* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Biology 22 Problem Set 1 Spring 2003
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Saethre–Chotzen syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Pathogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
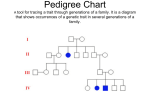
Biology 22 Problem Set 1 Winter 2011 Due January 19th at 10:30 am Hand in the solutions to each of the following problems. Put a box around each of your answers and show your work for partial credit. You may consult your book, lecture notes, other students and/or your instructor for assistance. 1. Chronic Granulomatous Disease (CDG), an immune deficiency characterized by a defect in phagocytosis, is inherited with the X-linked recessive allele g. The X-linked dominant allele G prevents the disease. A straight hairline is inherited with the autosomal recessive allele w. Individuals with the autosomal dominant allele W have a widow’s peak, where the hairline comes to a v-shape in the middle of the forehead. a. Robert has a widow’s peak and CDG. His wife Renee has a straight hairline and does not have CDG. Robert’s mother has a straight hairline. Renee’s father has CDG. Out of five children born to Robert and Renee, what is the probability that at least one will be a son with a widow’s peak who does not have CDG? b. For Robert and Renee, what is the probability that their first child will be either a son with a straight hairline and CDG or a daughter with a widow’s peak and CDG? c. Preston has a straight hairline and does not have CDG. His wife Patricia has CDG and a widow’s peak. Patricia’s mother has a straight hairline. For Preston and Patricia, what is the probability that their first child will be a son with a straight hairline and CDG and their second child will be a daughter with a widow’s peak who does not have CDG and their third child will be a daughter with a straight hairline who does not have CDG? d. Out of 3 children born to Preston and Patricia, what is the probability that 2 will be sons with widow’s peaks and CDG? 2. A prototrophic Hfr strain of E. coli with the genotype trp+ purB- pyrC+ is conjugated with an F- strain with the genotype trp- purB+ pyrC-. The trp gene is known to enter last. The following numbers of recombinants were isolated: trp+ trp+ trp+ trp+ purBpurB+ purB+ purB- pyrCpyrC+ pyrCpyrC+ 0 108 48 244 Draw a genetic map that shows the order in which these genes are arranged and the distances between them. 3. Four different Hfr strains of E. coli transfer their genes in the order given below: Strain 1 Strain 2 Strain 3 Strain 4 Gene Markers Entry Time (min) Gene Markers Entry Time (min) Gene Markers Entry Time (min) Gene Markers Entry Time (min) A 3 C 32 B 51 D 84 C 5 E 26 D 44 B 77 F 2 C 17 A 46 D 56 E 6 A 14 D 24 Using these results, construct a linkage map of the circular E. coli chromosome. Express the gene distances in transfer time (minutes) between adjacent pairs of genes. 4. A female rabbit with hemophilia, rickets and a tail was mated to a male rabbit that did not have hemophilia or rickets but lacked a tail. The F1 females were all wild type, that is, not having hemophilia or rickets but having a tail. The F1 males had hemophilia, rickets and tails. A cross of F1 females to F1 males produced the following offspring in the F2 generation: a. b. c. d. Hemophilia Rickets Tails Males Females Hemophilia No rickets Tail-less 2 0 No hemophilia Rickets Tail 3 48 Hemophilia Rickets Tail-less 63 0 No hemophilia No rickets Tail 57 194 Hemophilia No rickets Tail 40 52 No hemophilia Rickets Tail-less 35 0 Hemophilia Rickets Tail 146 206 No hemophilia No rickets Tail-less 154 0 What are the genotypes of the original parents in this cross? Write each genotype to show which alleles are linked together on the same chromosome. What are the genotypes of the F1 males and females? Write each genotype to show which alleles are linked together on the same chromosome. Draw a genetic map showing the distances between these genes. Express the distances in map units. What is the degree of interference? 5. In humans, deafness (d) and blindness (b, due to the disease retinitis pigmentosum) are determined by recessive alleles at X-chromosome loci that are 18 map units apart. Consider the pedigree shown below. a. What are the possible genotypes for individual III-3? What is the probability for each possible genotype? b. What is the probability that individual III-3 can have a son who is both blind and deaf? c. What are the possible genotypes for individual III-5? What is the probability for each possible genotype? d. What is the probability that individual III-5 can have a son who is both blind and deaf? Normal Vision Normal Hearing Blindness Normal Hearing Normal Vision Deafness Blindness Deafness I II III 1 2 3 4 5 6 7