* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 18 lectures as pdf
Woodward–Hoffmann rules wikipedia , lookup
George S. Hammond wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Enantioselective synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Ring-closing metathesis wikipedia , lookup
Diels–Alder reaction wikipedia , lookup
Hydroformylation wikipedia , lookup
Discodermolide wikipedia , lookup
Ene reaction wikipedia , lookup
Wolff rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
Wolff–Kishner reduction wikipedia , lookup
Asymmetric induction wikipedia , lookup
Hofmann–Löffler reaction wikipedia , lookup
Baylis–Hillman reaction wikipedia , lookup
Petasis reaction wikipedia , lookup
Strychnine total synthesis wikipedia , lookup
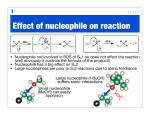
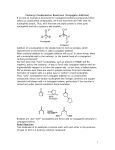
Enols, enolates, aldol • Problems – 16.23, 16.25, 16.26, 16,27, 16,28, 16.31, 16.33, 16.35 – 17.20, 17.23, 17.25, 17.26, 17.27, 17.28, 17.29, 17.32, 17.34, 17.36, 17.39, 17.43 – 18.23, 18.25, 18.31, 18.32, 18.35, 18.37, 18.39 Recap O Nuc-H OH Nuc if Nuc is strong base - not reversible O acid H if Nuc is weak base, may reverse, Drive to O completion by condensation base Nuc O Nuc Strong bases • Grignard • Hydrides • Alkynyl anions • Additional – no need for acid or base catalysis (reagents all strongly basic) Weaker bases • Water – hydration • Alcohols – hemiacetal, reversible, acid catalysis leads to loss of water, acetal isolated if water removed (protecting group) • Primary amines – imines if water removed • Secondary amines – enamines if water removed This chapter • Less basic sources of nucleophilic carbon • Formation of C-C bonds but some chance of reversibility • Strategies for control of reversibility • Use in synthesis • Related reactions Hydrocyanation H C N H CN Weak Acid Cyanide anion can be a nucleophile, but addition to C=O reversible Can't use acid catalysis, toxic gas Reaction only favorable where steric effects make it favorable (recall hydration) H NaCN N H N acid H O O HO OH O N O Poor yield Carbonyl species • We have seen as electrophile • Also exists in a nucleophilic form • These forms react with one another – Enol – Enolate anion • Useful – adds much complexity • Biomimetic Enol Equilibrium O O O OH H O OH O OH O Electron withdrawing groups O O O 9 15.5 H 9.1 HCN O O 15.8 O 11 O O O O 13 O O 22 O Acidic H is α hydrogen O O O H O H O H O O H α halogenation of carbonyls Br H acid H Br2 O O O O acid Br2 Br Haloform test – methyl ketones base O HO + CHBr3 Br2 O base O HO O + CHBr3 Br2 Aldol reaction – base catalyzed H H O O O O H H OH H H Aldol Reaction – acid catalyzed H H O OH O O H H OH H H Mixed Aldol reaction O O H H O H OH H H O O H Consider α,β-unsaturated C=O • Alkene now electron-poor, can react with nucleophiles • Thus two sites for nucleophilic attack • Called 1,2 and 1,4 (or conjugate addition) • 1,2 addition is kinetic • Conjugate addition is thermodynamic • Cuprates also do conjugate addition O O O Nuc Nuc Nuc HO 1,2-addition O conjugate addition Irreversible Additions O OH CH3Li H2O or CH3MgCl LiAlH4 or NaBH4 OH examples of kinetic reaction, 1,2-addition Conjugate Additions • • • • Reversible nucleophiles Cuprates Enolate anions – Michael Addition Robinson Annellation reaction O Nuc OH Nuc fast but reversible for many nucleophiles O slower but more stable, actually isolated Nuc Examples O O CH3NH2 N H O O CH3CH2OH O O O NaCN NC Cuprates O O (CH3)2CuLi mechanism complex example above - prostaglandin synthesis Enolates – Michael Addition O O O O O O O O O O O O O O Robinson Annelation • Alternative method to form six member rings • Michael addition followed by aldol condensation • Often used in steroid syntheses – alternative to Diels-Alder O O O O O O HO O O O H Alkylation of Enolates • Use in Sn2 reactions to make C-C bonds • Difficulty – competing aldol reaction • Alkylation will only work where the enolate can be formed in absence of starting C=O • Thus only useful for highly acidic enolates O O O O O O NaOCH 3 O O NaOCH 3 O O O O CH3-I O O CH3-I O O O O O O O need strong enough base to prevent reverse reaction, but will not add to C=O N Li LDA