* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 3.2 and 3.3
Biosequestration wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Isotopic labeling wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
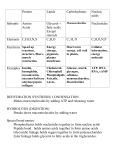
3.2: Carbon Compounds • All of the many compounds can be classified in TWO broad categories: ORGANIC COMPOUNDS AND INORGANIC COMPOUNDS. • The Chemistry of Carbon = Chemistry of Life ORGANIC • Made up of mostly what element? •CARBON • They are covalently bonded to another carbon atom and to other elements as well typically hydrogen, nitrogen, and oxygen • -C-C-C-C-C-C-C-C II. Carbon’s Bonding Behavior A. Outer shell of carbon has ____ electrons; but can hold ____ B. Each carbon atom can form __________ bonds with up to _________ atoms 4 covalent bonds C. Carbon atoms can form _______________ or ______________ • D. Carbon atoms covalently bonded form the ________________ of organic compounds • E. ______________ can project from the carbon backbone F. Carbon’s tendency to _______________ results in an enormous variety of ORGANIC COMPOUNDS Carbon can share two or even three pairs of electrons with another atom a) SINGLE BOND - A bond formed when two atoms share ONE pair of electrons. b) DOUBLE BOND - Atoms share TWO pairs of electrons. c) TRIPLE BOND - Atoms Sharing THREE pairs of electrons. STRONGEST!!! III. Functional Groups A. Atoms or clusters of atoms that are covalently bonded to a _____________________________ B. Gives organic compounds their different properties ex: HYDROXYL GROUP -OH attached makes an ALCOHOL Examples of Functional Groups Hydroxyl group - OH Amino group - NH3+ Carboxyl group - COOH Phosphate group - PO3- Methyl group - CH3 IV. LARGE CARBON MOLECULES A. Large Carbon Compounds are built up from smaller simpler molecules called _______________ (building blocks) (MONO = ONE) B. Monomers can bind to one another to form complex molecules known as _________________ (POLY = MANY) C. A Polymer consist of repeated, linked units, forming large polymers called ______________________ (MACRO = LARGE) V. Types of Reactions 1. Condensation Reaction AKA-Dehydration Synthesis 2. Hydrolysis 1) Condensation Reactions (Dehydration Synthesis) small to big a) Monomers link to form ______________ b) Monomers are CONDENSED and water (H2O) is squeezed out (DEHYDRATE) -H2O is a by-product of the reaction c) Enzymes remove from one molecule, from another bond formed between two molecules VIDEO!!! CONDENSATION (dehydration synthesis) enzyme action at functional groups Fig. 3.4a, p. 37 2) Hydrolysis (hydro-lys-is) a) The _________________ of complex molecules, such as polymers b) SPLITTING of a WATER molecule to ADD -OH group and an H bonds break that hold polymers together PUT THE WATER BACK IN!!!!! HYDROLYSIS enzyme action at functional groups Fig. 3.4b, p. 37 DO NOW: Turn to front of notes and do the first set (a-h), match left side to right side recap from Way back when….. yesterday 3.3 MOLECULES OF LIFE Four categories of organic compounds: • Carbohydrates • Proteins • Lipids • Nucleic Acids Human Body Oxygen 65% Carbon 18% Hydrogen 10% Nitrogen 3% Calcium 2% Phosphorus 1.1% Sulfur 0.25% Sodium 0.15% Chlorine 0.15% Magnesium 0.05 Iron 0.004% What is the difference between structural formula and molecular formula? • Molecular Formula: H2O – The way it is written formula describing its molecules • Structural Formula: H – O – H – The way it looks (arrangement) – Mickey mouse 1. Carbohydrates: sugars and starches contain C, H, and O in the ratio of CH2O -carbo (C) hydrate (H2O) a) monomers of sugars (simple sugars) - 1)eg: Glucose (manufactured by plants) Fructose (found in fruits) Both are C6H12O6 2) ____________: has the same molecular formula but a different structural formula 3) Used for _______________________ Isomers: same molecular formula (C6 H12O6) but different structural formula glucose fructose galactose