* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Organic Compounds
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Carbon sink wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Biosequestration wikipedia , lookup
Isotopic labeling wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
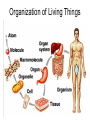
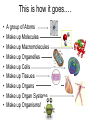
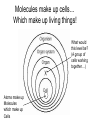
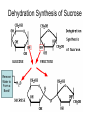
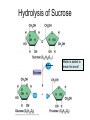
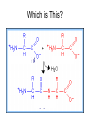
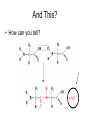
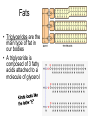
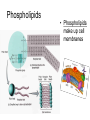
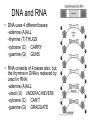
Bio-Chemistry Basics • Cells are complex chemical factories What Makes Up Everything? • Everything in you and around you is made up of Elements (atoms) • Living things are made up (mostly) of CARBON, HYDROGEN, OXYGEN, NITROGEN and PHOSPHOROUS – Remember PONCH – Mostly, CHON Elements….(ATOMS) The Principle… • Matter can not be created or destroyed • Matter can only change forms • So, how does the Oxygen we breathe in end up changing into Carbon Dioxide? • How does the Carbon Dioxide we breathe out end up in the Glucose we need? – Chemical Bonds Change… Bill Nye - Atoms Organization of Living Things Atoms become Molecules… • A molecule is formed when two or more atoms join together through chemical bonding – Molecules can be made of the same element: A molecule of oxygen = O2 – Molecules can be made of different elements: A molecule of water = H2O • Chemical Bonds are made and destroyed all of the time! – Synthesis and Digestion (Remember: LYS) This is how it goes…. • • • • • • • • • A group of Atoms Make up Molecules Make up Macromolecules Make up Organelles Make up Cells Make up Tissues Make up Organs Make up Organ Systems Make up Organisms! Molecules make up cells… Which make up living things! What would this level be? (A group of cells working together…) Atoms make up Molecules which make up Cells Metabolic Reactions • There are many different Metabolic Reactions that occur in your body Metabolism is the sum total (all) of the chemical activities that go on in your body Metabolic Reactions Cont’d • Your body can join two sugars together by removing a water (H2O) molecule – This is called dehydration synthesis (because you REMOVE water to BUILD a bond) • This reaction can be reversed and the sugars separated by adding water (H2O) to break the bond – This is called hydrolysis (because you DESTROY a bond by adding water) • “LYS” = destroy! Dehydration Synthesis of Sucrose Remove Water to Form a Bond! Hydrolysis of Sucrose Water is added to break the bond! Which is This? And This? • How can you tell? Dehydration Synthesis and Hydrolysis Occur ALL the Time in Your Body! • Let’s review the vocabulary words: – Metabolism • All the chemical reactions that happen in an organism – Dehydration (De: Remove Hydr: Water) • So, remove water! – Synthesis • Build/create something more complex – Hydrolysis (Hydr: Water Lys: Destroy) • Use water to break/destroy something Dehydration Synthesis and Hydrolysis Occur ALL the Time in Your Body! • Enzymes are responsible for ALL chemical reactions! – They lower the “activation energy” of the reaction • Enzymes help to build complex molecules • As well as break them down – “Digest” them! Metabolic Reactions • In our body... and in every cell, compounds are built up and broken down by enzymes • Enzymes assist the process of making and breaking bonds – Enzymes are proteins which control the rate of specific chemical reactions – Enzymes only work on one specific reaction • The lock and key model We will learn more about this later… Let's Go Back A Bit... • Living Organisms are mostly made up from the elements: C, H, O, N • Carbon is the MOST important of these elements! • Carbon is super cool because it kinda looks like this: Carbon • Matter can not be created nor destroyed... • Matter can only be changed... • Which means the bonds that hold the elements together can (and do) change! • And, Carbon is especially good at changing because it can make 4 bonds at one time! – Carbon can hook up with one type of element or 4 different elements to make something different! Carbon, Cont'd... • Carbon can form long chains: • Or, Carbon can fold back on itself to make a “ring” like this: Each “C” has 4 bonds! What’s Important about Carbon? • Carbon is the base of the main food source for all living organisms! GLUCOSE And WHERE does this process occur? (In which organelle???) SUGAR! • Fructose and Ribose are 5-carbon rings Glucose is a 6-carbon ring Hint…. YOU NEED TO KNOW THESE SHAPES!!!! Carbs have a “geometric shape” at their center! What else is in the cell? • Other than water and organelles, what else is in the cell? • Organic molecules – Large, complex molecules • Macromolecules The small subunits are called monomers • Many monomers bonded together makes a polymer 1+1+1+1+1+1+1+…..