* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Skinner`s views were slightly less extreme than those of Watson
Music psychology wikipedia , lookup
Experimental psychology wikipedia , lookup
Cross-cultural psychology wikipedia , lookup
Prosocial behavior wikipedia , lookup
Educational psychology wikipedia , lookup
Social psychology wikipedia , lookup
Behavioral modernity wikipedia , lookup
Learning theory (education) wikipedia , lookup
Symbolic behavior wikipedia , lookup
History of psychology wikipedia , lookup
Conservation psychology wikipedia , lookup
Observational methods in psychology wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Thin-slicing wikipedia , lookup
Transtheoretical model wikipedia , lookup
Organizational behavior wikipedia , lookup
Insufficient justification wikipedia , lookup
Abnormal psychology wikipedia , lookup
Theory of planned behavior wikipedia , lookup
Applied behavior analysis wikipedia , lookup
Adherence management coaching wikipedia , lookup
Attribution (psychology) wikipedia , lookup
Sociobiology wikipedia , lookup
Descriptive psychology wikipedia , lookup
Theory of reasoned action wikipedia , lookup
Classical conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Behavior analysis of child development wikipedia , lookup
Psychological behaviorism wikipedia , lookup
Verbal Behavior wikipedia , lookup
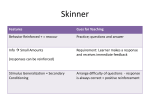
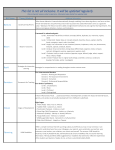
Skinner Operant Conditioning by Saul McLeod published 2007, updated 2015 By the 1920s John B. Watson had left academic psychology and other behaviorists were becoming influential, proposing new forms of learning other than classical conditioning. Perhaps the most important of these was Burrhus Frederic Skinner. Although, for obvious reasons he is more commonly known as B.F. Skinner. Skinner's views were slightly less extreme than those of Watson (1913). Skinner believed that we do have such a thing as a mind, but that it is simply more productive to study observable behavior rather than internal mental events. Skinner believed that the best way to understand behavior is to look at the causes of an action and its consequences. He called this approach operant conditioning. Skinner's theory of operant conditioning was based on the work of Thorndike (1905). Edward Thorndike studied learning in animals using a puzzle box to propose the theory known as the 'Law of Effect'. Influential People: Operant conditioning similarly know as instrumental learning, was observed as timely as the early twentieth century by a man named Edward L. Thorndike. He initially observed the behaviors of cats trying to escape from a homemade puzzle boxes. Numerous trials were conducted when he noticed ineffective responses occurring less frequently and successful responses occurring more frequently. In Thorndike’s law of effect he theorized that behaviors followed by satisfying consequence tend to be repeated and those who give unpleasant consequences are less likely to be repeated (McLeod, 2007). The expressions of operant conditions and replied behavior was promoted and simplified by Burrhus Frederic Skinner, commonly known as B.F. Skinner. Skinner’s assessments of operant conditioning has allowed for further reasoning. In fact, Skinner believed the efficiency to study and observe the brain was much more productive versus studying the internal mental proceedings. Skinner believed the best way to understand behavior was through the “cause of an action and its consequences” (Skinner, 1935). Operant behavior denotes “a response followed by a reinforcing stimulus” (Cherry, 2005). References: Cherry, K. A. (2005). Operant conditioning. Retrieved from http://psychology.about.com/od/behavioralpsychology/a/introopcond.htm Skinner, B. F. (1935) Two types of conditioned reflex and a pseudo type Journal of General Psychology, 12, 66-77. McLeod, S. A. (2007). Edward Thorndike. Retrieved from http://www.simplypsychology.org/edward-thorndike.html Key Findings: B.F. Skinner in 1938 devised the term “operant conditioning” by the changing of behavior by the use of reinforcement that is given after the requested response. Ultimemetly, Skinner identified three types of responses that can follow a behavior (McLeod, 2015). • Neutral operants: responses from the environment that neither increase nor decrease the probability of a behavior being repeated. • Reinforcers: Responses from the environment that increase the probability of a behavior being repeated. Reinforcers can be either positive or negative. • Punishers: Responses from the environment that decrease the likelihood of a behavior being repeated. Punishment weakens behavior. Here is a better detailed link References: McLeod, S. A. (2015). Skinner - Operant Conditioning. Retrieved from http://www.simplypsychology.org/operant-conditioning.html