* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download topic 4 - biochemistry - part 1 - organic compounds
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Bottromycin wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Intrinsically disordered proteins wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Protein (nutrient) wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Protein adsorption wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
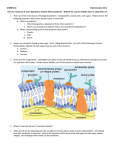
TOPIC 4: BIOCHEMISTRY PART 1: TYPES OF ORGANIC COMPOUNDS An ORGANIC COMPOUND is: _________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ Living organisms are made up of many different types of organic compounds. Organic compounds have many different jobs in living things: o _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ o _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ o _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ o _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ o _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ Organic compounds come in all shapes and sizes. Some organic compounds can be very big and some are small. o Small molecules are called: ______________________________________________________________________ These small subunits are able to link (or bond) together to form larger molecules. o Large molecules are called: ______________________________________________________________________ A polymer can be made up of thousands of monomers linked together! The linking up of many smaller molecules to form a polymer is called: ________________________________ The breaking down of a polymer into smaller monomers is called: ____________________________________ Chemical activities in our bodies are always putting things together and taking things apart. All the chemical activities that occur in a living organism is called: ______________________________________ Ex) Break-down activity in the body = _________________________________________ Build-up activity in the body = _____________________________________________ 4 FAMILIES OF ORGANIC COMPOUNDS FOUND IN LIVING THINGS 1. ________________________________________________________ 2. ________________________________________________________ 3. ________________________________________________________ 4. ________________________________________________________ 1. CARBOHYDRATES FUNCTIONS: 1)________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________________________ (Hint: Think about why a runner might eat a big bowl of pasta the night before a big run!) 2) _______________________________________________________________________________________________________ ELEMENTS THAT MAKE UP CARBOHYDRATES: _______________________________________________________________ Molecular formulas are generally multiples of ______________________ _____________ ratio of C: H : O 3 TYPES OF CARBOHYDRATES 1. MONOSACCHARIDES: SIMPLE SUGARS FUNCTION: ___________________________________________________________________________ End in: _______________ They are building blocks (________________________) of larger carbohydrates (_______________________) STRUCTURE OF MONOSACCHARIDES: o Formula for monosaccharides = multiple of CH2O o Have 3-6 carbons o Can be linear or ring shaped Examples: o ___________________________________ o ____________________________________ o ___________________________________ Take a closer look at fructose and glucose: Fructose (C6H12O6) Glucose (C6H12O6) (same formula but do these look the same?!) That’s because glucose and fructose are __________________________________ ISOMERS:_________________________________________________________________________________________________ Let’s look at glucose and fructose linearly to give you a better idea of what I mean: 2. DISACCHARIDES: DOUBLE SUGARS FUNCTION: _______________________________________________________________________________________ STRUCTURE ___________ monosaccharides joined together. How? _________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ Examples of dehydration synthesis reactions that form disaccharides: The opposite reactions are called: _____________________________________________________________________________ 3. POLYSACCHARIDES: MANY SUGARS FUNCTIONS: ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ Examples: __________________________________________________________________________________________________ STRUCTURE OF POLYSACCHARIDES What do you notice about the relationship between monosaccharides and polysaccharides? _________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ Why do you think starch (polysaccharides) need to break down into smaller subunits (simple sugars) in our bodies?? _________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ CARBOHYDRATE POLYMER(MACROMOLECULE): ___________________________________________________________ MONOMER SUBUNIT (BUILDING BLOCKS) OF A CARBOHYDRATE: ________________________________________ *SO: Many carbohydrate subunits(monosaccarides)chemically bonded together form a polysaccharide! 2. LIPIDS POLYMER (MACROMOLECULE) NAME: ______________________________________________________________________ MONOMER SUBUNITS (BUILDING BLOCKS) THAT MAKE IT UP: ____________________________________________________ + _____________________________________________________ LIPID STRUCTURE ELEMENTS THAT MAKE UP LIPIDS: ___________________________________________________________________ *SO: Many of these subunits (triglycerides) chemically bonded together form a lipid! 