* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cells Information Gap Activity
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
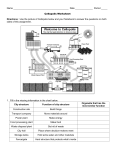
Cells Information Gap Activity - Sheet A Name: ___________ Homebase: _____________ There are two main types of cells – animal and ____________________ cells. Each cell is made up of parts called _______________________. Each organelle has a different ___________________ and carries out a different ________________ for the cell. Animal Cells Cells from ___________________ have several organelles in common. They include the cell membrane, __________________, mitochondrion, __________________, cytoplasm, __________________________ and many more. The cell membrane is a thin, flexible ___________________ ____________________that encases the cell and ____________________ what goes in or comes out. Cell membranes are ______________________________ under light microscopes, which is why it can be hard to ___________________ individual animal cells under light microscopes. The cytoplasm is a ______________________________ liquid that fills most of the cell and contains hundreds of different chemicals. New substances are ____________ and ___________________ is released and stored there. Think of the ____________________________________ as the chemical factory of the cell. Vacuoles are ______________________________areas that may contain air, ________________, wastes and __________________________________. ______________________________ cells often contain several small vacuoles. They are not normally visible under light microscopes. The ________________________________________ is the “control room” of the cell. It contains ____________, which is like a _________________________________________________________ that tells the cell how to develop and _______________________________. Nuclei are often visible under light microscopes. The mitochondria is a small organelle that can’t be seen using a light microscope. Its job is to ________________________________________ to release the ________________________ that the cell needs to __________________________. _________________________ break down, recycle and/or destroy _____________, old organelles, viruses and _________________________ into other chemicals which the cell can then _________ or dispose of. Plant Cells Like animal cells, plant cells also contain a ________________________, lysosomes, cytoplasm, _______________________, a cell membrane, but instead of many ________________________, plant cells contain _______________________________ filled with cell sap. Unlike _____________________ cells, plant cells contain ___________________________ and a cell wall. Unlike animals, plants need to make their own _________ in a process known as photosynthesis. This occurs in ________________________ called chloroplasts inside leaf cells. Chloroplasts may be seen using a light microscope. _______________________ in the cell use light energy from the _______ to convert ___________________________________ and water into chemical energy in the form of _______________________ (a type of sugar). This is then used as food for the plant. ________________________is made as a waste material. Unlike animal cells, plant cells have a ______________________which contains a tough, fibrous material called cellulose and provides the support needed by the ______________________ and the entire plant. Cell walls are easy to ___________ under microscopes, which makes it easy to identify individual plant cells under microscopes. There are other organelles, which you might want to know about, but we’ve kept it simple for Grade 6! Single-Celled (Unicellular) Organisms These organisms are called _______________________, meaning “one cell”. This cell carries out all the required ________________________________ such as food intake and ______________________. Since some unicellular organisms show both __________ and animal characteristics, they are often classified not as plants or animals, but as _____________________. Multicellular Organisms Organisms with ____________ than one cell are known as multicellular organisms. The larger the organism, the more specialized cells it has. A ________________________ cell carries out a very specific _____________________ for the organism. ____________________ contain more than 200 types of specialized cells. _____________________ cells carry food and oxygen around the body; muscle cells assist movement; while nerve cells send messages from the ____________________ to the muscles. What do you think the other specialized cells do? Bone cells?_______________________________ ________________________________________ Fat cells? _______________________________ ________________________________________ Groups of Cells, Tissues and Organs The different specialized cells in our bodies are organized into _________________ to help them work more effectively. Groups of similar________________________cells are called tissue. ________________ in turn may be grouped ___________________ to form an _____________. Just as ______________________ do a specific job for the cell, organs do a specific job for an organism. For example, _____________ cells form heart tissue, which makes up the heart, the _____________ specialized for pumping blood around the human body. Some other human organs made from specialized ___________________________________ are the skin, _______________, intestines, liver, kidneys and _______________. Completion and Accuracy Is it complete? Is it accurate? Always (100%) Exemplary = 5 points Usually (88%) Proficient = 4.4 points Somewhat (76%) Developing = 3.8 points Rarely (64%) Emerging = 3.2 points Cell Info Gap Reflection Questions Name_________________ Homebase_________________________ 1. Which organelle(s) is/are unique to animal cells?____________________________________________________ 2. Which organelle(s) is/are unique to plant cells?_____________________________________________________ 3. Which organelles did we see under the microscopes? ________________________________________________ 4. What do animals have that serves the same function as a cell wall? _____________________________________ 5. If ISM were a cell, what would be its? a) cell membrane__________________________________ Why?_______________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________ b) nucleus__________________________________ Why? ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________ c) cell wall_______________________________Why? __________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________ d) cytoplasm_____________________________ Why? _________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________ e) vacuoles______________________________ Why? _________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________ f) mitochondrion ___________________________ Why? _______________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________ g) chloroplasts_____________________________ Why? ________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________ h) lysosomes_____________________________ Why? _________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________ 6. What would ISM be like without the above structures? _______________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________ 7. What would our cells be like without organelles? ____________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________ 8. What do you think is the most important organelle? _____________________ Why?_______________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________ 9. What do you think is the least important organelle? _____________________ Why?_______________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________ 10. Why do humans have many different specialized cells? ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________ 11. Why do you think humans have specialized cells, tissues and organs?__________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________ 12. What is a: unicellular organism?______________________________________ a multicellular organism? ________________________________________ a protist?______________________________________________ 13. What are the similarities between unicellular and multicellular organisms?______________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________ 14. What are the differences between unicellular and multicellular organisms?______________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________ 15. Why study cells?_____________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________