b) Disaccharides – double sugar C6H12O6 + C6H12O6 C12H22O11 + H2O What type of reaction?? dehydration synthesis – combining of 2 monomers (monosaccharides) by squeezing out a H20 1) EXAMPLES of disaccharides sucrose (glucose + fructose = table sugar) maltose (2 glucose) 2) bond between two monosaccharides is called a ___________________ bond C-O-C 3) a disaccharide contains __________energy than the two units it is composed of (bc of bond) Disaccharides • Made up of? glucose fructose – Two monosaccharides • What type of bond? o – “Glyc sidic” • What type of reaction? – condensation reaction (dehydration synthesis) + H2O sucrose Other sugars: MONOSACCHARIDES OR DISACCHARIDES? c) _________________ – 3 or more monosaccharides complex carbohydrates, starches, cellulose, chitin 1) most abundant of carbohydrates 2) thousands of _____________ units bonded together by dehydration synthesis = type of: ____________________________ 3) energy storage molecules plants = animals = “animal starch” also important as _____________ components of organisms: eg. -cellulose = 50% of carbon in plants cell walls -chitin = exoskeleton of insects Glycogen • Sugar storage form in _____________ • Large storage in _______ and _______ cells -STABLE LEVEL OF INTERNAL CONDITIONS? • When blood sugar decreases, liver cells _____________ glycogen, releasing _____________ cells store energy as polysaccharides rather than monosaccharide units because the _________________________________ (warehouse of simple sugars) Cellulose & Starch • Differ in bonding patterns between monomers • Cellulose - tough, indigestible, structural material in plants (corn covering, celery strings ) • Starch - easily digested, storage form in plants (potato insides) Cellulose and Starch ReCap 1) 2) 3) 4) Monomer of a sugar (one sugar)? Two sugars? Many sugars? Bond name holding monomers of sugar together? 5) How do we break apart a polysaccharide? 6) Humans store sugar as? (animal starch) 2. Lipids A) Composed of C, H, and O b) Ratio of C to H to O higher than in carbohydrates c) Defined based on their solubility: 1) they are insoluble in ___________ 2) they are soluble in ____________ d) Primary function – to store large amounts of energy (twice as much energy as carbs and proteins due to all the CARBONHYDROGEN BONDS e) Secondary functions of lipids: 1. structural components eg. phospholipids - major building block in cell membranes 2. "messengers" (hormones) that play roles in communications within and between cells 3. insulation and padding f) Monomers of Lipids are: The fatty acids are composed of linked CH2 units Fatty Acids building blocks of: Lipids (fats, waxes, phospholipids, but not sterols) 1) Carboxyl group (-COOH) at one end Methyl (CH3 ) group at the other end 2) Carbon (CH2) backbone (up to 36 C atoms) 4) Saturated - __________ bonds between carbons _________ at room temperature 5) Unsaturated – One ________ bond (bent) ________ at room temperature 6) Polyunsaturated – more than one __________ bond (really bent) _________ at room temp. Three Fatty Acids Triglyceride formed by dehydration synthesis + 3H20 three fatty acid tails glycerol triglyceride Fig. 3.8b, p. 40 Glycerol backbone – fatty acids attach to the glycerol (3-Carbon Backbone) Dehydration synthesis removes the –H from the glycerol and -OH from the fatty acid to form a C-O-C glycosidic bond. 9) Phospholipids • Main components of cell membranes • Has a phosphate group and two fatty acids Phosphate group Phospholipid Bilayer 10) Waxes • Long-chain fatty acids linked to long chain alcohols or carbon rings • Firm consistency, repel water • Important in water-proofing • Ex: earwax 11) Sterols and Derivatives • No fatty acids • Rigid backbone of four fused-together carbon rings • Different functional groups • Cholesterol - most common type in animals 3. Nucleic Acids Includes DNA and RNA DNA strand What are the monomers of nucleic acids? • DNA deoxyribonucleic