2 TYPES OF FATS (FATTY ACIDS) 1. ___________________________________________________ 2. ___________________________________________________ Carbon chain contains all _________________ bonds Carbon chain contains at least one ___________ bond Mainly come from _____________________products Mainly come from ____________________ products __________________________at room temperature ______________________________at room temperature Major cause of heart disease The "better" of the two types of fats Example) _____________________________________ Example) ____________________________________ TYPES OF LIPIDS: 1. ___________________ 2. ______________________ 3. ______________________ 4. ____________________ FUNCTIONS OF LIPIDS: 1. SOURCE OF STORED ENERGY (for long term use) (Fats store energy more efficiently than carbohydrates) 2. INSULATION 3. MAKES UP PART OF THE BASIC STRUCTURE OF THE CELL MEMBRANE (phospholipid bi-layer) 4. STEROID HORMONES - Function in the endocrine system Have a skeleton of four fused carbon rings and vary according to attached functional groups, which determine the steroid function. ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ Steroid Examples) Cholesterol Testosterone Estrogen NOTE: Since lipids are non-polar they are considered: __________________________________________________ 3. PROTEINS POLYMER (MACROMOLECULE) NAME: ______________________________________________________________________ MONOMER SUBUNITS (BUILDING BLOCKS) THAT MAKE IT UP: ___________________________________________ PROTEIN STRUCTURE: ELEMENTS THAT MAKE UP PROTEINS: _______________________________________________________________ STRUCTURE OF AN AMINO ACID *There are 20 different types of amino acids. Have 4 parts Differ in their "R" group *SO: Many of these subunits (amino acids) chemically bonded together form a protein! As with all the other organic compounds: Amino Acids are linked together by the process of ___________________________________________________ Peptide Bond = covalent bond between 2 amino acids 2 amino acids = _______________________ 3-50 amino acids = _______________________________ 51+ amino acids = _________________________________ By what process do you think peptide bonds between amino acids break apart? _______________________________________________________________________________________________ (sound familiar?!) 20 TYPES OF AMINO ACIDS **Generally: The order in which the amino acids are linked together, determines the characteristics of the protein molecule. **Based on this sequence, the protein chains twist, turn, & bend into specific 3-D shapes. -The shape of a protein molecule is its: _______________________________________ -The shape determines a proteins' function!! TYPES/FUNCTIONS OF PROTEINS: 1. To _______________________________________________ muscles and tissues. 2. Cell membrane components that ______________________ substances into or out of cells. (protein channels) 3. To receive and send signals : ______________________________________________________________________________ 4. To help fight disease: ________________________________________________ 5. To regulate chemical reactions: ___________________________________________ (biological catalysts) 6. Blood components (____________________________________ on red blood cells) 7. Help maintain muscle structure 8. Hair, nail and silk structural components MORE ABOUT PROTEIN SHAPE The shape of a protein is a result of 4 levels of structure: 1. _________________________________________: The amino acid sequence of the protein. 2. ______________________________________________: Helical or pleated shape due to Hydrogen Bonding between amino acid side groups Ex) Hair, nails and silk only have primary and secondary protein structure 3. _________________________________________: The 3D shape of a protein Results from folding of the amino acid chains upon themselves The shape that results, determines the proteins specific function Ex) Enzymes and antibodies have primary, secondary, and tertiary structure. They recognize other molecules by their shape. 4. _________________________________________: Attractions and bonding between more than one polypeptide chain results in this structure Ex) Hemoglobin has all four levels of protein structure and consists of 4 polypeptide chains joined together. SUMMARY OF PROTEIN LEVELS OF STRUCTURE 4. NUCLEIC ACIDS POLYMER (MACROMOLECULE) NAME: ______________________________________________________________________ MONOMER SUBUNITS (BUILDING BLOCKS) THAT MAKE IT UP: ___________________________________________ NUCLEIC ACID STRUCTURE: ELEMENTS THAT MAKE UP NUCLEIC ACIDS: _________________________________________________________ NUCLEOTIDE STRUCTURE: 3 PARTS 1. ________________________________________________________ 2. ________________________________________________________ 3. ________________________________________________________ TWO TYPES OF NITROGENOUS BASES A. ____________________________________________ B. _____________________________________________ Many of these subunits (nucleotides) chemically bonded together form a nucleic acid! As with all other organic compounds: These nucleotides are joined together by the process of ___________________________________ TYPES/FUNCTIONS OF NUCLEIC ACIDS: DNA RNA Name: Name: 5- carbon sugar : 5- carbon sugar : Double Stranded Twisted Helix Shape Single Stranded – Not Twisted Strands held together by Hydrogen Bonds DNA RNA Function: Function: Location: Location: ADDITIONAL INFO ABOUT DNA Looks like a twisted ladder Backbone: Made up of alternating phosphates and sugars Antiparallel Chains Sugars: _____________________________________________ 5’ End: _______________________________________________ _______________________________________________ 3’ End: _______________________________________________ _______________________________________________ Rungs on Ladder: Complementary Base Pairs What do you notice about the nitrogen base pairs?? **DNA gets copied into RNA which is then used to build protein molecules. **Proteins make each individual unique. **Since proteins make us who we are -& because DNA makes our proteins--it is really our DNA that makes us unique!