* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 2 Packet
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
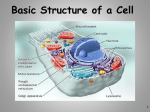
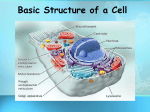
Chapter 2 Study Guide Name _______________________________ PD _____ 2.1 What Is Life? - Key Concepts All living things have a cellular organization, contain similar chemicals, use energy, respond to their surroundings, grow and develop, and reproduce. Living things arise from living things through reproduction. All living things must satisfy their basic needs for water, food, living space, and stable internal conditions. 2.2 Classifying Organisms - Key Concepts Biologists use classification to organize living things into groups so that the organisms are easier to study. The more classification levels that two organisms share, the more characteristics they have in common. Organisms are placed into domains and kingdoms based on their cell type, their ability to make food, and the number of cells in their bodies. 2.3 Discovering Cells - Key Concepts Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things. The cell theory states the following: All living things are composed of cells. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things. All cells are produced from other cells. The invention of the microscope enabled people to learn about cells. Light microscopes magnify an object by bending light. Electron microscopes use electrons instead of light. 2.4 Looking Inside Cells - Key Concepts A plant’s cell wall protects and supports the cell. The cell membrane controls what substances come into and out of a cell. The nucleus directs the cell’s activities. Mitochondria convert energy in food molecules to energy the cell can use. The endoplasmic reticulum carries materials throughout the cell. Ribosomes produce proteins. The Golgi bodies receive materials, package them, and distribute them. Chloroplasts capture energy from sunlight and use it to produce food for the cell. Vacuoles are the storage areas of cells. Lysosomes contain chemicals that break down certain materials in the cell. In many-celled organisms, cells are often organized into tissues, organs, and organ systems. NAME ____________________________________ Period 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Chapter 2 Vocabulary – Review your vocabulary any night that you do not have written homework in science! Section 1 What is Life? – pages 34 – 40 organism – cell – unicellular – multicellular – stimulus – response – development – spontaneous generation – autotroph – heterotroph – homeostasis – Section 2 Classifying Organisms – pages 42– 49 classification – taxonomy – binomial nomenclature – genus – species – prokaryote – nucleus – eukaryote – 1 Section 3 microscope - Discovering Cells – pages 50 - 57 cell theory – Section 4 organelle – Looking Inside Cells – pages 60 - 67 cell wall – cell membrane – cytoplasm – mitochondria – endoplasmic reticulum – ribosome – Golgi body – chloroplast – vacuole – lysosome – 2 Name ________________________ Reading Assignment 2.1 - pp. 34-40 Period 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Date _________________ What is Life? I. Before you read skim the section title, topics within the title, and sub-topics. Look at the visuals and read the captions. What will you read about? __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ II. Read the questions below. Look for answers as you read. 1. The scientific term for a living thing is ___________________________. 2. The basic building blocks of all organisms are__________________. 3. The most abundant chemical in cells is ______________. 4. _________________ organisms, such as bacteria, have only one cell. 5. _________________ organisms are composed of many cells. 6. A change in an organism’s environment that causes that organism to react is called a(n) ________________________. 7. A _________________ is a reaction to a stimulus. 8. Give five reasons (from the book) why living things need water: a. d. b. e. c. 9. Organisms that make their own food are called ___________________________. 10. Organisms that get energy by consuming other organisms are _______________. 11. Define “homeostasis”. ____________________________________________________ 3 Name _____________________________________________ Review and Reinforce 2.1 – pages 34 – 40 PD 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Date __________________ What Is Life? Understanding Main Ideas 1. What are six characteristics all living things share? __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ 2. How did Redi’s experiment help disprove the idea of spontaneous generation? __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ 3. What are the four basic needs all living things must satisfy? __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ 4. Describe the difference between growth and development. __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ Building Vocabulary - From the list below, choose the term that best completes each sentence. autotrophs unicellular spontaneous generation response manipulated variable heterotrophs multicellular homeostasis cell organisms stimulus reproduce 5. A change in an organism’s environment that causes the organism to react is called a(n) ____________________. 6. Organisms that make their own food are ____________________. 7. ____________________ organisms are composed of many cells. 8. _____________________________________ is the mistaken idea that living organisms arise from nonliving sources. 9. Living things are also called ____________________. 10. The ____________________ is the basic unit of structure in an organism. 11. Organisms that get energy by consuming other organisms are ____________________. 12. An organism reacts to a stimulus with a(n) ____________________. 13. A controlled experiment is conducted by performing two tests that are identical except for one factor called the ____________________ . 