* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CHE 297 Organic Workshop
Discodermolide wikipedia , lookup
Ring-closing metathesis wikipedia , lookup
George S. Hammond wikipedia , lookup
Hydroformylation wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Tiffeneau–Demjanov rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
Acetaldehyde wikipedia , lookup
Asymmetric induction wikipedia , lookup
Baylis–Hillman reaction wikipedia , lookup
Strychnine total synthesis wikipedia , lookup
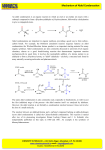
CHE 297 Organic Workshop Problem Set 7B March 5, 2007 Although the aldol condensation has not yet been covered in lecture, today’s problem set should teach you how to do it. A. Translate the following text into a mechanism with structures and conventional curved arrows. Step 1 A base (use hydroxide ion) removes the acidic alpha hydrogen from a molecule of acetaldehyde (ethanal) to form an enolate anion and a molecule of water. Step 2 The enolate anion attacks the carbonyl group of a second molecule of acetaldehyde. That intermediate is then protonated to form a beta-hydroxyaldehyde (3-hydroxybutanal). Step 3 The beta hydroxylaldehyde undergoes an elimination reaction (OH is the unusual leaving group here) to form an alpha, beta-unsaturated aldehyde called crotonaldehyde (2-butenal). B. Complete the following reactions. All except #2 are examples of the aldol condensation or variations on the same theme. In #2 the enolate anion formed with LDA is alkylated by benzyl bromide in an S N2 reaction. Write a mechanism for #5. H 1. 2 KOH, H2O heat O 2. 1) LDA O 2) PhCH2Br O 3. O NaOH, H2O H + heat O O 4. Ph Ph + Ph Ph heat O O KOH 5. heat O NaOH