* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
Ancestral sequence reconstruction wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Protein adsorption wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Bottromycin wikipedia , lookup
Protein (nutrient) wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Transfer RNA wikipedia , lookup
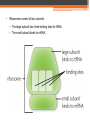
Unit 7c – Protein Synthesis (Part 2 ) Translation Chapter 8.4 & 8.5 Translation is the 2nd part of Protein Synthesis • Occurs in the cytoplasm • Quick Overview ▫ mRNA gives message to tRNA ▫ tRNA translates message to rRNA ▫ rRNA (ribosome) assemble protein by putting amino acids together Amino acids are coded by mRNA base sequences. • Translation converts mRNA messages into polypeptides (big work for protein). • A codon is a sequence of three nucleotides that codes for an amino acid. • There are 20 different amino acids codon for methionine (Met) codon for leucine (Leu) • The genetic code matches each codon to its amino acid or function. – three stop codons – one start codon, codes for methionine The genetic code matches each RNA codon with its amino acid or function. • A change in the order in which codons are read changes the resulting protein. • Regardless of the organism, codons code for the same amino acid. Amino acids are linked to become a protein. • An anticodon (tRNA) is a set of three nucleotides that is complementary to an mRNA codon. • An anticodon is carried by a tRNA. • Ribosomes consist of two subunits. – The large subunit has three binding sites for tRNA. – The small subunit binds to mRNA. • For translation to begin, tRNA binds to a start codon and signals the ribosome to assemble. – A complementary tRNA molecule binds to the exposed codon, bringing its amino acid close to the first amino acid. – The ribosome helps form a polypeptide bond between the amino acids. – The ribosome pulls the mRNA strand the length of one codon. – The now empty tRNA molecule exits the ribosome. – A complementary tRNA molecule binds to the next exposed codon. – Once the stop codon is reached, the ribosome releases the protein and disassembles. • Summary: DNA: TTG AAC CGA TAT mRNA: AAC UUG tRNA: UUG AAC CGA UAU rRNA: Protein: GCU AAC UUG GCU AUA AUA What is this called? Transcription Where does this take place? Nucleus What is this called? Translation Where does this take place? Cytoplasm Asparagine – Leucine – Alanine - Isoleucine • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=NJxobgkPEAo