14. An organism’s ability to maintain stable internal conditions is called ____________________. 15. To ____________________ is to produce offspring that are similar to the parents. 16. Bacteria, the most numerous organisms on Earth, are ____________________ organisms. 4 2.1 Vocabulary Name ______________________________ PD ____ Across 5. an organism that cannot make its own food 6. an action or change in behavior that occurs in reaction to a stimulus 7. a change in an organism’s surroundings that causes the organism to react 9. organisms that consist of many cells 10. made of a single cell Down 1. the process of change that occurs during an organism’s life to produce a more complex organism 2. the mistaken idea that living things arise from non-living sources 3. an organism that makes its own food 4. a living thing 5. the maintenance of stable internal conditions in an organism 8. the basic unit of structure and function in an organism 5 Name _________________________ Reading Assignment 2.2 - pp.42 - 49 Period 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Date _________________ Classifying Organisms I. Before you read skim the section title, topics within the title, and subtopics. Look at the visuals and read the captions. What will you read about? ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ II. After you have read complete the following questions. 1. The scientific study of how living things are classified is called _________________. 2. Linnaeus placed organisms into groups based on their features that he could ______________. 3. In Linnaeus’s naming system, called ______________________________, each organism is given a two-part name. 4. A ________________ is a group of similar organisms that can mate with each other and produce offspring that can also mate and reproduce. 5. Felis concolor is the scientific name for mountain lions. To which genus do mountain lions belong? What is the species? Genus: ________________________ Species: ________________________ 6. Circle the letter of the sentence that is not true about binomial nomenclature. a. A scientific name is written in italics. b. Many scientific names are in Latin because Latin was the language of scientists during Linnaeus’s time. c. The genus name begins with a small letter. d. Binomial nomenclature makes it easier for scientists to talk about an organism. 7. List the seven levels of classification used by modern biologists in order from the broadest level to the most specific level. 1.__________________________ 5.__________________________ 2.__________________________ 6.__________________________ 3.__________________________ 7.__________________________ 4.__________________________ 8. T or F? The more classification levels that two organisms share, the more characteristics they have in common. 6 9. Circle the letter of the sentence that is true about bacteria. a. Bacteria can be either autotrophic or heterotrophic. b. Bacteria are prokaryotes. c. Bacteria have a cell nucleus. d. Bacteria do not have nucleic acids. 10. A dense area in a cell that contains nucleic acids is a(n) _____________________. 11. The Greek meaning of the word “archaea” is ___________________. Why is that an appropriate name for members of this kingdom? ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ 12. Some members of Domain Eukarya called __________ can be either unicellular or multicellular. 13. Protists differ from bacteria and archaea because they have a(n) ________________. 14. Circle the letter of each characteristic of fungi. a. c. eukaryotes autotrophs b. d. prokaryotes heterotrophs 15. Plants are ________________________; they can make their own food. 16. Circle the letter of each characteristic of animals. a. c. unicellular eukaryotes b. d. heterotrophs autotrophs 7 Life Science - 2.2 Vocabulary NAME ______________________________ PD ___ Across 3. the scientific study of how living things are classified 6. an organism whose cells contain nuclei 7. a group of organisms that are physically similar and can mate with each other & produce offspring that can also mate & reproduce 8. control center of a eukaryotic cell - directs cell’s activities & contains information that determines the cell’s form & function Down 1. the process of grouping things based on their similarities 2. an organism whose cells lack a nucleus and some other cell structures 4. system of naming organisms - each organism is given a unique, 2 part scientific name 5. a classification grouping that consists of a number of similar, closely related species 8 We will complete this graphic organizer in class. 2.2 – Classifying Organisms Organisms are placed into one of six kingdoms based on: The number of cells they have. The type of cells they have. The way they get their food. 9 Name _____________________________________________ PD 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Review and Reinforce 2.2 – pages 42 – 49 Date _______________________ Classifying Organisms Understanding Main Ideas - Answer the following questions in the space provided. 1. List the major levels of classification, starting with the highest level. ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 2. What three characteristics are used to place organisms into domains and kingdoms? