Endosafe®-PTS™ Gram ID for Rapid Gram Positive and Negative
... The PTS™ Gram ID is a fast, simple test that measures the presence of the cell walls in a microbial isolate. The measurement is interpreted by the software to indicate whether a sample contains Gram-negative or -positive bacteria or yeasts/molds. Eliminating technician variability that can occur in ...
... The PTS™ Gram ID is a fast, simple test that measures the presence of the cell walls in a microbial isolate. The measurement is interpreted by the software to indicate whether a sample contains Gram-negative or -positive bacteria or yeasts/molds. Eliminating technician variability that can occur in ...
Virulence factors of enteropathogenic Escherichia co/i
... heat-stable enterotoxins which induced fluid secretion in this system. These toxins were distinct from LT and ST of ETEC strains and there was a correlation in this assay between the potency of the toxin and the severity of the disease caused by a particular strain of EPEC. Although the results from ...
... heat-stable enterotoxins which induced fluid secretion in this system. These toxins were distinct from LT and ST of ETEC strains and there was a correlation in this assay between the potency of the toxin and the severity of the disease caused by a particular strain of EPEC. Although the results from ...
histophilus somni - Revistas Científicas de la Universidad de Murcia
... be carriers of non-pathogenic variants of the organism, mainly in the genital mucosa. The causes of these differences in virulence between strains are not defined. Several determinants of virulence of the pathogen are proposed. However, many of these factors cannot be clearly related to clinical dis ...
... be carriers of non-pathogenic variants of the organism, mainly in the genital mucosa. The causes of these differences in virulence between strains are not defined. Several determinants of virulence of the pathogen are proposed. However, many of these factors cannot be clearly related to clinical dis ...
Burkholderia pseudomallei: AN UPDATE ON DISEASE
... Despite several decades of clinical research, the mortality rate for melioidosis remains high. Genomics-based studies have demonstrated the plasticity of the B. pseudomallei genome and the coding sequences consists of a myriad of functions that enable the bacteria to adapt to these hostile environme ...
... Despite several decades of clinical research, the mortality rate for melioidosis remains high. Genomics-based studies have demonstrated the plasticity of the B. pseudomallei genome and the coding sequences consists of a myriad of functions that enable the bacteria to adapt to these hostile environme ...
Etiology and Pathogenesis of Periodontal Disease - Beck-Shop
... The search for the etiological agents for destructive periodontal disease has been in progress for over 100 years. However, until recently, there were few consensus periodontal pathogens. Some of the reasons for the uncertainty in defining periodontal pathogens were determined by the following circu ...
... The search for the etiological agents for destructive periodontal disease has been in progress for over 100 years. However, until recently, there were few consensus periodontal pathogens. Some of the reasons for the uncertainty in defining periodontal pathogens were determined by the following circu ...
Ecological fitness and strategies of adaptation of Bartonella
... Abstract – Bartonella spp. are facultative intracellular bacteria that cause characteristic hostrestricted hemotropic infections in mammals and are typically transmitted by blood-sucking arthropods. In the mammalian reservoir, these bacteria initially infect a yet unrecognized primary niche, which s ...
... Abstract – Bartonella spp. are facultative intracellular bacteria that cause characteristic hostrestricted hemotropic infections in mammals and are typically transmitted by blood-sucking arthropods. In the mammalian reservoir, these bacteria initially infect a yet unrecognized primary niche, which s ...
Ecological fitness and strategies of adaptation of Bartonella species
... Abstract – Bartonella spp. are facultative intracellular bacteria that cause characteristic hostrestricted hemotropic infections in mammals and are typically transmitted by blood-sucking arthropods. In the mammalian reservoir, these bacteria initially infect a yet unrecognized primary niche, which s ...
... Abstract – Bartonella spp. are facultative intracellular bacteria that cause characteristic hostrestricted hemotropic infections in mammals and are typically transmitted by blood-sucking arthropods. In the mammalian reservoir, these bacteria initially infect a yet unrecognized primary niche, which s ...
All Vaccines Are Dangerous
... must provide some context. Disease attributed to H. influenzae type B, like pneumococcal ...
... must provide some context. Disease attributed to H. influenzae type B, like pneumococcal ...
Haemophilus influenzae and the complement system
... is also catalyzed by sialyltransferases, and several types have been characterized in H. influenzae. The main one is Lic3A, which is involved in serum resistance and also essential for bacterial survival in an animal model of otitis media [53, 57]. Furthermore, the complement system has a central ro ...
