* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download BI 200 – Final Exam
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
DNA damage theory of aging wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
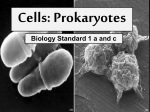
BI 200 – Final Exam A Fall 2004 Name Disclaimer Consider each question, and answer each in the appropriate format (i.e., multiple choice). You may qualify your answer if you have reservations. If your comments have merit, you may receive partial or full credit. Multiple choice. 2 points each 1. The bacterium E. coli is about how long? a. 2 m b. 0.02 m c. 0.002 mm d. 200 m 2. Which of the following are made up of eukaryotic cells? a. b. c. d. e. Bacteria and Algae Archaea and Fungi Protozoa and Metazoa Bacteria and Archaea Protozoa and Viruses 3. Which of the following is not a protozoan? a. Saccharomyces b. Paramecium c. Amoeba d. all of the above are not protozoa e. none of the above are protozoa 4. The bacteria in the image are best described as a. cocci b. spirochaetes c. dinoflagellates d. bacilli e. psedopods 5. The synthesis of protein is carried out by ______________ and is referred to as _______________. a. b. c. d. e. RNA polymerase; Translation Ribosomes; Transcription Reverse Transcriptase; Translation DNA polymerase; Replication Ribosomes; Translation 6. Beijerinck is credited with developing which technique to study lithotrophic bacteria a. enrichment technique b. aseptic technique c. genome sequencing d. pure culture technique e. polymerase chain reaction (PCR) 7. Discovery of the cause of Anthrax is credited to a. Pasteur b. Koch c. Winogradsky d. Lister e. Fleming 8. Which of the 10 chemical structures represents an ester? Put a circle around the structure. Given the structure of the side chain of the amino acid leucine: CH3 - CH2-CH CH3 9. Would the side chain be a. polar and hydrophobic b. non-polar and hydrophobic c. polar and hydrophilic d. non-polar and hydrophilic 10. The progenote or universal ancestor would have which of the following traits a. be a virus b. be a prokaryote c. be a psychrophile d. be an obligate aerobe e. be a little green man with antennae 11. Banded iron formations or “red beds” containing Fe3+ indicate the presence of _________ in the atmosphere. They probably began to form __________ years ago. a. insects; 3.5 billion b. sunlight; 1.9 billion c. oxygen; 900 million 1.4 billion; eukaryotes d. land plants; 60 million e. methane; 6,000 12. Phospholipids of bacteria differ from those in eukaryotic membranes because bacterial membranes have ring structures called ______________ rather than _______________. a. b. c. d. e. tetrapyroles; porphoryn esters; isoprenes isoprene sub-units; ether hopanoids; sterols none of the above, they have identical phospholipids 13. Lactose enters the cell with the help of a permease protein that simultaneously allows the entry of a proton. This is an example of a. b. c. d. e. an antiporter Primary active transport a symporter Group translocation a uniporter 14. Which structure below occurs in the phospholipid monolayer of some thermophilic archaea? Mark the correct letter a. glycerol diether b. diglycerol tetraether 15. Cell walls of fungi are made of a polymer called _________________ which is composed of _________________. a. b. c. d. e. cellulose; 1->4 linked glucose chitin; 1->4 linked N-acetylglucosamine peptidoglycan; 1->4 linked N-acetylglucosamine and muramic acid the S-layer; proteins none of the above, algae don’t have cell walls. 16. In the gram-negative cell envelope, which is the correct order of constituents as you move from the inside of the cell (cytoplasm) to the outside? a. b. c. d. e. porin, peptidoglycan, lipoprotein, outer membrane, lipopolysaccharide cytoplasmic membrane, peptidoglycan, lipoprotein, outer membrane, periplasm cytoplasmic membrane, porin, peptidoglycan, lipoteichoic acid, outer membrane porin, peptidoglycan, lipoprotein, outer membrane, periplasm cytoplasmic membrane, peptidoglycan, lipoprotein, outer membrane, lipopolysaccharide 17. Would the structure on the left be part of a. DNA b. RNA c. either DNA or RNA 18. How many genes in the E. coli chromosome? a. b. c. d. e. 4 4,000 4.5 x 106 none, DNA is usually single stranded in prokaryotes none, prokaryotes have plasmids, but not chromosomes 19. Which of the following is generally true about DNA in eukaryotes? a. b. c. d. e. DNA is supercoiled around histone proteins DNA is single stranded There is one copy of each chromosome Chromosomes are usually circular rather than linear There are usually more chromosomes than plasmids 20. Endospores a. are phase bright b. can germinate to form vegetative cells c. contain diaminopimelic acid and Ca2+ ions d. all of the above e. none of the above 21. The bright spots in