* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Science 8 Unit 1- Chapter 2 Oceans are important because: 1
Survey
Document related concepts
Atlantic Ocean wikipedia , lookup
History of research ships wikipedia , lookup
Marine geology of the Cape Peninsula and False Bay wikipedia , lookup
Pacific Ocean wikipedia , lookup
Marine debris wikipedia , lookup
Anoxic event wikipedia , lookup
Southern Ocean wikipedia , lookup
Indian Ocean Research Group wikipedia , lookup
Marine biology wikipedia , lookup
Marine pollution wikipedia , lookup
Abyssal plain wikipedia , lookup
Ocean acidification wikipedia , lookup
Ecosystem of the North Pacific Subtropical Gyre wikipedia , lookup
Indian Ocean wikipedia , lookup
Arctic Ocean wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on oceans wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
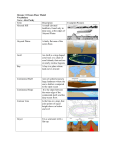
Science 8 Unit 1- Chapter 2 Oceans are important because: 1. Primary source for the _____water cycle___ 2. Have a major influence on weather and _climate_ 3. Support diverse life 4. Provide humans with food, minerals, and other resources_ The 5 major oceans are: 1. Atlantic 2. Pacific 4. Arctic 5. Southern 3. Indian 4 Factors that formed the oceans 1. Tectonic Plates Tectonic plates are slow moving sections of rock that flow over a layer of _magma__ the surface of the earth is made up of tectonic plates Tectonic plates _seperating__ formed the oceans we know today 2. Volcanic Action Water trapped in volcanic materials was released as _water vapour__ It cooled, condensed and fell back to the earth. This water collected in the lowest parts of the Earth’s surface...the ocean basins_ Volcanic activity continues to occur at ocean ridges, spreading tectonic plates apart and adding new material to the sea floor 3. Erosion Erosion is a type of weathering in which surface soil and rock are worn away through the action of glaciers, water, and wind Has aided the further development of continental drainage systems as material is removed and deposited into ocean basins 4. Glaciation Glaciers move materials towards the ocean and also cause erosion Science 8 Unit 1- Chapter 2 Components of the Ocean Floor Continental margin the area between the shoreline and the ocean basin includes the continental shelf and continental slope Continental shelf: the submerged part of the continent between the shoreline and slope Continental slope: The slope between the continental shelf and the deep ocean floor Abyssal Plain: Wide, open plains (flat areas) on the deep sea floor Formed of thick deposits of sediments Mid Ocean Ridge: Long, undersea mountain chains formed from volcanic eruptions They are a result of magma that has oozed up between plates and then hardened Draw and label a diagram showing these components from coastal shoreline to mid-ocean ridge. Include: Continental shelf Continental slope Abyssal Plain Mid-ocean ridge *See pgs 41-43 Science 8 Unit 1- Chapter 2 Ocean Currents: A continuous and directional__ movement of ocean water There are 2 types of ocean currents; surface currents and deep currents Deep ocean currents are caused by temperature differences___& _salinity differences___ 2 currents important to Newfoundland and Labrador are: 1. The Labrador Current (_cold_ water) 2. The Gulf Stream (warm_water) When the cold air above the Labrador Current meets the warm air above the Gulf Stream, the warm air cools, condenses and forms fog Ocean Wave: a disturbance on the surface of the ocean that transmits energy waves are typically caused by _wind__ Type Swell Describe Smooth waves caused by wind and storms far out in the ocean Breaker the tumble of water when a wave collapses onshore Tsunamis -giant waves caused by earthquakes, landslides or volcanic eruptions -Can be very destructive Sketch x Tides: The slow rise and fall of the ocean The upper and lower edges of a beach are determined by the high and low _tide marks_ tides are caused by _the gravitational pull of the moon_ Tidal Range: The difference in level between a high and a low tide Occurs when.. Spring Tide Neap Tide the Earth, Sun and Moon are _in line__ the Sun and the Moon are at right angles to one another Causes.. Increased tidal range -extra high and low tides Decreased tidal range -little difference between low and high tides Draw Science 8 Unit 1- Chapter 2 Shaping Our Shorelines • Waves have the power to erode and deposit sediments on the shore. • Tides work with waves to determine the range of shoreline that can be affected by wave action. Factors that affect the interaction of waves and tides on the shorelines are: 1. Slope of the shoreline 3. Type of rock material 2.Shape of the shoreline 4.Wave energy Wave energy is concentrated at headlands and spread out at bays Think-Pair-Share... write down two-three points get together with a partner and discuss share with the class How can coastal communities minimize the damage to shoreline property due to waves and tides?