... is also catalyzed by sialyltransferases, and several types have been characterized in H. influenzae. The main one is Lic3A, which is involved in serum resistance and also essential for bacterial survival in an animal model of otitis media [53, 57]. Furthermore, the complement system has a central ro ...
Insights on the interaction between macrophages Haemophilus parasuis
... upper respiratory tract of healthy pigs and the etiological agent of Glässer’s disease. Differences in virulence among H. parasuis strains have been widely observed by different tests, including in vivo infections and in vitro phagocytosis assays with porcine alveo ...
... upper respiratory tract of healthy pigs and the etiological agent of Glässer’s disease. Differences in virulence among H. parasuis strains have been widely observed by different tests, including in vivo infections and in vitro phagocytosis assays with porcine alveo ...
Potential Transmission of Bartonella Species by Ticks Sarah Arnao
... (Under the direction of Michael G. Levy and Edward B. Breitschwerdt). ...
... (Under the direction of Michael G. Levy and Edward B. Breitschwerdt). ...
Mosaic 545 - Infinity Medical Engineering
... Time is Critical When a patient presents with an infection during emergency or intensive care, blood culture can be a race against time. The typical process of pathogen identification in blood takes at least 24 hours. Current methods include culture techniques using agar plates and culture mediums ( ...
... Time is Critical When a patient presents with an infection during emergency or intensive care, blood culture can be a race against time. The typical process of pathogen identification in blood takes at least 24 hours. Current methods include culture techniques using agar plates and culture mediums ( ...
Identification of signaling pathways important for Borrelia burgdorferi
... subsequently named Borrelia burgdorferi (Bb) sensu stricto, is the main causative agent ...
... subsequently named Borrelia burgdorferi (Bb) sensu stricto, is the main causative agent ...
ZOONOSES –PROTECTION OF PUBLIC AND ANIMAL HEALTH
... zoonotic cycles between vertebrate hosts and tick vectors [1] and most zoonotic species are maintained in wildlife reservoirs. Various Babesia species have been detected in a wide range of different mammal species [1]. However, the occurrence in natural mammal hosts is still incompletely known for s ...
... zoonotic cycles between vertebrate hosts and tick vectors [1] and most zoonotic species are maintained in wildlife reservoirs. Various Babesia species have been detected in a wide range of different mammal species [1]. However, the occurrence in natural mammal hosts is still incompletely known for s ...
Bordetella Pertussis
... materials formed during bacterial growth ; growth takes 48- 72 hours, bisected pearls or ...
... materials formed during bacterial growth ; growth takes 48- 72 hours, bisected pearls or ...
Role of Special Histochemical Stains in Staining
... however, histochemical stains do not offer an advantage over H&E in the visualization of viruses and immunohistochemistry is the preferred method for this purpose. Histochemical stains also help to identify and classify bacteria, fungi and protozoa. The Giemsa and Gram’s stains help to visualize bac ...
... however, histochemical stains do not offer an advantage over H&E in the visualization of viruses and immunohistochemistry is the preferred method for this purpose. Histochemical stains also help to identify and classify bacteria, fungi and protozoa. The Giemsa and Gram’s stains help to visualize bac ...
2. Equine Periodontal Anatomy
... inflammatory cells such as neutrophils in the lamina propria (Fig 7) and adjacent connective tissues ...
... inflammatory cells such as neutrophils in the lamina propria (Fig 7) and adjacent connective tissues ...
Genetic modification of a vaginal strain of L actobacillus fermentum
... flora in a wide variety of Moreover, they are harmless commensals, devoid of pathogenic potential. To be useful as vaccine vehicles, lactobacilli need to carry and express foreign antigens. The genetic modification of lactobacilli only became a practical proposition in 1988 when electroporation was ...
... flora in a wide variety of Moreover, they are harmless commensals, devoid of pathogenic potential. To be useful as vaccine vehicles, lactobacilli need to carry and express foreign antigens. The genetic modification of lactobacilli only became a practical proposition in 1988 when electroporation was ...
intestinal colonization, microbiota, and probiotics
... and commensals.21 Intracellular signalling pathways of TLRs result in production of proinflammatory cytokines through activation of the transcription nuclear factor B. These gut microbiota impact healthy immunophysiologic regulation, contributing to the anti-inflammatory tone in the gut. Indeed, se ...
... and commensals.21 Intracellular signalling pathways of TLRs result in production of proinflammatory cytokines through activation of the transcription nuclear factor B. These gut microbiota impact healthy immunophysiologic regulation, contributing to the anti-inflammatory tone in the gut. Indeed, se ...