the lithotrophic bacterium Beggiatoa are most likely which prokaryotic cell feature? a. carboxysomes b. sulfur granules c. RuBisCo enzymes d. any of the above e. none of the above 22. Which of the following protein structures would be found on the outside of archaea lacking pseudomurein and some bacteria? a. silicon dioxide frustule b. cilia c. S-Layer d. Lipopolysachharide 23. Microtubules are part of the structure of all of the following, except: a. cilia b. eukaryotic flagella c. prokaryotic flagella d. cytoskeleton e. spindle apparatus 24. The chloroplast is organized into highly folded inner membranes called _____________ and an internal space called the ____________. a. christae; matrix b. thylakoids; stroma c. chlorosomes; cytoplasm d. nitrosomonas; periplasm e. mitochondria; hydrogenosome 25. Which of the following is not correct regarding Hydrogenosomes? a. They occur in some anaerobic protozoa b. They are probably related to the bacterium Paracoccus c. Hydrogen is a byproduct of their metabolism d. all of the above correct e. none of a-c are correct 26. In chemical reactions that support the growth of microorganisms a. ΔG > 0 b. ΔG = 0 c. ΔG < 0 d. ΔG is irrelevant 27. Which of the following is true about glycoysis and fermentation? a. ATP are formed by substrate phosphorylation b. cytochrome and succinyl-CoA are high energy intermeidates c. it is also called the Z-scheme d. water is the electron donor for ETP e. oxygen gas is the electron acceptor 28. Which of the following is true about the reduction of pyruvate to ethanol and CO2 by yeast? a. NAD+ is regenerated from NADH b. the key enzyme is lactate dehydrogenase c. ATP is produced by electron transport phosphorylation d. ATP is produced by substrate level phosphorylation e. none of the above is correct 29. Which of the following is true about the Krebs (TCA) cycle? a. b. c. d. e. oxygen is consumed oxygen is produced ATP is produced by electron transport phosphorylation ATP is produced by substrate level phosphorylation none of the above is correct 30. Which of the following is not true about electron transport phosphorylation in aerobic respiration? a. a proton gradient, H+, is formed b. ubiquinone is involved c. ATP is produced by ATPase d. oxygen is produced e. none of the above, all are true 31. Which enzyme would be unique in the fermentation of glucose to lactic acid? a. b. c. d. e. -galactosidase lactase alcohol dehydrogenase aldolase lactate dehydrogenase 32. Which bacterium would carry out the fermentation of glucose to lactic acid? a. b. c. d. e. Saccharomyces Escherichia Zymomonas Streptococcus Methanosarcina 33. Which of the following organisms grows by transferring electrons from acetic acid to Fe3+ (ferric iron)? It is an obligate anaerobe, and produces Fe2+ (ferrous iron) as end product. a. b. c. d. e. Gallionella Thiobacillus ferrooxidans Rusticyanin Geobacter Leptothrix 34. The unique enzyme in substrate oxidation for Thiobacillus ferrooxidans a. b. c. d. e. APS nitrite oxidase ammonium monooxygenase rusticyanin nitrite reductase 35. Methanogens a. have a large separation between the electron donating couple and accepting couple b. fluoresce under ultraviolet light due to chlorophyll c. are obligate anaerobes d. are not widely distributed in nature e. can be found in cows, but not termites 36. Denitrification a. is carried out by Nitrosomonas b. is an example of lithotrophy c. depletes nitrogen from the soil d. is associated with acid mine drainage 37. The purple pigment associated with Halobacterium is a. b. c. d. e. phycobillin bacteriochlorophyll a bacteriorhodopsin -carotene chlorophyll g 38. Anoxygenic photosynthesis a. is also called non-cyclic photosynthesis b. is carried out by cyanobacteria (among others) c. involves central chlorophyll molecules P680 of photosystem II d. evolved before aerobic respiration and oxygenic photosynthesis 39. Which of the following is a purple non-sulfur phototrophic bacterium? a. Volvox b. Oscillatoria c. Halobacterium d. Rhodospirillum e. Clostridium 40. Carbon fixation occurs in the ______________ of chloroplasts, while nitrogen fixation occurs in special cyanobacterial cells called __________________. a. carboxysomes; akinetes b. chlorosomes; grana c. matrix; auxotrophs d. stroma; heterocysts e. endospores; phycobillisomes 41. All of the following are features of gene expression in eukaryotes, except a. Intron excision during RNA processing of the primary transcript b. Translation at the endoplasmic reticulum c. Tanscription of polycistronic mRNA from operons d. 5’ capping and 3’ polyadenylation of mature mRNA 42. Treatment for Anthrax includes ciprofloxin which inhibits the enzyme that introduces supercoiling in bacteria. This enzyme is a. Histone b. Topoisomerase I c. Topoisomerase II (gyrase) d. Nuclease e. RecA 43. A piece of double stranded DNA has 14% Adenine bases. Which of the following would not be true? a. there would be 36% cytosine in the DNA b. there would be 14% uracil in the DNA c. there would be 36% guanine in the DNA d. none of the above, all are true in the DNA 44. The inability to ferment lactose is an example of a. a visible phenotypic marker b. a differential phenotypic marker c. a selectable phenotypic marker 45. An individual able to synthesize the amino acid tryptophan is an example of _______and their phenotype would be _____. a. a phototroph; trpE b. a prototroph; Trp+ c. an autotroph; RX7 d. an auxotroph; Trp46. The exchange of homologous DNA molecules in general recombination requires all of the following, except: a. b. c. d. e. RecA protein single stranded binding protein strand invasion pili high levels of DNA homology 47. Which of the following is not a means of gene exchange among bacteria? a. transcription b. transformation c. conjugation d. transduction 48. Which of the following is not true about transformation? a. Viruses are not involved. b. The process is not sensitive to the enzyme DNase. c. DNA can be transferred between species. d. The donor cell must be lysed before transfer can take place. 49. Genes on plasmids may be responsible for all of the following except: a. expression of a virulence factor b. synthesis of ribosome protein c. synthesis of pili d. transfer of drug resistance e. degradation of pollutants 50. In conjugation genes on plasmids are transferred in matings between: a. two F- strains b. F+ and F- cells c. two F+ strains d. a and b e. b and c BONUS 51. Viruses may be as small as a. 0.02 nm b. 0.02 m c. 0.02 mm d. 0.02 inches 52. When lysogenized the bacterial host a. is immune to further infection b. may produce additional toxins as with diptheria and scarlet fever c. can reproduce indefinitely d. all of the above e. none of the above 53. When an animal virus leaves its host cell and takes some membrane with it, its structure is referred to as a. helical b. prion c. enveloped d. complex 54. The type of infection caused by the HIV is best characterized as a. Lytic b. Tumerogenic c. Persistent d. Latent BI 200 Final Exam Topics 1. Size of E. coli 2. 7 types of microorganisms – eukaryotes, prokaryotes, and viruses 3. Representatives of protozoa 4. Representative shapes of bacteria 5. Central dogma of biology – DNA replication, transcription, and translation 6. History of microbiology – enrichment, pure culture, and aseptic technique 7. Diseases discovered by Pasteur, Koch, Winogradsky, Lister, etc. 8. Recognizing ethers, carboxyls, ethers, hydroxyls, and amines 9. Hydrophobic nature of polar amino acids 10. Early Earth’s conditions and the universal ancestor 11. Time of events in Earth’s history 12. Phospholipid structure – archaea, bacteria, and eukaryotes 13. Transport mechanisms of glucose lactose and maltose 14. Structure of thermophilic archean membranes 15. Cell wall materials – cellulose, chitin, peptidoglycans, S-layers, etc. 16. Gram-negative cell envelopes – porins, periplasm, LPS, etc. 17. Differences between DNA and RNA 18. DNA in prokaryotes – genome size 19. DNA in eukaryotes – chromosome structure 20. Endospores 21. Internal prokaryotic features – carboxysomes, sulfur granules, Rubisco 22. External prokaryotic features – pili, capsules, flagella, fimbriae, S-layers 23. Microtubules 24. Structure of chloroplasts/mitochondria 25. Hydrogensomes 26. Energy changes during chemical reactions (the Energy diagram) 27. Glycolysis, oxygen and ATP production (ETP, SLP) 28. Reduction of pyruvate to ethanol 29. TCA cycle, oxygen and ATP production (ETP, SLP) 30. Aerobic respiration, oxygen and ATP production (ETP, SLP) 31. Enzymes of lactic acid and ethanol fermentation 32. Organisms of lactic acid and ethanol fermentation 33. Iron-reducing organisms 34. Enzymes of chemolithotrophic substrate oxidation 35. Methanogens 36. Denitrification 37. Photosynthesis in archaea 38. Anoxygenic/Oxygenic photosynthesis - general properties 39. Anoxygenic/Oxygenic photosynthesis - organisms 40. Carbon and nitrogen fixation in photosynthetic organisms 41. Contrast of genetics in prokaryotes and eukaryotes (Fig. 7.2) 42. Supercoiling in prokaryotes 43. Percent base composition of DNA and RNA – complementarity 44. Visible, differential, and selectable markers 45. Selectable mutants unable to synthesize growth factors and their designation 46. Requirements for homologous recombination 47. Mechanisms of gene exchange in bacteria 48. Features of transformation 49. Genes found on plasmids 50. Conjugation BONUS 51. The size of viruses 52. Phage conversion and properties of lysogenized cells 53. Structure of animal viruses 54. 4 outcomes or courses of animal viral infections