* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 5cap` AAUGAGUACCGGGCGAUAAUC AGAAA 3`
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
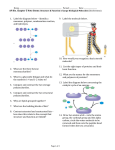
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS You will need to use a copy of the genetic code to complete this practice exercise 1. Shown below is the base sequence of the coding strand of a region of a DNA molecule. Draw the complementary (template) strand in the space provided. (Label the 5’ and 3’ ends) -5’ A A T G A G T A C C G A C T G G C G A T A A T C A G 3’-3’ T T A C T C A T G G C T G A C C G C T A T T A G T C 5’- b. Do the following in the diagram above. Circle a base. Put a box around a complementary base pair. Label where the sugar and phosphate parts of the DNA are found. 2. Transcribe the “gene” shown above and draw the product in the space below. (Label the 5’ and 3’ end) -5’ A A U G A G U A C C G A C U G G C G A U A A U C A G 3’b. What kind of molecule have you diagrammed in the #2a? RNA c. Name four ways that the molecule diagrammed in 1a differ structurally from the molecule diagrammed in 2a? 1) has U (uracil) instead of T (thymine) as its fourth base 2) has ribose instead of deoxyribose as its sugar 3) is single rather than double stranded 4) is only one gene in length d. Where does this process (transcription) occur in a eukaryotic cell? 3. Modify the molecule diagrammed in #2a into a mature mRNA. and write the sequence in the space below. Note: Bases #12,13, and 14 are an intron. in nucleus -5cap’ A A U G A G U A C C G G G C G A U A A U C A G A A A 3’’b. Where does this process occur in a eukaryotic cell? modification occurs in nucleus c. Where does the molecule diagrammed in #3a go next in a eukaryotic cell? to cytoplasm 4. Translate the molecule in #3a and draw the product in the space below. (be sure you start with AUG closest to 5’ end and stop with “stop codon”). b. met – ser – thr – gly - argWhat kind of molecule have you just drawn in #4a? c. Put a circle around one amino acid in the diagram above (#4a). polypeptide (protein) d. Besides the mRNA, what else is required to carry out the process of translation? tRNA (charged with appropriate amino acids), ribosome (small and large subunit), ATP e. Where does this process (translation) occur in a eukaryotic cell? in cytoplasm 5. If molecule #4a was destined to function within the cell, what kind of ribosome would be involved in its translation? a free ribosome 6a. If molecule #4a was destined to be secreted from the cell and used elsewhere in the body, what kind of ribosome would be involved in its translation? a bound ribosome (bound to RER) b. Where would such a molecule (destined for secretion) be found immediately after synthesis? inside the RER c. List the pathway of organelles throught which it would travel before it was secreted from the cell. 1) pinches off enclosed in a vesicle 2) vesicle travels to Golgi complex where the two membranes join 3) protein moves inside Golgi complex where carbohydrates are added making the protein a glycoprotein 4) glycoprotein pinches off in another vesicle and travels to cell membrane 5) glycoprotein is secreted when vesicle joins with cell membrane 7a. Shown below are three molecules. What kind of molecules are they? b c. Put a circle around one anticodon. These molecules are important in what step in protein synthesis? d. Fill in the appropriate amino acid to attach to each molecule. tRNA translation e. How many amino acid charging enzymes would be required to do this? A G ser ser G U A ile ile U U C ser ser A two