* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 21, Lesson 3 – Common Infectious Diseases
Chagas disease wikipedia , lookup
Herpes simplex virus wikipedia , lookup
Ebola virus disease wikipedia , lookup
West Nile fever wikipedia , lookup
Influenza A virus wikipedia , lookup
Yellow fever wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
Eradication of infectious diseases wikipedia , lookup
Whooping cough wikipedia , lookup
Human cytomegalovirus wikipedia , lookup
Foodborne illness wikipedia , lookup
Typhoid fever wikipedia , lookup
Trichinosis wikipedia , lookup
Traveler's diarrhea wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Middle East respiratory syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Gastroenteritis wikipedia , lookup
Orthohantavirus wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Neisseria meningitidis wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis C wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Rocky Mountain spotted fever wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Neglected tropical diseases wikipedia , lookup
Infectious mononucleosis wikipedia , lookup
Coccidioidomycosis wikipedia , lookup
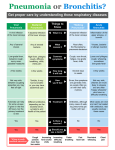
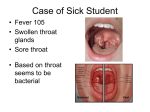
COMMON INFECTIOUS DISEASES CHAPTER 21, LESSON 3 PRUITT, ALLEGRANTE, PROTHROW-STITH, HEALTH, PEARSON, 2014 WRITE: WERE ANY OF THE LEADING CAUSES OF DEATH IN 2000 INFECTIOUS DISEASES? EXPLAIN WHY YOU THINK THIS IS THE CASE. BACTERIAL DISEASES • Of thousands of infectious diseases and over 40 commonly occurring in the U.S., 4 caused by bacteria STREP THROAT • Common among teens • Usually found in nose and throat • Spread by contact with mucus • Symptoms: sore throat, swollen lymph nodes on sides of neck, headache, fever • Doctor can diagnose with throat culture LYME DISEASE • Bitten by infected tick • Symptoms: red rash at site of bite, fever, chills, body aches • Wear long-sleeved shirts and long pants, tuck pants into socks BACTERIAL MENINGITIS • Infection of fluid in spinal cord and fluid surrounding brain • Symptoms: high fever, headache, vomiting, stiff neck – SEEK MEDICAL ATTENTION IMMEDIATELY • Two types – one bacterial; other viral • Bacterial – more serious • Early treatment can prevent serious illness and death TUBERCULOSIS • Highly contagious – in the lungs • Transmitted through droplets in cough or sneeze inhaled by another person • Symptoms: fatigue, weight loss, mild fever, constant cough • 1/3 of world’s population infected • 2 million dies each year TREATING BACTERIAL DISEASES • Antibiotic – drug to inhibit or kill bacteria • Use as prescribed and complete dose VIRAL DISEASES COMMON COLD • Group of symptoms caused by different viruses – sneezing, sore throat, runny nose, coughing, chest congestion, fever, headache, muscle ache • Last 3 – 7 days • Spread when touch contaminated object or inhale droplets of sneeze or cough • NO CURE! INFLUENZA • Common upper respiratory viral infection • Spread by airborne droplets and contact with contaminated objects • Typical symptoms: high fever, sore throat, headache, cough • More serious for infants, elderly, and people with heart and lung diseases • Between 3,000 and 49,000 die each year in the U.S. because of influenza • Some types can be prevented by immunization PNEUMONIA • In elderly, heart disease, breathing problem people, flu may develop into pneumonia • Serious infection of the lungs • Many die each year – caused by viruses, bacteria, or fungi HEPATITIS • Group of viruses infecting the liver • Important to many body functions • Symptoms: fever, nausea, pain in abdomen, jaundice • SEEK MEDICAL ATTENTION HEPATITIS A • Transmitted in human wastes and in contaminated water and food • Begins 4 weeks after exposure • Recovery takes several weeks • Vaccine can prevent disease HEPATITIS B • More severe than A • Transmitted in blood or during sexual contact; during tattooing and body piercing • Over 1 million carry • There is a vaccine HEPATITIS C • More serious than A • Transmitted by blood, during sexual contact, during tattooing or body piercing • Number one reason for liver transplants in the U.S. • About 3 million carry TREATING VIRAL DISEASES • No particular medicine that can cure a virus • Bed rest, well-balanced diet, plenty of fluids • Over-the-counter medicines can treat symptoms – may make you feel better, BUT do NOT cure infection PREVENTING INFECTIOUS DISEASES • Avoid contact with pathogens • Immunizations current • Choose healthful behaviors • Wash hands several times a day – before eating and after using restroom • Don’t share towels, eating utensils, cups, or hairbrushes • Cook and store food properly • Avoid close contact with those who are ill • Sneeze into your sleeve or elbow • Manage stress in healthful ways – 8 hours of sleep • Eat well-balanced meals – don’t skip meals • Exercise regularly – 3 or more times a week • Avoid unhealthful substances – tobacco, alcohol, illegal drugs