Biochemical and molecular characterization of putative immunoprotective molecules of the soft
... Ticks are obligate blood-feeding ecto-parasites that transmit pathogenic organisms such as viruses, bacteria and protozoa. They parasitize mammals, birds, amphibians and occasionally reptiles (Sonenshine, 1991). Tick-borne diseases greatly impact both human and animal health (Estrada-Peña & Jongejan ...
... Ticks are obligate blood-feeding ecto-parasites that transmit pathogenic organisms such as viruses, bacteria and protozoa. They parasitize mammals, birds, amphibians and occasionally reptiles (Sonenshine, 1991). Tick-borne diseases greatly impact both human and animal health (Estrada-Peña & Jongejan ...
Clostridium Clostridium is a genus of Gram
... Clostridium perfringens is the most common bacterial agent for gas gangrene, which is necrosis, putrefaction of tissues, and gas production. It is caused primarily by Clostridium perfringens alpha toxin. The gases form bubbles in muscle (crepitus) and the characteristic smell in decomposing tissue. ...
... Clostridium perfringens is the most common bacterial agent for gas gangrene, which is necrosis, putrefaction of tissues, and gas production. It is caused primarily by Clostridium perfringens alpha toxin. The gases form bubbles in muscle (crepitus) and the characteristic smell in decomposing tissue. ...
ID_299_Special- clinical- ecological _English_sem_5
... Each of the following statements concerning infection with Chlamydia psittaci is correct EXCEPT: C psittaci can be isolated by growth in cell culture and will not grow in blood agar The organism appears purple in Gram-stained smears of sputum The infection is more readily diagnosed by serologic test ...
... Each of the following statements concerning infection with Chlamydia psittaci is correct EXCEPT: C psittaci can be isolated by growth in cell culture and will not grow in blood agar The organism appears purple in Gram-stained smears of sputum The infection is more readily diagnosed by serologic test ...
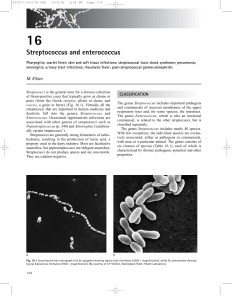
Streptococcus and enterococcus
... resembles that of Staphylococcus aureus, but the clinical characteristics associated with these two groups of pyogenic cocci are often distinct. Similarities and differences can be explained by the virulence factors expressed by the two species. ...
... resembles that of Staphylococcus aureus, but the clinical characteristics associated with these two groups of pyogenic cocci are often distinct. Similarities and differences can be explained by the virulence factors expressed by the two species. ...
Probiotics and Antibiotics - Should they be Given Together? - Bio-Kult
... antibiotics suffer from diarrhoea. As well as being an unpleasant side effect, it can in some cases, lead to chronic or persistent diarrhoea. It is estimated that 25% of cases of AAD are caused by Clostridium difficile. Infection with this pathogen can lead to colitis and is a common complication of ...
... antibiotics suffer from diarrhoea. As well as being an unpleasant side effect, it can in some cases, lead to chronic or persistent diarrhoea. It is estimated that 25% of cases of AAD are caused by Clostridium difficile. Infection with this pathogen can lead to colitis and is a common complication of ...
Primer 01 Microbiology 101
... Clostridium perfringens • C. perfringens (arrows) in a mixed culture with E. coli and K. pneumoniae. • This is one of the most common species of Clostridium isolated from clinical specimens. • C. perfringens spores are almost never seen; rods are described as “boxcar shaped” or rectangular and are ...
... Clostridium perfringens • C. perfringens (arrows) in a mixed culture with E. coli and K. pneumoniae. • This is one of the most common species of Clostridium isolated from clinical specimens. • C. perfringens spores are almost never seen; rods are described as “boxcar shaped” or rectangular and are ...
Lyme disease microbiology

Lyme disease, or borreliosis, is caused by spirochetal bacteria from the genus Borrelia, which has at least 37 known species, 12 of which are Lyme related, and an unknown number of genomic strains. Borrelia species known to cause Lyme disease are collectively known as Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato.Borrelia are microaerophilic and slow-growing—the primary reason for the long delays when diagnosing Lyme disease—and have been found to have greater strain diversity than previously estimated. The strains differ in clinical symptoms and/or presentation as well as geographic distribution.Except for Borrelia recurrentis (which causes louse-borne relapsing fever and is transmitted by the human body louse), all known species are believed to be transmitted by ticks.