* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download L16 - sRNA Overview
Secreted frizzled-related protein 1 wikipedia , lookup
RNA polymerase II holoenzyme wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
Promoter (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Eukaryotic transcription wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Endogenous retrovirus wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Gene regulatory network wikipedia , lookup
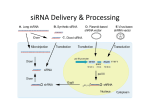
Lecture 16 – Overview of sRNA Signaling BIOL 5190/6190 Cellular & Molecular Singal Transduction Prepared by Bob Locy Last modified -13F Introductory • Brief History of sRNAs • Bacterial – riboswitches • Eukaryotes – • miRNA synthesis & function • Plant paradigm • Animal paradigm • siRNA synthesis & function • Plant paradigm • Animal paradigm Introductory • Brief History of sRNAs • lin-4 – C. Elegans in 1993 – turned out to be the first small regulatory RNA to be discovered in eukaryotes. • Mutant with developmental defects – Animals look terrible, elogated growth, larval skin, stop molting, apparently partial larval growth arrest • Independently, RNA interference (RNAi) was discovered • RNAi involved in control of viral pathogenesis, and artificial RNAi for study of gene regulation. • Ultimately demonstrated that “natural” RNAi was viable regulatory process, and • The discovery of multiple small regulatory RNAs in eukaryotes, and post transcriptional gene silencing, translational gene silencing, and transcriptional gene silencing. Introductory • Brief History of sRNAs • RNAi – Post transcriptional gene silencing. • Originally discovered in transgenic plants, as antisense knockdown of transcription • Led to the discovery of hairpins as RNAi agents • Ultimately, found natural antisense constructs, and naturally produced hairpins miRNAs Module 04: Animal miRNA biogenesis Cell Signalling Biology - Michael J. Berridge - www.cellsignallingbiology.org - 2012 Animal miRNA Function - Overview The task of establishing microRNA properties and function of individual miRs is ongoing and already there are indications that each miR can modulate the activity of up to 100 mRNAs to influence a large number of key biological processes: • • • • • • • • Maintenance of embryonic stem (ES) cell pluripotency. MicroRNA modulation of cell-cycle regulatory mechanisms p53 functions and microRNAs MicroRNA regulation of differentiation • Differentiation of cardiac cells • Differentiation of smooth muscle cells Cell proliferation Apoptosis Stress responses. MicroRNA dysregulation and cancer Module 11: Cell Proliferation siRNAs • Short (small) Interfering RNAs – siRNAs • NOT miRNAs, produced by different pathways, have different functions • ARE dsRNA-produced, are non-coding RNAs with regulatory functions • PTGS • TGS • epigenetics • Usually does not involve hairpin • Usually does involve an RNA-dependent RNA polymerase • May be cut by same RNAse III type proteins, but may be isoforms with miRNA cutters • Load into RISC complexes siRNAs • Animals • piRNAs – Piwi-interacting siRNAs • endo-siRNAs • Plant • • • • • Repeat-associated siRNA – ra-siRNA Trans-acting siRNA – ta-siRNA Phased secondary – siRNA – pha-siRNA cis natural antisense siRNA - cis-NAT-siRNA trans natural antisense siRNA - trans-NAT-siRNA Module 11: miRNA Function – Embryonic Stem Cell miRNA