* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download sce-13-introduction
Global warming controversy wikipedia , lookup
Michael E. Mann wikipedia , lookup
German Climate Action Plan 2050 wikipedia , lookup
Instrumental temperature record wikipedia , lookup
Economics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change denial wikipedia , lookup
Global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change feedback wikipedia , lookup
Climate resilience wikipedia , lookup
Climate change adaptation wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Climatic Research Unit documents wikipedia , lookup
Politics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate sensitivity wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on human health wikipedia , lookup
Fred Singer wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in Tuvalu wikipedia , lookup
Climate engineering wikipedia , lookup
Atmospheric model wikipedia , lookup
Media coverage of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Citizens' Climate Lobby wikipedia , lookup
Solar radiation management wikipedia , lookup
Numerical weather prediction wikipedia , lookup
Climate governance wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and poverty wikipedia , lookup
Scientific opinion on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in the United States wikipedia , lookup
General circulation model wikipedia , lookup
Public opinion on global warming wikipedia , lookup
Attribution of recent climate change wikipedia , lookup
IPCC Fourth Assessment Report wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on Australia wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on humans wikipedia , lookup
Surveys of scientists' views on climate change wikipedia , lookup
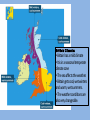
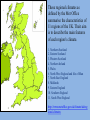
Introduction to Weather and Climate Tutor: Roy Doyon MA: University of Georgia, Geography Dept. Teaching Assistant in Weather and Climate courses Assistant Professor at Ball State University, Muncie, Indiana. Geography Dept. 1998 – 2005 Courses taught include Global Regional Geography, Map Reading, and a variety of cartography classes. Contact information: [email protected] Mobile phone: 07599-08997 Housekeeping • • • • How to leave the building in case of a fire The location of the gathering point during a fire drill Why we keep the attendance register Yes, you’re right, I’m originally an American and I talk funny, please stop me when you don’t understand what I’m saying and I’ll attempt to clarify the point. Course Overview and Objectives • To explain and illustrate the basic factors involved in weather and climate on a global, regional and local scale. Where appropriate we will briefly describe some of the issues involved in global climate change. • At the conclusion of the course you will understand how the weather and climate system works and have a better appreciation of what the various media are presenting to you in their daily weather reports. • Note: The weather system is a very logical one. Once you grasp a few concepts you’ll be able to make sense of what’s going on. Topics • • • • • • • • • • • • • • Definition of weather and climate. Introduction to the Met Office website Earth/sun relationships and geometry. Solar radiation Atmospheric structure and composition Changing states of water Barometric pressure, high and low pressure systems Global circulation patterns: the ITCZ, prevailing winds, jet streams Air masses; high and low pressure systems; fronts and depressions; land and sea breezes Atmospheric moisture Ocean currents - their influence on weather and climate Storm systems: frontogenesis, hurricanes, tornadoes, monsoons Weather reporting networks and instruments Climate classification and global distribution of climates Climate is the sum total or composite of the weather conditions that prevail at a place or region. It includes the statistics (means, or averages, variability, ranges and extremes) of temperature, humidity, atmospheric pressure, wind direction and velocity, cloud cover, precipitation, and other meteorological variables over a long period of time. The standard interval used by the World Meteorological Society (WMO) is 30 years and these are called “normals.” First used for 1901-1930 data. The current normal is 1961-1990 or 1981-2010, depending on data availability. The 30 years must be consecutive and the normals are updated each decade. Weather is the condition of these same variables over the period of a few days. Conventionally weather extends out 10 to 15 days which is the limit of numerical weather prediction. The Met Office definition: Climate, which comes from the Greek klima meaning 'area', usually refers to a region's long-term weather patterns. This is measured in terms of average precipitation (i.e. the amount of annual rainfall, snow etc), maximum and minimum temperatures throughout the seasons, sunshine hours, humidity, the frequency of extreme weather, and so on. The Met Office is the UK’s national weather service and a worldleading provider of climate science and services. Their weather forecasts help to keep the UK moving every day on land and by sea, and protect anyone taking to the air. Around the world, our knowledge of the weather and climate informs the long-term decisions and policies of businesses and governments. Critically, we contribute to the global understanding of climate change and inform the UK Government’s international negotiations on greenhouse gas emissions. http://www.metoffice.gov.uk The Met Office http://www.metoffice.gov.uk •Introduction to the Met Office web site •Activate the“Weather” heading at the top left–scroll down and select the “Surface pressure” charts. •Also under the “weather” heading and to the right you will find “Specialist Forecasts” which include climate information for aviation and marine forecasts. •I would recommend that you look at the Met Office web site weekly during the term and especially the surface pressure map, it’s the most useful product and brings together many of the concepts we will be discussing. This is a little heuristic device you may find useful The climate system involves the interaction of many aspects of the environment British Climate: • Britain has a mild climate • It is in a seasonal temperate climate zone • The sea affects the weather. • Britain gets cool, wet winters and warm, wet summers. • The weather conditions are also very changeable. These regional climates as defined by the Met Office summarise the characteristics of 11 regions of the UK. Their aim is to describe the main features of each region's climate. 1. Northern Scotland 2. Eastern Scotland 3. Western Scotland 4. Northern Ireland 5. Wales 6. North West England and Isle of Man 7. North East England 8. Midlands 9. Eastern England 10. Southern England 11. South West England http://www.metoffice.gov.uk/climate/uk/reg ional-climates