolysis may continue. 34. How many acetylCoA’s are produced from a 12 carbon fatty acid? _____ By what pathway? ___________________________ Producing the equivalent of how many ATP? _____ 35. Which stage of catabolism produces the bulk of the CO2 ____, ...the H2O _____ ...the ATP? _____ 36. Stage one of catabolism is commonly called _____________. For fats this occurs in the ______________ forming __________________ and ______________. 37. Which pathway, cycle, or spiral produces a GTP that is converted to an ATP?