* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Study Link Help - Everyday Mathematics
Infinitesimal wikipedia , lookup
Philosophy of mathematics wikipedia , lookup
Numbers (TV series) wikipedia , lookup
Positional notation wikipedia , lookup
Location arithmetic wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics of radio engineering wikipedia , lookup
Georg Cantor's first set theory article wikipedia , lookup
List of important publications in mathematics wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics wikipedia , lookup
Collatz conjecture wikipedia , lookup
History of mathematics wikipedia , lookup
Large numbers wikipedia , lookup
Proofs of Fermat's little theorem wikipedia , lookup
Non-standard analysis wikipedia , lookup
Secondary School Mathematics Curriculum Improvement Study wikipedia , lookup
Real number wikipedia , lookup
Foundations of mathematics wikipedia , lookup
Hyperreal number wikipedia , lookup
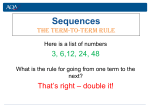
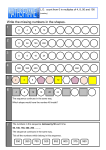
Everyday Mathematics S C H O O L M AT H E M AT I C S P R O J E C T Study Link Help: Number Sequences Number Sequences are lists of numbers. Some number sequences you might be familiar with are odd numbers, even numbers, or square numbers. Number sequences usually have a rule for what number will come next. In Everyday Mathematics, the rules for number sequences generally involve one or more arithmetic operations. Help with Study Link Problems A visual form for number sequences in early grades is the Frames-and-Arrows diagrams. Drawing a Frames-andArrows diagram might support your child in figuring out the missing numbers. For more information about Framesand-Arrows diagrams see Student Reference Book pages 160 and 161. Example: Find the missing numbers in the number sequence below For the above example, the rule might be written as “add 2” or “+2” and the missing numbers are 30, 34, and 36. Extra Practice Ideas • Skip counting with your child is one way to practice number sequences. You might skip count by easier intervals like 2, 5, or 10. (by 5s –5, 10, 15, 20, etc.) As appropriate, use more difficult intervals like 3, 4, or 7. (by 7s –7, 14, 21, 28, etc.) • Increase the difficulty by starting at different numbers when skip counting. For example, count by 3s, but begin with 5. (by 3s –5, 8, 11, 14, etc.) • Encourage your child to record the rule in both words and a number model. When skip counting by threes, the rule might be “plus three,” “add three” or “+3.” CENTER FOR ELEMENTARY MATHEMATICS AND SCIENCE EDUCATION Home of the author group of Everyday Mathematics 1