* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Types of Hormones
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
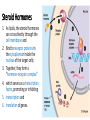
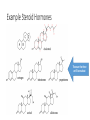
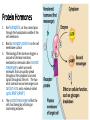
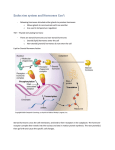
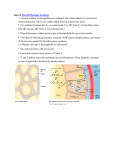
Types of Hormones Steroid Hormones 1. As lipids, the steroid hormones can cross directly through the cell membrane and 2. Bind to receptor proteins in the cytoplasm or inside the nucleus of the target cells; 3. Together, they form a “hormone-receptor complex” 4. which serves as a transcription factor, promoting or inhibiting 5. transcription and 6. translation of genes. Example Steroid Hormones These are the three we’ll learn about estrogen Protein Hormones 1. 2. 3. Are hydrophilic, so they cannot pass through the hydrophobic middle of the cell membrane. Bind to receptor proteins on the cell membrane surface. The binding of the hormone triggers a cascade of chemical reactions mediated by chemicals called second messengers, which are small molecules that can quickly spread throughout the cytoplasm and send signals throughout the cell. The two most common second messengers are calcium ions and a molecule called cyclic AMP (cAMP) 4. The second messengers effect the cells functioning by activating or inactivating enzymes. Example Protein Hormones D.5.U2 Steroid hormones bind to receptor proteins in the cytoplasm of the target cell to form a receptor– hormone complex. Describe the mechanism of steroid hormone action. List two example steroid hormones. D.5.U3 The receptor–hormone complex promotes the transcription of specific genes. List locations at which a steroid hormone binds its receptor. Review the function of a “transcription factor” D.5.U4 Peptide hormones bind to receptors in the plasma membrane of the target cell. State the location at which a protein hormone binds its receptor. List two example protein hormones. D.5.U5 Binding of hormones to membrane receptors activates a cascade mediated by a second messenger inside the cell. List the two most common second messengers. Define “second messenger system.”