=11111 Monomers (MONO=One) Polymer (POLY=Many) Organic Vs. Inorganic • Organic Molecules contain at least one Carbon atom and one Hydrogen atom together! – C + H = organic! • Inorganic do not have both C + H together – Inorganic molecules can have one or the other (or neither), but once Carbon and Hydrogen are together… the molecule is Organic! – Is Water (H2O) organic or inorganic? – Carbon Dioxide (CO2)? – Glucose (C6H12O6)? Four Basic Types of Complex Organic Molecules (aka Macromolecules) –Carbohydrates (sugars and starches) –Lipids (fats) –Proteins –Nucleic acids (DNA and RNA) Carbohydrates • Sugars and starches – “Saccharides” • “Carbohydrate” means a “hydrated carbon” – Every carbon has a water attached • Carbohydrate rings are made of 5 or 6 carbon sugars rings – Simple sugars • Carbs are used for energy production and for structure This is Glucose C6H12O6 Sugars (aka saccharides) • Simple sugars, like glucose, are a single carbon ring • Glucose is the organic food molecule used by ALL living things – Inorganic molecules are converted to organic glucose through photosynthesis – Glucose is used by EVERY organism to make ATP (the energy molecule) • Ribose and Deoxyribose sugars are part of RNA and DNA – They are 5 carbon sugars Sugars • Disaccharides are two simple sugars joined together – Most of the sweet things we eat are disaccharides: table sugar is sucrose -> glucose joined to fructose (fructose is the sugar found in corn). – Lactose, milk sugar, is a glucose joined to another simple sugar called galactose. – Maltose, malt sugar, is what yeast converts to ethanol when beer is brewed. Notice anything about the “ending” of the names of sugars? They usually end with the letters OSE Complex Carbohydrates • Are polysaccharides (many sugars linked together) – STARCH • Large Molecules • Animals store excess sugar as glycogen • Plants store excess sugar as cellulose – We don’t have enzymes that can digest these polymers • Think about corn kernels! Lipids • Lipids are the main component of cell membranes – Also used for energy storage • 4 main types: – fats (energy storage) – phospholipids (cell membranes) – waxes (waterproofing) – steroids (hormones) Fats • Triglycerides are the main type of fat in our bodies • A triglyceride is composed of 3 fatty acids attached to a molecule of glycerol Phospholipids • Phospholipids make up cell membranes Steroids and Waxes (Examples of Lipids) • Steroids are hydrocarbons with the carbon atoms arranged in a set of 4 linked rings. • Cholesterol is found naturally in cell membranes. But, too much of it in the blood can clog blood vessels. • Steroid hormones are made from cholesterol. • Waxes: waterproof coating on plants and animals. – Where do WE have wax? Proteins • The most important type of macromolecule! • Structure: collagen in skin, keratin in hair, crystallin in eyes – Protein makes you – YOU! • Enzymes: all metabolic reactions -- building up, rearranging, and breaking down organic compounds -are done by enzymes Amino Acids • Amino Acids are the subunits (monomers) of proteins. – Proteins are long chains of amino acids • There are 20 different kinds of amino acids. – Each one has a different head (the “R group”) attached to it What’s it look like??? Protein Structure • A protein is sometimes called a polypeptide – Special “Peptide Bonds” hold the amino acids together in the chain • After the ribosome makes the polypeptide, they fold into a shape which allows them to be work correctly • The proper shape is super important for proteins • Denaturation destroys the shape of the protein – Denaturation is caused by pH and/or temperature Nucleic Acids • Nucleic acids store genetic information in the cell. • Two types of nucleic acid: – RNA (ribonucleic acid) – DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) • Each “nucleotide” has 3 parts: a sugar, a phosphate, and a base. – Nucleotides are the subunits (monomers) of nucleic acids What’s it look like?? DNA and RNA • DNA uses 4 different bases: -adenine (A)ALL -thymine (T) THUGS -cytosine (C) CARRY -guanine (G) GUNS • RNA consists of 4 bases also, but, the thymine in DNA is replaced by uracil in RNA: -adenine (A)ALL -uracil (U) UNDERACHIEVERS -cytosine (C) CAN'T -guanine (G) GRADUATE DNA • The order of the 4 bases in a chain of DNA determines the genetic information. • DNA has 2 complementary chains twisted into a double helix and held together by hydrogen bonds. • DNA is found in the nucleus of every cell. – And every single cell in your body has the SAME DNA! RNA • RNA is a COPY of the DNA code • RNA consists of a single chain (which can pass through the nuclear membrane to attach to a Ribosome) – What does the Ribosome do????? – Why do you think RNA can pass through the nuclear membrane, but DNA can't?????