acid • Holds genetic info • Double stranded • RNA ribonucleic acid • Holds instructions to make proteins • Single stranded Nucleotide Structure made up of Three Parts: 1) Sugar –Ribose or deoxyribose 2) Phosphate group 3) Nitrogen Base -A, T, G, C, U Nucleic Acids Adenine Cytosine • Composed of nucleotides • Single- or double-stranded • Sugar-phosphate backbone – Nitrogen makes up the steps ATP - A Nucleotide base three phosphate groups sugar ATP I. = ATP - energy currency of cell A. Temporarily stores large amounts of energy in phosphate bonds B. Regulates many biological pathways C. is made in a process called nucleic acids D. ATP is a monomer of __________ made up of three components 1) = nitrogen containing base 2) = 5 carbon sugar • What is ribose’s molecular formula? – What is the ratio again….. 3) 3 inorganic How ATP releases ENERGY • When break a ______________ group off by _________________ • It becomes _______ (adenosine DIphosphate • And ___________________ energy II. = ADP A. Adenine - ribose- P ~ P B. When the last phosphate group is released from ATP, ADP is formed. ATP ----> ADP + P + energy Why would you need ENERGY from ATP in a cell? • build larger molecules • carry substances into the cell • remove wastes from the cell • for mechanical work (like muscular activity). Recap!! • • • • Monomer of Nucleic acids are….. Name the three groups in one monomer… Nucleic acids primary function is to …… What process puts these monomers together to form long chains…. • What process breaks down ATP for energy….. 4. Proteins A. Most complex and important substances in living organisms B. Composed of C, H, O, N C. Monomer of a protein is: D. Types of Proteins: 1) structural (makes up) – parts of cells, tissues, collagen and elastin 2) movement – in muscle; myosin and actin 3) hormones – insulin and growth factor 4) transport – hemoglobin 5) defense – immunoglobin 6) enzymes – largest group of proteins; regulate reactions (organic catalyst) E. Amino Acid amino group carboxyl group R group – 20 different kinds with distinct properties 1) Properties of Amino Acids a) Determined by the “R group” b) there are 20 different Amino Acids c) Amino acids may be: tyrosine (tyr) lysine (lys) glutamate (glu) glycine (gly) valine (val) phenylalanine (phe) methionine (met) proline (pro) Fig. 3.12, p. 42 2) Protein Synthesis A Protein is a chain of amino acids linked by peptide bonds • Peptide bond: – Type of covalent bond – Links amino group of one amino acid with carboxyl group of next – Forms through condensation reaction (dehydration synthesis) newly forming polypeptide chain Fig. 3.14, p. 43 If there are only 20 amino acids, how are there so many types of proteins? • The sequence (arrangement) of amino acids • The kinds of amino acids present • The number of amino acids in a protein Protein Synthesis • Two linked amino acids = dipeptide • Three or more amino acids= polypeptide • Protein – two or more polypeptide chains Protein Shapes • Fibrous proteins – Polypeptide chains arranged as strands or sheets • Globular proteins – Polypeptide chains folded into compact, rounded shapes Mila Kunis Jolie Primary Structure Amino acids bonded together by peptide bonds (straight chains) Amino Acids (aa) aa1 aa2 aa3 Peptide Bonds aa4 aa5 aa6 Denaturation • Disruption of three-dimensional shape • Breakage of weak bonds • Causes of denaturation: – pH – Temperature • Destroying protein shape disrupts function Substrate reactant being catalyzed Lock and Key mechanism Enzyme is present at beginning and end of reaction!!! A + enzyme B+C Answer the following: 1. What carbohydrate is energy storage in plants? 2. What do 2 amino acids make? 3. What reaction holds 2 monomers together? 4. What lipid has 3 fatty acids and a glycerol? 5. Why are some hormones lipids? 6. What are the 3 parts to a nucleotide? 7. What part of an amino acid differs? 8. What can cause an amino acid to denature?