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ Building Vocabulary - Match each term with its definition by writing the letter of the correct definition in the right column on the line beside the term in the left column. ____ 3. classification a. naming system developed by Carolus Linnaeus ____ 4. binomial nomenclature b. process of grouping things based on their similarities ____ 5. eukaryote c. first word in an organism’s scientific name ____ 6. genus ____ 7. species ____ 8. taxonomy ____ 9. prokaryote ____ 10. nucleus d. organism whose cell lacks a nucleus e. a group of organisms that can mate and produce offspring that can also mate and reproduce f. the scientific study of how things are classified g. organism whose cell(s) contain a nucleus h. dense area in a cell that contains nucleic acids 10 Name ___________________________________________ Reading Assignment 2.3 – Pages 50-57 Period 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Date ___________________________ I. Before you read – Skim the section titles, topics within the title, and subtopics. Look at the visuals and read the captions. What will you read about? ________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ II. As you read, look for the answers to the questions below. III. After you have read, complete the questions below. If you are unsure of an answer, refer to the reading! Use Target Reading Skills As you read, construct a flowchart showing how the work of Hooke, Leeuwenhoek, Schleiden, Schwann, and Virchow contributed to scientific understanding of cells. For each cell, be sure to answer the questions: Who? What? When? DISCOVERING CELLS Hooke sees cells in cork. ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ An Overview of Cells 1. What are cells? ________________________________________________________________ 2. What did the invention of the microscope make possible? ______________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ 3. An instrument that makes small objects look larger is a(n) ______________________________. 11 4. Is the following sentence true or false? (circle one) A compound microscope has only one lens. 5. Complete the following table about the first people to observe cells. The First People to Observe Cells Questions Robert Hooke Anton van Leeuwenhoek What kind of microscope did he use? What did he first look at with the microscope? Development of the Cell Theory 6. Is the following sentence true or false? Theodor Schwann worked alone to develop the cell theory. 7. List the three points of the cell theory. a. ___________________________________________________________________ b. ___________________________________________________________________ c. ___________________________________________________________________ 8. TRUE or FALSE? Magnification is the ability to make things look larger than they are. 9. How do the lenses of a light microscope make an object look larger? ______________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ 10. In a convex lens, the _______________ of the lens is thicker than the _______________ . 11. What is resolution? __________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ 12. A microscope that uses a beam of electrons to examine a specimen is called a(n) ____________ 13. Circle the letter of the microscope that has better resolution. a. light microscope b. electron microscope 12 Name _____________________________________________ PD 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Review and Reinforce 2.3 – pages 50 – 57 Date _____________________ Discovering Cells Understanding Main Ideas - Fill in the blanks in the table below. Discovering Cells Scientist Contribution 1. _________________________ One of the first people to observe cells __ Leeuwenhoek 2. ___________________________ 3. _________________________ Concluded that all plants are made up of cells __ Schwann 4. ___________________________ 5. _________________________ Proposed that all cells come from other cells __ Answer the following questions below. 6. Compare and contrast magnification and resolution. ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 7. State how an electron microscope differs from a light microscope. ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 8. Explain how cells are related to living things. ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ Building Vocabulary - Match each term with its definition by writing the letter of the correct definition in the blank beside the term. ____ 9. cell ____ 10. microscope ____ 11. cell theory a. a widely accepted explanation of the relationship between cells & living things b. the basic unit of structure and function in living things c. an instrument that makes small objects look larger 13 Name ________________________________ Period 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Read the passage below and then answer the questions on the back of this sheet. Robert Hooke One of the first people to observe cells was the English scientist and inventor Robert Hooke. Hooke built his own compound microscope, which was one of the best microscopes of his time. In 1663, Hooke used his microscope to observe the structure of a thin slice of cork. Cork, the bark of the cork oak tree, is made up of cells that are no longer alive. To Hooke, the empty spaces in the cork looked like tiny rectangular rooms. Therefore, Hooke called the empty spaces cells, which is a word meaning “small rooms.” Hooke described his observations this way: “These pores, or cells, were not very deep, but consisted of a great many little boxes.. . .” What most amazed Hooke was how many cells the cork contained. He calculated that in a cubic inch there were about twelve hundred million cells—a number he described as “almost incredible.” Anton van Leeuwenhoek At about the same time that Robert Hooke made his discovery, Anton van Leeuwenhoek (lay vun hook) also began to observe tiny objects with microscopes. Leeuwenhoek was a Dutch businessman who sold cloth. In his spare time, he built simple microscopes. Leeuwenhoek looked at drops of lake water, scrapings from teeth and gums, and water from rain gutters. In many materials, Leeuwenhoek was surprised to find a variety of one-celled organisms. Leeuwenhoek noted that many of these tiny organisms moved. Some whirled, some hopped, and some shot through water like fast fish. He called these moving organisms animalcules (an ih mal kyoolz), meaning “little animals.” Development of the Cell Theory Leeuwenhoek’s exciting discoveries caught the attention of other researchers. Like Hooke, Leeuwenhoek, and all good scientists, these other researchers were curious about the world around them, including things they couldn’t normally see. Many other people began to use microscopes to discover what secrets they could learn about cells. Schleiden, Schwann, and Virchow Three German scientists made especially important contributions to people’s knowledge about cells. These scientists were Matthias Schleiden (shly dun), Theodor Schwann, and Rudolf Virchow (fur koh). In 1838, Schleiden concluded that all plants are made of cells. He based this conclusion on his own research and on the research of others before him. The next year, Theodor Schwann concluded that all animals are also made up of cells. Thus, stated Schwann, all living things are made up of cells. Schleiden and Schwann had made an important discovery about living things. However, they didn’t explain where cells came from. Until their time, most people thought that living things could come from nonliving matter. In 1855, Virchow proposed that new cells are formed only from cells that already exist. “All cells come from cells,” wrote Virchow. What the Cell Theory Says Schleiden, Schwann, Virchow, and others helped develop the cell theory. The cell theory is a widely accepted explanation of the relationship between cells and living things. The cell theory states the following: - All living things are composed of cells. - Cells are the basic units of structure & function in living things. - All cells are produced from other cells. The cell theory holds true for all living things, no matter how big or small. Since cells are common to all living things, they can provide information about the functions that living things perform. Because all cells come from other cells, scientists can study cells to learn about growth and reproduction. 14 How did Schleiden, Schwann, and Virchow contribute to the understanding of cells? Give specific examples from the selection to support your answer. Approximately how much time passed between the contributions of Hooke and Virchow? Why do you think it took so long for the conclusion that “All cells come from cells,” to be developed? Limit your response to the space provided below. ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 15 Name __________________________________________ Period 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Using a Microscope The importance of the microscope in the history of medicine and our understanding of diseases should not be underestimated. Microscopes are expensive instruments and require special care when using them. Identify the parts of the compound microscope. Directions: Show that you know something about a microscope by filling in the blanks below. 15. If you have to carry a microscope, put one hand on the ____________ and the other hand on the _________________. 16. When finished with the microscope, turn off the _______________ and turn the _______________ in place. 17. What power objective do you use first when focusing a specimen? ______________. 18. You should NOT use the coarse adjustment when using high power because you could damage the _____________________. 19. some microscopes do not have an electric light source. Instead they have a ____________________. 20. When focusing the high power objective, you should only use the _________________ focus. 21. What is the magnification power of the eyepiece? ___________X. 16 Name ________________________________________________ Class 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Reading Assignment 2.4 – Pages 60-67 Date ____________________ I. Before you read – Skim the section titles, topics within the title, and subtopics. Look at the visuals and read the captions. What will you read about? _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ II. As you read, look for the answers to the questions below. III. After you have read, complete the questions below. If you are unsure of an answer, refer to the reading! 1. What are organelles? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ Enter the Cell 2. The rigid layer of nonliving material that surrounds plant cells is the ______________________ 3. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about the cell wall. a. Cell walls are made of cellulose. b. Plant cells have cell walls. c. Animal cells have cell walls. d. Water & oxygen cannot pass through the cell wall. 4. What does the cell wall do? _______________________________________________________________________ 5. Where is the cell membrane located in cells that have cell walls? _______________________ 6. Where is the cell membrane located in cells that do NOT have cell walls? ________________ 7. TRUE or FALSE? The main function of the cell membrane is to control what comes into and out of a cell. Sail On to the Nucleus 8. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about the nucleus. a. Materials pass in and out of the nucleus through pores in the nuclear envelope. b. Chromatin contains the instructions that direct the functions of a cell. c. The nucleolus is part of the nuclear envelope. d. Ribosomes are made in the nucleolus. Organelles in the Cytoplasm 9. Circle the letter of the part of the cell that is the region between the cell membrane and the nucleus. a. organelle c. cytoplasm b. nucleus d. chromatin 17 10. In the table below, describe the function of each organelle in the cytoplasm. Organelles in Cytoplasm Organelle Mitochondria Endoplasmic reticulum Ribosomes Golgi bodies Chloroplasts Vacuoles Lysosomes Function Specialized Cells 11. In a many-celled organism, cells are specialized to perform different ___________________. 12. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about specialized cells. a. In many-celled organisms, cells are often organized into tissues. b. An organ system is made up of similar tissues. c. A tissue is a group of cells that work together to perform a specific function. d. A group of organs that work together to perform a major function is called an organ system. 18 Name _____________________________________________ PD 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Review and Reinforce 2.4 – pages 60 – 67 Date _____________________ Understanding Main Ideas - Identify each of the cell structures in the simplified animal cell. ______________________________ 1. ______________________________ 2. ______________________________ 3. ______________________________ 4. ______________________________ 5 . Building Vocabulary Fill in the blank to complete each statement. cell wall nucleus mitochondria Ribosomes chloroplasts lysosomes organelles cell membrane cytoplasm endoplasmic reticulum Golgi bodies vacuole 6. _________________________ are tiny cell structures that carry out specific functions within the cell. 7. The rigid layer of nonliving material that surrounds the cells of plants and other organisms is called the _________________________ . 8. In cells without cell walls, the _________________________forms the outside boundary that separates the cell from its environment. 9. The _________________________ is a large, oval structure that directs all of the cell’s activities. 10. The region between the cell membrane and the nucleus is called the _________________________. 11. _________________________ produce most of the energy the cell needs to carry out its functions. 12. A maze of passageways called the _________________________ carries proteins and other materials from one part of the cell to another. 13. _________________________ function as factories to produce proteins. 14. _________________________ receive proteins & other newly formed materials & distribute them to other parts of the cell. 15. Organelles called _________________________ capture energy from sunlight and use it to produce food for the cell. 16. The storage area of a cell is called a(n) _________________________. 17. _________________________ are small, round structures in cells that break down large food particles into smaller ones. 19 2.3 & 2.4 Vocabulary Name __________________________________ PD ___ Across 1. a widely accepted explanation of the relationship between cells and living things 6. a rigid layer of nonliving material that surrounds the cells of plants & some other organisms 8. a structure in a cell that receives proteins & other newly formed materials from the endoplasmic reticulum, packages them, and distributes them to other parts of the cell 10. a cell structure that forms passageways in which proteins and other materials are carried through the cell 11. the outside cell boundary that controls which substances can enter or leave the cell 12. a small grain-like structure in the cytoplasm of a cell where proteins are made Down 2. a tiny cell structure that carries out a specific function within the cell 3. a sac inside a cell that acts as a storage area 4. an instrument that makes small objects look larger 5. a small, round cell structure containing chemicals that break down large food particles into smaller ones 6. a structure in the cells of plants & some other organisms that captures energy from sunlight & uses it to produce food 7. the material within a cell apart from the nucleus 9. rod-shaped cell structures that convert energy in food molecules to energy the cell can use to carry out its functions 20 Name ______________________________________ Organelles in the Cytoplasm ORGANELLE cell wall cell membrane cytoplasm nucleus mitochondria endoplasmic reticulum ribosomes golgi bodies chloroplasts vacuoles lysosomes PLANT ANIMAL BOTH Period 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 FUNCTION stiff wall surrounding the membrane; giving cell a rigid, boxlike shape forms a barrier between the cytoplasm and the environment outside the cell. gel-like fluid in which many different organelles are found directs all the cell’s activities including reproduction most of the cell’s energy is produced in this rod-shaped organelle passageways that carry proteins and other materials from one part of the cell to another small grain like bodies attached to some surfaces of the endoplasmic reticulum; factories to produce proteins receive materials from the endoplasmic reticulum and send them to other parts of the cell; also release materials outside the cell capture energy from sunlight and use it to produce food for the cell store water, food, waste products, and other materials; most mature plant cells have one large vacuole; some animals cells have vacuoles also contain chemicals that break down food particles 21 Name ____________________________________ Period 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Color the plant cell according to the key below. Cell Membrane (orange) Golgi Body (dark blue) Mitochondria (red) Ribosomes (purple) Vacuole (light blue) Cytoplasm (white) Cell Wall (dark green) Endoplasmic Reticulum (pink) Nucleus (brown) Chloroplasts (light green) Analysis: Answer the questions using complete sentences. 1. Name two things found in a plant cell that are not found in an animal cell. 2. How does the shape of a plant cell differ from that of an animal cell? 3. What is the function of the chloroplasts? 4. What is the function of the vacuole? 22 Name ______________________________________ Vocabulary Bingo – Chapter 2 Period 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Use a pen and your vocabulary terms to complete the Bingo card below. Add one term per space. Do not use any terms more than once! This must be completed before class to participate! B I N G O FREE SPACE Choose your terms from the list below. Be sure to spell each term correctly! organism autotroph prokaryote mitochondria cell heterotroph nucleus endoplasmic reticulum unicellular homeostasis eukaryote ribosome multicellular classification cell theory Golgi body stimulus taxonomy organelle chloroplast response binomial nomenclature cell wall vacuole development genus cell membrane lysosome spontaneous generation species cytoplasm microscope 23