DNA RNA-Protein Synthesis Homework
... What is a protein? Why are they important? Where are they made in the cell? What makes them? Why are they so different? ...
... What is a protein? Why are they important? Where are they made in the cell? What makes them? Why are they so different? ...
protein synthesis - Jannali
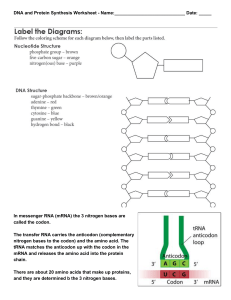
... The information about the number, type and sequence of amino acids, needed to make a protein molecule, is found as a code in DNA. The code- a sequence of bases. One gene sequence codes for one polypeptide (a single chain of many amino acids) A set of 3 bases (a codon) codes for one amino acid of a ...
... The information about the number, type and sequence of amino acids, needed to make a protein molecule, is found as a code in DNA. The code- a sequence of bases. One gene sequence codes for one polypeptide (a single chain of many amino acids) A set of 3 bases (a codon) codes for one amino acid of a ...
Standard Genetic Code
... DNA/RNA – for storing information about how to make proteins The building blocks for proteins are 20 different types of amino acids, and these amino acids are strung together one after another when a protein is built. The instructions for building each particular protein is encoded in DNA in the c ...
... DNA/RNA – for storing information about how to make proteins The building blocks for proteins are 20 different types of amino acids, and these amino acids are strung together one after another when a protein is built. The instructions for building each particular protein is encoded in DNA in the c ...
Quiz 2
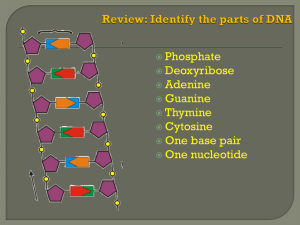
... - Polymers that store, transmit, and express genetic information: this information is stored in sequences of monomers of nucleic acids - Two types of Nucleic acids: Deoxyribonucleic acid and Ribonucleic acid - DNA stores and transmits information, RNA intermediates specific specific sequences for pr ...
... - Polymers that store, transmit, and express genetic information: this information is stored in sequences of monomers of nucleic acids - Two types of Nucleic acids: Deoxyribonucleic acid and Ribonucleic acid - DNA stores and transmits information, RNA intermediates specific specific sequences for pr ...
Protein Synthesis - Los Gatos High School
... • RNA is single stranded and thus smaller & able to leave the nucleus of the cell ...
... • RNA is single stranded and thus smaller & able to leave the nucleus of the cell ...
Name
... 2. Define transcription. 3. What is the full name of RNA? 4. What nucleotides are found in RNA? 5. Where in the eukaryotic cell does transcription take place? 6. What are the differences between DNA and RNA (include at least 3 differences)? 7. What are the differences between replication and transcr ...
... 2. Define transcription. 3. What is the full name of RNA? 4. What nucleotides are found in RNA? 5. Where in the eukaryotic cell does transcription take place? 6. What are the differences between DNA and RNA (include at least 3 differences)? 7. What are the differences between replication and transcr ...
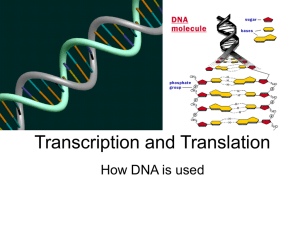
Transcription and Translation
... • DNA unwinds, and separates to expose 1 side of the code. • mRNA is built by connecting nucleotides 1 at a time that are complimentary to the code. • RNA replaces (T)hymine with (U)racil so it can leave the nucleus. ...
... • DNA unwinds, and separates to expose 1 side of the code. • mRNA is built by connecting nucleotides 1 at a time that are complimentary to the code. • RNA replaces (T)hymine with (U)racil so it can leave the nucleus. ...
Begin by going to the address below
... On the left side of the page you will see several topics. Click on those topics that are listed below in bold print and underlined and answer the questions. ...
... On the left side of the page you will see several topics. Click on those topics that are listed below in bold print and underlined and answer the questions. ...
Transcription - smithlhhsb121
... The interaction of tRNA and mRNA takes place in a ribosome Consists of two protein subunits and ribosomal RNA (rRNA) Within the ribosome are three binding sites ◦ P site (peptidyl-tRNA site) where the tRNA holding the polypepetide chain ◦ A site (aminoacyl-tRNA site) where next tRNA in line is held ...
... The interaction of tRNA and mRNA takes place in a ribosome Consists of two protein subunits and ribosomal RNA (rRNA) Within the ribosome are three binding sites ◦ P site (peptidyl-tRNA site) where the tRNA holding the polypepetide chain ◦ A site (aminoacyl-tRNA site) where next tRNA in line is held ...
Ecology
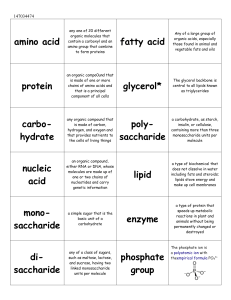
... is made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen and that provides nutrients to the cells of living things ...
... is made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen and that provides nutrients to the cells of living things ...
PP-Protein Synthesis
... Proteins have MANY different functions Enzymes to help control/speed up chemical reactions Help to build and repair cell structures Determine the structure & function of living organisms ...
... Proteins have MANY different functions Enzymes to help control/speed up chemical reactions Help to build and repair cell structures Determine the structure & function of living organisms ...
Biomolecules Review
... 18. What is the net charge on cysteine, pI=5.1, when the pH=6.3? Which way will it move during electrophoresis? 19. The site on the enzyme where reaction occurs is known as the ___________ site. 20. DNA is sometimes made from RNA by ________ viruses. This process is called _____________________? 21. ...
... 18. What is the net charge on cysteine, pI=5.1, when the pH=6.3? Which way will it move during electrophoresis? 19. The site on the enzyme where reaction occurs is known as the ___________ site. 20. DNA is sometimes made from RNA by ________ viruses. This process is called _____________________? 21. ...
proteins
... Protein: chain of amino acids Triplets of nucleotides specify each amino acid Each nucleotide triplet is called a codon Genetic code: table that gives the correspondence between each possible triplet and each amino acid ...
... Protein: chain of amino acids Triplets of nucleotides specify each amino acid Each nucleotide triplet is called a codon Genetic code: table that gives the correspondence between each possible triplet and each amino acid ...
Biosynthesis

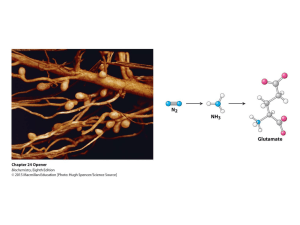
Biosynthesis (also called biogenesis or anabolism) is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined together to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides.The prerequisite elements for biosynthesis include: precursor compounds, chemical energy (e.g. ATP), and catalytic enzymes which may require coenzymes (e.g.NADH, NADPH). These elements create monomers, the building blocks for macromolecules. Some important biological macromolecules include: proteins, which are composed of amino acid monomers joined via peptide bonds, and DNA molecules, which are composed of nucleotides joined via phosphodiester bonds.