* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Pathogens: An organism that causes disease.
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
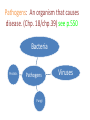
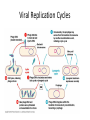
Pathogens: An organism that causes disease. (Chp. 18/chp.39) see p.550 Bacteria Protists Pathogens Fungi Viruses Types of Diseases Contagious…if it spreads quickly • Non-communicable Disease: cannot be transmitted from one person to another • Heart attach • Depression • Stroke • Hypertension/hypo. • Cancer • Genetic disorders (only to their children) • Communicable Disease: can spread from one person to another • Diarrhea • Pneumonia • Tuberculosis (TB) • Sexually transmitted diseases (STD’s) Bacteria • Unicellular and everywhere • Some damage cells and tissues • Others release Toxins: poisons that travel through the body and may cause diseases • There are environmental toxins: Lead and Mercury Other toxins:Botulism> improperly prepare food Diseases Caused by Bacteria Disease Bacterium Effect on Body Strep Throat Streptococcus Fever, sore throat swollen neck glands Tuberculosis Mycobacterium Fatigue, weight loss, mild fever, chronic cough Tetanus Clostridium tenani Muscle spasms, paralysis, death Lyme Disease Borrelia burgdorferi Rash at site of tick bite, fever, chills Bacterial Meningitis Neisseria meningitidis High fever, headache, stiff neck, nausea Diphtheria Sore throat, lowgrade fever Corynebacterium diphtheria Viruses: Nonliving..Must have a LivingHost • Consist of genetic material enclosed in a protein coat (Capsid [head], nucleic acid, Sheath, Tail) • Bacteriophage (phage): a virus that infects a bacterium. The virus will attach its legs to a cell and then inject its genetic material into it. The virus takes control of the bacterial cell and directs it to produce viral material. A single infected cell may replicate thousands of viruses. A typical Bacteriophage, a type of virus Protein coat Attaches to a cell Viruses Cause…. • • • • • • HIV Influenza Chickenpox Colds Measles Rabies Viral Replication Cycles p. 478/479 • (1)Lytic Cycle: immediately takes over killing the host cell • (2) Lysogenic Cycle: does not kill host cell immediately integrates its genetic material with the host cell…creates a provirus…..sits dormant….then one day takes over the host Viral Replication Cycles