Chapter 3 Section 4 Protein Synthesis
... • Transcription – the DNA strand is unzipped to allow a strand of mRNA to be created from its exposed nitrogen bases • The new strand of mRNA are made by matching new nitrogen bases with the exposed nitrogen bases from the unzipped strand of DNA. ...
... • Transcription – the DNA strand is unzipped to allow a strand of mRNA to be created from its exposed nitrogen bases • The new strand of mRNA are made by matching new nitrogen bases with the exposed nitrogen bases from the unzipped strand of DNA. ...
Protein Synth Notes GO New
... A protein and its function is determined by: What’s another word for phenotype? Which macromolecule does the phenotype describe? Which macromolecule does the genotype describe? Which macromolecule does variation describe? ...
... A protein and its function is determined by: What’s another word for phenotype? Which macromolecule does the phenotype describe? Which macromolecule does the genotype describe? Which macromolecule does variation describe? ...
Gene expression PPT
... DNA sequence is transcribed into RNA sequence only one of two DNA strands (template or antisense strand) is transcribed non-transcribed strand is termed coding strand or sense strand same as RNA (except T’s are U’s) RNA polymerase unzips and adds the nucleotides unlike in replication where helicase ...
... DNA sequence is transcribed into RNA sequence only one of two DNA strands (template or antisense strand) is transcribed non-transcribed strand is termed coding strand or sense strand same as RNA (except T’s are U’s) RNA polymerase unzips and adds the nucleotides unlike in replication where helicase ...
Review Problems #2 (Enzyme Review, Phosphatases
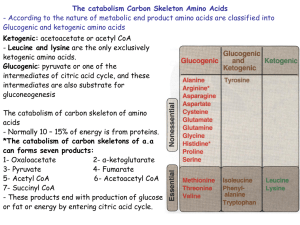
... 6) Methionine is degraded to a four carbon molecule- outline the steps in this conversion. What other amino acid is required for this transformation? What amino acid is synthesized in this process? 7) The four carbon molecule derived from methionine is coverted into a Krebs cycle intermediate. What ...
... 6) Methionine is degraded to a four carbon molecule- outline the steps in this conversion. What other amino acid is required for this transformation? What amino acid is synthesized in this process? 7) The four carbon molecule derived from methionine is coverted into a Krebs cycle intermediate. What ...
Sex linked inheritance, sex linkage in Drosophila and man, XO, XY
... prokaryotes and (B) eukaryotes. ...
... prokaryotes and (B) eukaryotes. ...
Protein synthesis and Enzyme test review
... Trp, Glu, Ile Trp= UGG Glu= GAA or GAG Ile= AUU or AUC or AUA 11. mRNA has (codons / anticodons), and tRNA has (codons / anticodons). 12. What is the function of tRNA? Transfer amino acids to the ribosome ...
... Trp, Glu, Ile Trp= UGG Glu= GAA or GAG Ile= AUU or AUC or AUA 11. mRNA has (codons / anticodons), and tRNA has (codons / anticodons). 12. What is the function of tRNA? Transfer amino acids to the ribosome ...
PIG - enzymes
... • Fits into site on enzyme away from the active site • Attaches to tertiary structure of enzyme • Changes shape of the active site • Substrate can no longer bind with active site • Permanent ...
... • Fits into site on enzyme away from the active site • Attaches to tertiary structure of enzyme • Changes shape of the active site • Substrate can no longer bind with active site • Permanent ...
A20-Protein Synthesis
... reads it 3 bases at a time, and matches these with bases on tRNA attached to an amino acid. An amino acid chain is formed from many peptide bonds. ...
... reads it 3 bases at a time, and matches these with bases on tRNA attached to an amino acid. An amino acid chain is formed from many peptide bonds. ...
ICAR ARS NET Previous Questions on Agricultural
... 66. In PCR, the double stranded DNA is generally denatured by ...
... 66. In PCR, the double stranded DNA is generally denatured by ...
Protein Synthesis
... Purpose: To create a fictional protein, illustrated by a chain of colorful beads. 1. Imagine that the following string of letters are nitrogen bases on one side of a DNA molecule. The DNA molecule has opened to this particular section of itself (called a gene) to allow a messenger RNA to be formed f ...
... Purpose: To create a fictional protein, illustrated by a chain of colorful beads. 1. Imagine that the following string of letters are nitrogen bases on one side of a DNA molecule. The DNA molecule has opened to this particular section of itself (called a gene) to allow a messenger RNA to be formed f ...
DNA
... b. Protein synthesis, translation, transcription c. Transcription, translation, protein synthesis d. Translation, transcription, protein synthesis ...
... b. Protein synthesis, translation, transcription c. Transcription, translation, protein synthesis d. Translation, transcription, protein synthesis ...
