* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Regulation of the Cell Cycle
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
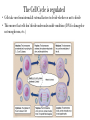
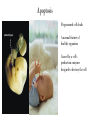
Regulation of the Cell Cycle Page 65 EQ: What happens if the cell cycle isn’t controlled? The Cell Cycle is regulated • Cells take cues from internal & external factors to decide whether or not to divide • This ensures that cells don’t divide under unfavorable conditions (DNA is damaged or not enough room, etc.) The Cell Cycle is regulated Checkpoints • G1: Checks for cell size, nutrients, growth factors, DNA damage • If it doesn’t have the right signals, cell can go back to G0 • G2: Checks for DNA damage, makes sure DNA was replicated properly • If there are mistakes, cell tries to fix them; if mistakes can’t be fixed cell will undergo apoptosis • Spindle checkpoint: Checks that chromosomes are correctly attached to spindle during metaphase Apoptosis Programmed cell death webbed fingers A normal feature of healthy organisms Caused by a cell’s production enzymes designed to destroy the cell Cell Cycle Regulation Problems If something goes wrong in the cell cycle, A disease can occur One example is cancer. OTHER DISEASES CAN BE CAUSED BY CELL CYCLE ERRORS Cell Cycle Regulation Problems 2 Types of tumors: - Benign: remain clustered and can be removed - Malignant: metastasize (spread) to different areas of the body and can form more tumors; cancer is this type of tumor normal cell cancer cell bloodstream Cell Cycle Regulation Problems: Cancer • Cancer cells come from normal cells with damage to genes involved in cell-cycle regulation. • Genes are damaged by things called carcinogens • Carcinogens – things known to cause cancer (ex: UV rays, cigarette smoke, pollution, alcohol, asbestos, etc.) • Cancer cells do not receive the signals telling the cell to not divide, so they divide constantly • Cancer is uncontrolled cell division • Cancer cells do not carry out normal cell functions Cell Cycle Regulation Problems: Cancer Treatments for cancer kill cancer cells & healthy cells