* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 5 – Chemical Reactions
Isotopic labeling wikipedia , lookup
Fine chemical wikipedia , lookup
Acid–base reaction wikipedia , lookup
Al-Shifa pharmaceutical factory wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear transmutation wikipedia , lookup
Nucleophilic acyl substitution wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Marcus theory wikipedia , lookup
Inorganic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Chemical weapon proliferation wikipedia , lookup
Safety data sheet wikipedia , lookup
Enantioselective synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Chemical weapon wikipedia , lookup
Chemical Corps wikipedia , lookup
Chemical plant wikipedia , lookup
Organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Chemical industry wikipedia , lookup
Supramolecular catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Chemical equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Multi-state modeling of biomolecules wikipedia , lookup
Asymmetric induction wikipedia , lookup
Chemical potential wikipedia , lookup
Chemistry: A Volatile History wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
Rate equation wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
George S. Hammond wikipedia , lookup
Ring-closing metathesis wikipedia , lookup
Hydroformylation wikipedia , lookup
Photoredox catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
History of chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry 2005 wikipedia , lookup
Process chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogen-bond catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Bioorthogonal chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Strychnine total synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Transition state theory wikipedia , lookup
Click chemistry wikipedia , lookup
VX (nerve agent) wikipedia , lookup
Chemical reaction wikipedia , lookup
Lewis acid catalysis wikipedia , lookup
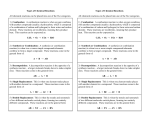
Chapter 5 – Chemical Reactions Nuclear change – change in the nucleus of an atom (This will cause one element to change into another.) Examples: nuclear power plants, atomic bombs or radioactive decay Physical change – no new chemical produced Examples: melting or boiling change of particle size Chemical Change – when a chemical reaction produces a new (different) chemical Examples: Burning paper Rusting iron Vinegar and baking soda How do we know if a chemical reaction has taken place? Clues 1. 2. 3. 4. Color change Heat given off Gas produced Solid formed when two liquids are mixed (precipitate) 5. A different smell Chemical Equation H2 + O2 Reactants (what you start with) H2O Products (what you end up with) A chemical equation tells you what compounds you start with and what compounds you end up with. A balanced chemical equation also tells you how much of each material you need. 2H2 + O2 2H2O For every one oxygen we need two hydrogen and we get two water molecules An equation is balanced if you have the same number of each kind of atom on each side. Na + Cl2 NaCl Not Balanced Balancing equations Rule 1 – Balance equations by placing coefficients in front of the formulas. Rule 2 – Do not change the subscripts of the formulas. 2 Na Balanced + Cl2 2 NaCl Types of Chemical Reactions Synthesis A + B AB Two substances are combined to form a third substance. Na + Cl NaCl Decomposition AB A + B Breaking apart one substance into two substances. This is the opposite of a synthesis reaction NaCl Na + Cl Draw a diagram of each reaction 1. C + O2 CO2 2. 2 P + 3 Cl2 2 PCl3 3. N2 + 3 H2 4. CH4 + 2 O2 2 NH3 CO2 + 2 H2O Types of Chemical Reactions Single Replacement A + BC AC + B One element replaces another in a compound. A more reactive element will always replace a less reactive element. F + NaI NaF + I +- +- Double Replacement AB + CD AD + CB Elements exchange partners to form different compounds. +- + - HCl + NaOH + - + - HOH + NaCl Factors affecting the rate of reactions Particle size – the smaller the particles the faster the reaction (example – dust explosion) Higher temperature – the higher the temperature the faster the reaction Increase concentration of solution (a more concentrated acid will react faster than a dilute acid) Add a catalyst – a catalyst is a chemical that speeds up a reaction but does not get used up by the reaction Predicting Chemical Reactions If two elements are being combined the reaction will be synthesis. Two metals will not combine chemically Noble gases will not combine Write the symbol for the more positive element first and then use the criss-cross method to determine the formula. Predicting Decomposition Reactions If there is just one compound, the only thing it can do is decompose (break down) This often requires energy If a product is a diatomic molecule you must place a 2 after the element symbol. (The diatomic molecules are marked on your chart.) Predicting Single Replacement Reactions If there is an element and a compound, the reaction will be a single replacement. A more reactive metal will replace a less reactive metal or hydrogen. The more reactive metals are located near Cs and Fr on the chart. A more reactive non-metal will replace a less reactive non-metal. The more reactive non-metals are near F on the chart. Predicting a Double Replacement Reaction If there are two compounds containing positive and negative groups, the reaction will be a double replacement. A double replacement reaction will take place if there is a very stable compound such as HOH produced.