* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Virus - Waukee Community School District Blogs
Whooping cough wikipedia , lookup
Onchocerciasis wikipedia , lookup
Meningococcal disease wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Tuberculosis wikipedia , lookup
Foodborne illness wikipedia , lookup
Yellow fever wikipedia , lookup
Neglected tropical diseases wikipedia , lookup
Typhoid fever wikipedia , lookup
Trichinosis wikipedia , lookup
Gastroenteritis wikipedia , lookup
Influenza A virus wikipedia , lookup
Ebola virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Human cytomegalovirus wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Traveler's diarrhea wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Rocky Mountain spotted fever wikipedia , lookup
Henipavirus wikipedia , lookup
West Nile fever wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis C wikipedia , lookup
Middle East respiratory syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
Sexually transmitted infection wikipedia , lookup
Antiviral drug wikipedia , lookup
Herpes simplex virus wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Orthohantavirus wikipedia , lookup
Neisseria meningitidis wikipedia , lookup
Coccidioidomycosis wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Infectious mononucleosis wikipedia , lookup
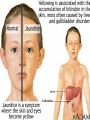
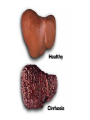
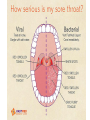
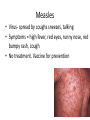
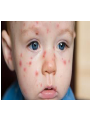
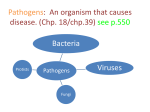
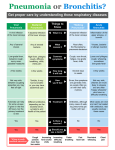
Chapter 23 lesson 1 Understanding Communicable Diseases page 628-632 and lesson 2 Common Communicable Diseases. Pages 633-637 What is another word for germs? Pathogen What does communicable mean? A disease that is spread from one living organism to another or through the environment. Other names are contagious and infectious How are Viruses different from Bacteria? • A piece of genetic material surrounded by a protein coat • Must have a host • Antibiotics do not work against viruses • Immune system has to destroy a virus • Viruses take over other body cells by making clones of them self. • • • • • • • • • • • • • Common cold Influenza (flu) Viral pneumonia Viral hepatitis Polio Mononucleosis Measles AIDS Viral meningitis Chicken pox Herpes Rabies West Nile Virus Bacteria • Single celled microorganisms that live almost everywhere • Some are helpful, most are harmless • Disease causing bacteria produce toxins. Substances that kill cells or interfere with their function • Can be treated with antibiotics • Food illnesses, strep throat, tuberculosis, diptheria, gonorrhea, lyme disease, bacterial pinkeye, bacterial pneumonia, bacterial meningitis Fungus • Athletes food • Ring worm • Vaginal yeast infections • Plant like organisms than can cause diseases of lungs, mucous membranes, and the skin Protozoa • Single celled microorganisms that are larger and more complex than bacteria. • Malaria • Sleeping Sickness Rickettsias • • • • Resemble bacteria Often enter body through insect bites Typhus Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever Vectors • Organisms that carry and transmit pathogens to humans or other animals • Common vectors include: flies, mosquitos, spiders, ticks Direct Contact • Touching, kissing, sexual contact, biting • Puncture wounds • Childbirth • Contact with infected animals Indirect Contact • Touching objects that have germs on them, such as a door knob, then you eat chips or rub your eyes • Vectors • Contaminated food or water Airborne Transmission • Sneezes • Coughs • Breathing in a closed room Chapter 23 Lesson 2 Common Communicable Diseases pages 633-637 Respiratory tract passageway that makes breathing possible nose, throat, lungs common infections: colds, flu, tuberculosis, strep throat, pneumonia 5 ways to avoid respiratory infections • Avoid close contact with sick people. • Stay home if sick • Wash hands often • Avoid touching mouth, eyes,nose • Eat right, exercise regularly • Do not smoke Jaundice • Yellowing of the skin and eyes Cirrhosis • Scarring of the liver Single and Double Pneumonia • Single = 1 lung • Double = both lungs Pneumonia • Flu sometimes leads to pneumonia • Infection of the lungs in which air sacs fill with pus and other fluids • Can be caused by bacteria or virus • Can be fatal- especially for older people and people with lung or heart problems Common Cold • Viral infection that causes inflamation of the mucous membrane, the lining of nose, ears, mouth • No cure cause caused by virus • Allergies have some of same symptoms, but allergies come and go and there is no fever with an allergy Influenza Flu • Viral infection of respiratory tract • High fever, fatigue, headache, muscle ache,coughing • Drink a lot of liquids, plenty of rest, good nutrition, once a year vaccine to prevent it Strep Throat • • • • Bacterial infection Can be treated with antibiotics Airborn or direct contact transmission Left untreated can lead to serious damage to heart • Symptoms = sore throat, swollen lymph glands in the neck, fever Tuberculosis--TB • Disease that attacks the lungs • Spreads through the air • Symptoms = fatigue, coughing, fever, weight loss, night sweats • Treated with antibiotics Hepatitis A,B,C • • • • Attacks the liver Causes jaundice and cirrhosis Vaccines for A and B No cure as it is caused by virus A • Enters though digestive system. • Good hand washing and clean food and water prevents B • Spread through sexual contact or with an infected person’s blood • To avoid do not share toothbrushes, razors • Avoid body piercings, tattoos and illegal drugs C • Most common blood born infection in United States • Infected by contaminated blood and sexual contact, dirty needles • No vaccine or cure Mononucleosis • Virus-direct contact, kissing, sharing a drinking glass, eye make up eating utensils • Symptoms = chills, fever, sore throat, fatique, swollen lymph nodes • Treatment- rest Measles • Virus- spread by coughs sneezes, talking • Symptoms = high fever, red eyes, runny nose, red bumpy rash, cough • No treatment. Vaccine for prevention Encephalitis • Virus – carried by mosquitoes • Symptoms = headache, fever, hallucinations, confusion, paralysis, disturbances of speech, memory, behavior and eye movement • Treatment – anti viral medicine if caused by virus, no known treatment Meningitis • Viral, or bacterial caused • Fever, severe headache, nausea, vomiting, sensitivity to light, stiff neck • Treatments=viral meningitis (anitviral meds) bacterial meningitisantibiotics. Vaccine available Chicken Pox • Virus-spread through air or contact with fluids from blisters • Symptoms=rash, itching, fever,fatigue • Treatment- rest stay home so others are not infected, vaccine available