* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Changes in DNA and results of changes
Bisulfite sequencing wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom National DNA Database wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
DNA damage theory of aging wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Zinc finger nuclease wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
SNP genotyping wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
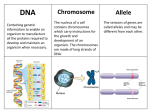
Components of DNA and how DNA relates to traits 1. The structures marked 3 in the diagram are responsible for – a. Absorbing oxygen b. Carrying genetic codes c. Lining up amino acids d. Serving as an anticodon 2. Why will knowledge of the human genome enable scientists to better understand proteins involved in human diseases? a. DNA contains the information used to make proteins. b. Nucleic acid molecules have shapes similar to those of proteins c. The bases that make up DNA are also present in RNA. d. Chromosomes can combine to form proteins. 3. Which of the following features of DNA is most important in determining the phenotype of an organism? a. The direction of the helical twist b. The number of deoxyribose sugars c. The sequence of nitrogen bases d. The strength of hydrogen bonds 4. A particular strand of DNA has the base sequence ATT-CCG. What is the base sequence of the complementary strand? a. ATT-CCG b. TAA-GGC c. CCG-TTA d. TAT-CGC (1 – B) (2 – A) (3 – C) (4 – B) Changes in DNA and results of changes 1. A DNA segment is changed from AATTAG to AAATAG . This is a(n) a. Frame shift mutation b. Point mutation c. Inversion d. Deletion 2. What type of mutation has occurred in the figure? a. Point mutation b. Frame shift c. Lethal d. Protein 3. What will be the result of the preceding mutation? a. It will have no effect on protein function b. Only one amino acid will change c. Nearly every amino acid in the protein will be changed d. The organism will die 4. A strand of DNA with the sequence AAC AAG CCC undergoes a mutation, is changed to CAC AAG CCC. How will this mutation affect the amino acid sequence? a. One amino acid will change b. Two amino acids will change c. All of the amino acids will change d. The amino acids will remain the same 5. Most mutations a. have no effect on an organism. b. are fatal to an organism. c. are helpful to an organism. d. are harmful to an organism. (1-B, 2-B, 3-C, 4-A, 5-A) Genetics – Predict outcomes of crosses 1. In humans, freckles are encoded by a dominant allele. An individual woman is heterozygous for freckles. According to the law of segregation, which of the following would apply to a child of this woman? A. The child must inherit the dominant allele for freckles. B. The child must inherit the recessive allele for freckles. C. The child has an equal chance of inheriting the dominant allele or the recessive allele for freckles from her mother. D. The child has a greater chance of inheriting the dominant allele than the recessive allele for freckles from her mother. 2. The illustration below shows two adult rabbits and their offspring. In rabbits, the allele for spots (R) is dominant to the allele for solid color (r). What is the most likely genotype of the parent rabbits in the illustration? A. rrrr B. Rrrr C. RrRr D. RRrr 3. In pea plants, the allele for purple flowers (P) is dominant to the allele for white flowers (p). A plant that is heterozygous for purple flowers is crossed with a plant with white flowers. What percentage of the offspring plants are expected to have purple flowers? A. 25% B. 50% C. 75% D. 100% 4. In a certain variety of chicken, some offspring have a feather pattern that is black-and-white checkered. Chickens with this checkered feather pattern result from the cross of a black chicken with a white chicken. Which of the following types of inheritance is most likely responsible for the checkered feather pattern? A. codominant B. dominant C. polygenic D. sex-linked 5. In sheep, the allele for white wool (W) is dominant, and the allele for black wool (w) is recessive. A farmer has mated two Suffolk sheep for a few years. These matings have resulted in six offspring, four with white wool and two with black wool. One parent has white wool and the other has black wool. Which of the following could be the genotypes of the parent sheep? A. WW and Ww B. WW and ww C. Ww and Ww D.Ww and ww 6. Female cattle that have white coats are crossed with male cattle that have red coats. Both male and female offspring have roan coats, which are coats with both red hairs and white hairs. Which of the following best describes the genetics of coat color in the cattle? A. The red and white alleles are sex-linked. B. The red and white alleles are codominant. C. The red allele is recessive to the white allele. D. The red allele is dominant to the white allele. 7. A partial Punnett square is shown below. Which of the following statements describes the parental genotypes that would result in this Punnett square? A. Both parents are heterozygous. B. Both parents are homozygous dominant. C. One parent is homozygous recessive and the other parent is heterozygous. D. One parent is homozygous dominant and the other parent is heterozygous. Key 1. C 2. B 3. B 4. A 5. D 6. B 7. D