* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Name
Lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
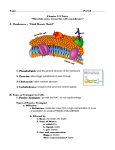
Name Class Cell Transport Diagramming: 1.Cell 2.Polar Head 3. Phospholipid 5. Hydrophobic 4. Non-polar tails Use the word bank below to answer the diagram questions above: Phospholipid Non-polar Tails Hydrophilic Hydrophobic Polar Head Cell Use the diagram above to answer the following question 6. Explain why the water shown in the diagram must use a channel protein to get through the membrane. Water is polar and the tails of the phospholipids are non-polar, so they don’t mix. Instead water must use a protein channel to enter the cell (facilitated diffusion). The protein channel is called an aquaporin. Multiple Choice Write the letter that best answers the question or completes the statement on the line provided. _____ 7. Which of the following is a function of the cell membrane? a. breaks down lipids, carbohydrates, and proteins from foods b. stores water, salt, proteins, and carbohydrates c. keeps the cell wall in place d. regulates the movement of materials into and out of the cell _____ 8. The cell membrane contains channels and pumps that help move materials from one side to the other. What are these channels and pumps made of? a. carbohydrates c. bilipids b. lipids d. proteins _____ 9. Diffusion occurs because a. molecules are attracted to one another. b. molecules constantly move and collide with each other. c. cellular energy forces molecules to collide with each other. d. cellular energy pumps molecules across the cell membrane. _____ 10. An animal cell that is surrounded by 100% water will burst because the osmotic pressure causes a. water to move into the cell. c. solutes to move into the cell. b. water to move out of the cell. d. solutes to move out of the cell. Completion Complete each statement on the line provided using the word bank below Solute Solvent Phospholipid Polar/non-polar Facilitated Carbohydrate 11. ____Phospholipids____________________ has polar and non-polar parts and makes up the majority of the cell membrane. 12. The material that gets dissolved in a solution is called the _solute______. 13. ___Solvent______________ is the material that does the dissolving in a solution. 14. Identification (ID) tags that are displayed on the surface of the cell are made from the organic molecule __carbohydrates_______ and are used for cell recognition. 15. The cell membrane can rearrange itself if it is disturbed because the tiny parts that make up the bilayer are _polar/nonpolar_____________, which pull them back into place. 16. ___Facilitated__________diffusion uses a protein to help large molecules move through the membrane Use the diagram below to answer the following questions on the lines provided. (2pts ea.) A student put together the experimental setup shown below. The selectively permeable membrane is permeable to water, but not the solute shown. Figure 7–4 17. How does the solution on Side A of the apparatus shown in Figure 7–4 differ from the solution on Side B? Side A has more water and less solute (particles) than side B. Side B has more solute, which means it has less water. 18. Describe the movement of water in the experimental setup. In other words, predict which way the water will move. The water will move from Side A toward Side B. We know this because less solute on side A means “high water” and water moves from high to low. 19. The diagram shows a special type of diffusion. List what type of diffusion is shown and explain how it works. The type of diffusion is osmosis, or the movement of water from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration.