* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Use Integers and Rational Numbers (2
Numbers (TV series) wikipedia , lookup
History of logarithms wikipedia , lookup
Ethnomathematics wikipedia , lookup
Foundations of mathematics wikipedia , lookup
Law of large numbers wikipedia , lookup
Infinitesimal wikipedia , lookup
Location arithmetic wikipedia , lookup
Georg Cantor's first set theory article wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics of radio engineering wikipedia , lookup
Collatz conjecture wikipedia , lookup
Bernoulli number wikipedia , lookup
Surreal number wikipedia , lookup
Proofs of Fermat's little theorem wikipedia , lookup
Large numbers wikipedia , lookup
Positional notation wikipedia , lookup
Real number wikipedia , lookup
Use Integers and Rational Numbers (2.1)
Definition: A Whole Number belong to the set of numbers
{0, 1, 2, 3, …}.
Whole numbers do NOT have a fractional or decimal part.
Whole numbers are NOT negative
Is the number a Whole Number? If NOT, explain.
Ex. 17 __________________
Ex. 3.4 __________________
Ex. 3 ½ __________________
Ex. -6 ___________________
Ex. 0 ____________________
Ex. ¾ ___________________
Definition: Integers belong to the set of all whole numbers and their opposites {… -3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, …}
Integers do NOT have a fractional or decimal part.
Integers CAN BE Positive or Negative.
Is the number an Integer? If NOT, explain.
Ex. 17 __________________
Ex. 3.4 __________________
Ex. 3 ½ __________________
Ex. -6 ___________________
Ex. 0 ____________________
Ex. ¾ ___________________
Definition: Rational Numbers belong to the set of all numbers that can be written in the form
In other words, a rational number is any number that can be written as a fraction
a
.
b
Whole Numbers and Integers can ALL be written as a fraction by putting the number over 1.
Ex. 6 = ______ , so 6 is ____________________________
Ex. -9 = ______, so -9 is ___________________________
Proper Fractions and Improper Fractions are already in the form
Ex. 3/5 = _______, so 3/5 is __________________________
Ex. 7/3 = _______, so 7/3 is _________________________
Mixed Fractions can be turned into Improper Fractions
Ex. 2 ¾ = _______, so 2 ¾ is _______________________
Terminating Decimals can be written as fractions
Ex. 0.3 = ________, so 0.3 is _______________________
Ex. 0.23 = __________, so 0.23 is ____________________
Ex. 1.7 = __________, so 1.7 is ________________________
1
Repeating Decimals can be written as fractions
_
_
Ex. 0.3 = __________, so 0.3 is __________________
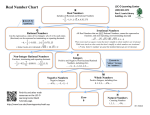
Rational Numbers Can Be ALL of the Following:
Whole Numbers
Integers
Fractions (Proper and Improper)
Mixed Fractions
Decimals
o Terminating (End)
o Repeating
**In other words, the only numbers that are NOT RATIONAL are decimals that do NOT TERMINATE (end)
or DON’T REPEAT.
Rational Numbers
Integers
Whole
Numbers
Fractions
Decimals
Is the number a Rational Number? If NOT, explain.
Ex. 17 __________________
Ex. 3 ½ __________________
Ex. -6 ___________________
Ex. 3.4 __________________
Ex. ¾ ___________________
__
Ex. 0.18 _________________
Ex. 0 ____________________
Ex. 0.5 ___________________
Ex. 2.39582034… _________
_
Ex. 0.5 _______________
Ex. Tell whether each of the following numbers is a whole number, an integer, or a rational number: 5, 0.6, - 2
2
/3, -24, 0.45
5 _______________________________________
0.6 ______________________________________
-24 _____________________________________
__
0.45 _____________________________________
- 2 2/3 ____________________________________
2
Understanding Numbers on a Number Line
Numbers get bigger to the right
Numbers get smaller to the left
-5
-4 -3
-2
-1
Negative Numbers
0
1
2
3
4
Positive Numbers
5
0 is neither positive or negative
Which number is greater? You may use a number line.
Ex. - 4 or 2
________
Ex. -3 or 0
________
Ex. -2 or -5
________
Ex. -2 or 2
________
Order the numbers from Least to Greatest
**If you have to compare fractions and decimals it is easiest to change all of the fractions to decimals to
compare.
**To change fractions to decimals remember to divide
Ex. 3, -1.2, -2, 0
a
b= a b
_______, _______, _______, _______
Ex. 3.6, -1.5, -0.31, -2.8
_______, _______, _______, _______
Ex. 4.5,
_______, _______, _______, _______
-3/4,
-2.1, 1/2
Definition: Opposites are two numbers that the same distance from 0 on a number line but are on opposite
sides of 0.
Definition: The Absolute Value of a number is the distance a number is from 0. The symbol | a | represents
the absolute value of a
Find the -a and | a | for each
Opposites
Absolute Value
Ex. a = 14
-a = ________
| a | = ________
Ex. a = -6
-a = ________
| a | = ________
Ex. a = -1.23
-a = ________
| a | = ________
3
4