1 Name Chapter 3 Reading Guide Nucleic Acids, Proteins, and
... 8. What are the major functions of proteins in living organisms? ...
... 8. What are the major functions of proteins in living organisms? ...
Practice Quiz
... 4. Atoms that share electrons are said to possess ____________ bonds. 5. Elements with the same number of protons and electrons but different number of neutrons is called a(an) ____________________. 6. According to the periodic chart from the Appendix of your text, the atomic symbol for sulfur is __ ...
... 4. Atoms that share electrons are said to possess ____________ bonds. 5. Elements with the same number of protons and electrons but different number of neutrons is called a(an) ____________________. 6. According to the periodic chart from the Appendix of your text, the atomic symbol for sulfur is __ ...
DNA Protein synthesis Review Answer Key.doc
... Questions What are genes Short strtches of DNA that code for protein Proteins are made of chains of _______________. Amino acids How do cells use proteins? For structural and functional uses such as transport and chemical reactions The subunits making up polypeptides are called _____________ ...
... Questions What are genes Short strtches of DNA that code for protein Proteins are made of chains of _______________. Amino acids How do cells use proteins? For structural and functional uses such as transport and chemical reactions The subunits making up polypeptides are called _____________ ...
Transcription
... The genetic instructions for a polypeptide chain are ‘written’ in the DNA as a series of 3-nucleotide ‘words’ – Codons ...
... The genetic instructions for a polypeptide chain are ‘written’ in the DNA as a series of 3-nucleotide ‘words’ – Codons ...
Translation Notes
... 2. ribosome holds mRNA and tRNA together for accurate reading and assembly of proteins ...
... 2. ribosome holds mRNA and tRNA together for accurate reading and assembly of proteins ...
RNA and Protein Synthesis Quiz
... D. four 22) Amino acids are held together by __?__ bonds. A. hydrogen B. peptide C. ionic D. high energy 23) How many codons are needed to specify three amino acids? A. 3 C. 9 B. 6 D. 12 24) One similarity between DNA and messenger RNA molecules is that they both contain a. the same sugar b. genetic ...
... D. four 22) Amino acids are held together by __?__ bonds. A. hydrogen B. peptide C. ionic D. high energy 23) How many codons are needed to specify three amino acids? A. 3 C. 9 B. 6 D. 12 24) One similarity between DNA and messenger RNA molecules is that they both contain a. the same sugar b. genetic ...
Review Game
... replication? Deoxynucleoside triphosphate (dNTP) 500 What are Okazaki fragments? Short sections of DNA formed during DNA replication on the lagging strand ...
... replication? Deoxynucleoside triphosphate (dNTP) 500 What are Okazaki fragments? Short sections of DNA formed during DNA replication on the lagging strand ...
Step two: Translation from mRNA to protein
... the bonds that link bases into strands the bonds that make strands into double helix RNA: basic parts and bonds differences between it and DNA types of RNA in the cell Transcription: Copying genetic information from DNA to mRNA what are the steps? (transcription and processing) where does it occur? ...
... the bonds that link bases into strands the bonds that make strands into double helix RNA: basic parts and bonds differences between it and DNA types of RNA in the cell Transcription: Copying genetic information from DNA to mRNA what are the steps? (transcription and processing) where does it occur? ...
Name: Period:_____ Date
... 18. What is the function of a protein? Building blocks of life support life 19. What is a dehydration reaction? Produces water as a product 20. What is a hydrolysis reaction? ...
... 18. What is the function of a protein? Building blocks of life support life 19. What is a dehydration reaction? Produces water as a product 20. What is a hydrolysis reaction? ...
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Proteins made on free ribosomes will be
... SUMMARY OF PROTEIN SYNTHESIS 1) mRNA makes a copy of DNA in nucleus. 2) mRNA leaves the nucleus and goes to a ribosome in the cytosol. 3) The ribosome (made of rRNA) is the site of ...
... SUMMARY OF PROTEIN SYNTHESIS 1) mRNA makes a copy of DNA in nucleus. 2) mRNA leaves the nucleus and goes to a ribosome in the cytosol. 3) The ribosome (made of rRNA) is the site of ...
Biosynthesis

Biosynthesis (also called biogenesis or anabolism) is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined together to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides.The prerequisite elements for biosynthesis include: precursor compounds, chemical energy (e.g. ATP), and catalytic enzymes which may require coenzymes (e.g.NADH, NADPH). These elements create monomers, the building blocks for macromolecules. Some important biological macromolecules include: proteins, which are composed of amino acid monomers joined via peptide bonds, and DNA molecules, which are composed of nucleotides joined via phosphodiester bonds.