* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch. 14 Notes - 7th - Lee County Schools
Meningococcal disease wikipedia , lookup
Yellow fever wikipedia , lookup
Henipavirus wikipedia , lookup
Chagas disease wikipedia , lookup
Brucellosis wikipedia , lookup
Gastroenteritis wikipedia , lookup
Human cytomegalovirus wikipedia , lookup
Typhoid fever wikipedia , lookup
Whooping cough wikipedia , lookup
Herpes simplex virus wikipedia , lookup
Eradication of infectious diseases wikipedia , lookup
Ebola virus disease wikipedia , lookup
West Nile fever wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
Neglected tropical diseases wikipedia , lookup
Orthohantavirus wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Rocky Mountain spotted fever wikipedia , lookup
Visceral leishmaniasis wikipedia , lookup
Middle East respiratory syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Neisseria meningitidis wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Coccidioidomycosis wikipedia , lookup
Sexually transmitted infection wikipedia , lookup
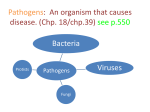
7th Chapter 14 Notes – Infectious Diseases Lesson One Infectious Disease - Is an illness that is caused by microorganisms Microorganisms – very small things that are found everywhere Contagious Diseases - Spread directly or indirectly from one person to another How Diseases Spread - Touching, Coughing or Sneezing, Sharing, Sexual Contact Bacteria - Very simple single-celled microorganisms that are found everywhere. Reproduce very quickly. Strep Throat - Caused by a type of bacterium called streptococcus. Pain when you swallow, fever. Throat Culture - A test in which a doctor uses a cotton swab to wipe the back of the throat Rheumatic Fever - Caused when strep throat infections are not treated properly. Can affect your heart valves and large joints. Sinuses - Spaces located within the front of the skull - Many have small tubes that drain fluid down into the nose or throat, if tube gets blocked, the sinuses become clogged and become inflamed. - Inflammation of a sinus - Usually not contagious. Symptoms of Sinusitis: congestion, runny nose, fever, headache. Lesson Two Sinusitis Tuberculosis - Serious disease caused by a slow-growing bacterium Symptoms of TB - Very tired, have a fever, night sweats, cough. Carriers - Few or no symptoms. Can pass to disease to others. - Kills about 3 million people worldwide a year. All cases must be reported to the health department. Avoiding Bacterial Infections - Limit contact with people who have bacterial infection, avoid sharing food or drink with others, wash hands frequently, take warm showers, eat properly and get enough sleep. Antibiotics - A drug that can kill bacteria or slow the growth of bacteria. - Penicillin - first antibiotic, discovered by accident 1928. Alexander Fleming – bacteria in a Petri Dish were dying where mold was growing. - 1940s – became available to many people - One of the smallest and simplest diseasecausing agents. They are EVERWHERE. Responsible for many diseases, some deadly. - Not considered to be living things. Cannot reproduce on its own. Must reproduce by invading a living thing Genetic Material - Chemical information that is passed on during reproduction How Viruses Can be Passed - Touching living or nonliving objects, coughing, sneezing, insect bites, blood, sexual contact. Lesson Three Virus Common Cold - Most common viral infection. Caused by many different kinds of viruses. - On average, person gets about 2 colds a year. - Spread by coughing, sneezing, touching. - Congestion, runny nose, sore throat, sneezing, and coughing. - Medicines available. Drink lots of fluids and get rest. - “Flu” – viral infection that is very common in winter months. - Spread by coughing, sneezing, touching. - Body aches, headaches, high fever, chills, congestion, cough, sore throat. - HIGH FEVER – main difference between cold and flu Vaccine - Substance that helps the body build resistance to a certain disease. Cannot completely stop the spread of a virus. Mononucleosis - Mono or “kissing disease” is caused by a virus called EBV. - Common in older teens and young adults. - Spread by coughing, sneezing, kissing or sharing food and drink. - Make you tired for weeks, bad sore throat, fever, swollen spleen, swollen lymph nodes (small oval structures located throughout body that help remove harmful substances from fluids surrounding cells). Symptoms of Cold Influenza Symptoms Ways to Prevent Viral Infections - Best ways to prevent viral diseases are vaccines. Students are legally required to get vaccines before they are allowed to go to school Lesson Four Sexually Transmitted Disease - Any disease that can be passed from person to person by any form of sexual contact. Caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi, parasites 1 in 4 newly infected people is a teenager Millions of new cases each year - Symptoms vary. Brain damage, paralysis, and death. Infertility - Inability to produce children Sexual Abstinence - Refusal to take part in sexual activity Common STDs - TABLE 2 – pg. 311 look at and discuss. AIDS - Acquired immune deficiency syndrome – deadly disease. Caused by HIV, an infectious virus. HIV - Virus that attacks the immune system, which is the group of cells and tissues that defends your body against disease. - Slowly destroys the person’s ability to fight disease Symptoms of AIDS - Fever, weight loss, sores covering body. Gradually becomes more ill and eventually dies. How HIV is Spread - Sexual Contact, Mother to Child, Drug Use, Blood Transfusion - First reported in 1981, since spread worldwide. Lesson Five Preventing Spread of Infectious Disease - Keep Clean – practice good hygiene, avoid infection, protect others – cover mouth when you sneeze or cough