* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Alkenes - MsReenChemistry
Survey
Document related concepts
Woodward–Hoffmann rules wikipedia , lookup
Fischer–Tropsch process wikipedia , lookup
Marcus theory wikipedia , lookup
George S. Hammond wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Baylis–Hillman reaction wikipedia , lookup
Ring-closing metathesis wikipedia , lookup
Stille reaction wikipedia , lookup
Ene reaction wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogenation wikipedia , lookup
Asymmetric induction wikipedia , lookup
Cracking (chemistry) wikipedia , lookup
Wolff–Kishner reduction wikipedia , lookup
Hofmann–Löffler reaction wikipedia , lookup
Strychnine total synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
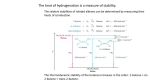
Organic Chemistry Lesson 5 Alkenes Refresh https://quizlet.com/_1r6zhg Write an equation for the reaction between methane and chlorine to form chloromethane. Explain this reaction in terms of a free-radical mechanism. We Are Here Lesson 5: Alkenes Objectives: Describe the main addition reactions of the alkenes Extract an alkene from a citrus fruit Organic vocabulary Nucleophile Nucleus loving Seeking + Electron rich with lone pairs and/or negative charges Examples Cl-, OH-, :NH3 Electrophile Electron loving Seeking – Electron deficient with positive or partial positive charges Examples NO2+, H+, Nu : E+ Nu - E Reactivity of Alkenes Alkenes are considerably more reactive than alkanes and are a major industrial feedstock The reactivity is due to the double bond: The double bond contains 4 electrons This is a significant amount of charge which: Makes it attractive to electrophiles Enables it to polarise approaching molecules Most reactions of alkenes are addition reactions where two molecules come together to make one new one Trigonal planar, 120⁰ Alkenes and hydrogen Alkene + hydrogen alkane Reaction conditions: Hot Ni catalyst This is an addition reaction, in which the hydrogen adds across the double bond Alkenes and hydrogen halides Alkene + hydrogen halide halogenoalkane Reaction conditions: This reaction occurs very readily and needs no special conditions This is an addition reaction, in which the hydrogen halide adds across the double bond Markovnikov’s Rule There are 2 possible products for hydrogen halide additions. Which occurs? Discuss. Markovnikov’s Rule states "when an unsymmetrical alkene reacts with a hydrogen halide to give an alkyl halide, the hydrogen adds to the carbon of the alkene that has the greater number of hydrogen substituents, and the halogen to the carbon of the alkene with the fewer number of hydrogen substituents." This is an empirical rule based on Markovnikov's experimental observations in 1870 on the addition of hydrogen halides to alkenes. Today we say that the reaction occurs via protonation to give the more stable carbocation. The halide will add to the more stable 2⁰carbocation rather than a less stable 1⁰carbocation. Alkenes and halogens Alkene + halogen dihalogenoalkane Reaction conditions: This reaction occurs very readily and needs no special conditions If the halogen used is an aqueous solution of bromine (bromine water), the orange-brown colour of bromine solution is decolourised. This is the standard test for alkenes. Alkenes and water Alkene + water alcohol Reaction conditions: Water must be steam Phosphoric or sulphuric acid catalyst This is the process used to make industrial ethanol Fermentation from sugar would be far too expensive! Extracting an alkene Alkenes occur widely in nature, one such being the compound limonene which is found in many citrus fruits. In this experiment you will extract limonene from orange skin and test it to confirm its alkene properties. Follow the instructions here Polymerisation Under the right conditions, alkene molecules will add to each other creating a polymer In this case, 1-bromo-2-fluoroethene polymerises to form poly-1-bromo-2-fluroethene Conditions: Vary from alkene to alkene but often include high pressure, temperature and a catalyst The carbons in the C=C double bonds form the carbon chain, everything else hangs off this chain Drawing polymers Draw three-monomer lengths of the polymers formed by: Propene Styrene Pent-2-ene Homework Research the economic importance of alkenes including: Manufacture of margarine Manufacture of ethanol Polymerisation Key Points Alkenes undergo addition reactions with: Hydrogen Hydrogen halides Halogens Water (steam) Alkenes undergo addition polymerisation Alkenes are very economically important due to the range of products they can make We can deduce the product of asymmetric addition of hydrogen halides using Markovnikov’s rule