* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ethers General formula R-O-R` Properties Ethers are generally
Kinetic resolution wikipedia , lookup
Fischer–Tropsch process wikipedia , lookup
Asymmetric induction wikipedia , lookup
Bottromycin wikipedia , lookup
Tiffeneau–Demjanov rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
1,3-Dipolar cycloaddition wikipedia , lookup
Diels–Alder reaction wikipedia , lookup
George S. Hammond wikipedia , lookup
Wolff–Kishner reduction wikipedia , lookup
Stille reaction wikipedia , lookup
Petasis reaction wikipedia , lookup
Hofmann–Löffler reaction wikipedia , lookup
Hydroformylation wikipedia , lookup
Ring-closing metathesis wikipedia , lookup
Enantioselective synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Elias James Corey wikipedia , lookup
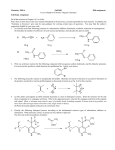
Ethers General formula R-O-R' Properties Ethers are generally unreactive, but due to the presence of the lone pairs on oxygen, unlike hydrocarbons, they are soluble in concentrated sulfuric acid: R-O-R' + H 2 SO4 R-O-R' + HSO 4 Nomenclature The IUPAC rules name the R-O- group as an alkoxy group attached to the longest chain, however the compounds are often named as ethers. CH3OCH3 CH3OCH2 CH3 CH3CH2OCH3 CH2 dimethyl ether diethyl ether or ether methylethyl ether methoxymethane ethoxyethane methoxyethane OCH3 O O O anisole methoxybenzene methylphenyl ether ethylene oxide oxirane oxycyclopropane furan tetrahydrofuran oxacyclopentane O Cl O Cl O Cl O Cl 1,4-dioxane 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzodioxin Synthesis 1. From alcohols and phenols - the Williamson ether synthesis 2 ROH + 2 Na 2 RO- Na+ + H2 R-O-R' + X 2 RO- + R'X This is an SN 2 reaction so is fast when R'X is a primary halide, but does not go when R'X is a tertiary halide. for example 2 CH3CH2O- Na+ + H2 2 CH3CH2OH + 2 Na CH3CH2Obut CH3CH2O however H3C + CH3 CH2 Cl - + H3C CH3 C O CH3 CH3CH2OCH2 CH3 CH3 C Cl CH3 CH3 C H2C + Cl + CH3CH2OH + Cl CH3 CH3 C O CH2CH3 CH3 H3C + CH3 CH2Cl For the Williamson ether synthesis to go, the alkoxide can be primary, secondary or tertiary, but the alkyl halide should be primary or secondary. O OH + + H2 O NaOH OCH2 CH2 CH3 O + CH3 CH2CH2Br Br but CH3CH2CH2O + no reaction Preparation of epoxides by internal Williamson type synthesis CH2=CH 2 + Br2 + H2O Br H2C CH2 OH OHOH 1) Br2/H2 O 2) HO Br H2C CH O O O -Br 2. Alkoxymercuration CH3 CH3 Hg(OCOCH 3)2/CH3 CH2OH H2C C CH 3 H2C C CH 3 Hg OCH2 CH3 O C CH 3 NaBH 4, HO- CH 3 H3C C CH 3 OCH2 CH3 O Almost any alkene and any alcohol can be used in this synthesis HC CH 2 e.g. OH 1) Hg(OCOCH3)2/CH3 CHCH3 CH 3 O C CH 3 H CH CH3 2) NaBH4, OHReactions of ethers Inert chemically The most important reaction is cleavage by hydrogen iodide 2 RI R-O-R' + 2HI e.g. H 3C excess HI CH O CH CH3 CH 3 CH 3 HI 100oC + H2 O 2 H3C CH-I CH3 + H2 O I-CH 2CH2CH 2CH2-I O Epoxides are very reactive due to the angle strain in the 3-membered ring. They are very useful in syntheses O HO H 2C 0oC + HCl CH2 Cl Epoxides can be used in the synthesis of alcohols O RCH 2CH2OMgX + RMgX H2O RCH 2CH2OH This reaction can be used to increase the alkyl chain by 2 carbon units Synthesis of cis-7,8-epoxy-2-methyloctadecane H H O cis 7,8-epoxy-2-methyl-octadecane Synthesise this molecule from HC and any inorganic reagents needed. CH , Br (CH 2)9CH3 and Br