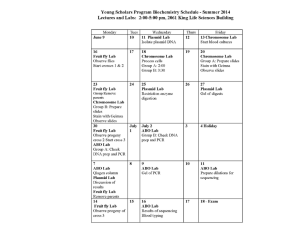
homework 3 assigned
... Homework 3, due Friday, May 12 (10 points) Given the following table of the amino acid associated with each triple of nucleotides, construct a map that has triples of nucleotides as keys and amino acids as values. Append a main function that converts a string of nucleotides into a vector of the corr ...
... Homework 3, due Friday, May 12 (10 points) Given the following table of the amino acid associated with each triple of nucleotides, construct a map that has triples of nucleotides as keys and amino acids as values. Append a main function that converts a string of nucleotides into a vector of the corr ...
RNA and protein synthesis
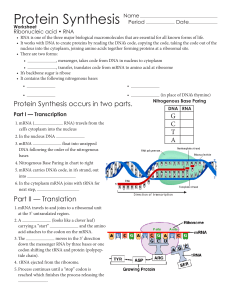
... 4. A sequence of three mRNA nucleotides is called a codon. 5. One codon codes for one amino acid. 6. tRNA molecules enter the ribosome carrying the correct amino acid. The tRNA has an anticodon that matches the codon on the mRNA. 7. Amino acids are linked together to form a protein! ...
... 4. A sequence of three mRNA nucleotides is called a codon. 5. One codon codes for one amino acid. 6. tRNA molecules enter the ribosome carrying the correct amino acid. The tRNA has an anticodon that matches the codon on the mRNA. 7. Amino acids are linked together to form a protein! ...
Protein Synthesis (Gene Expression) Notes
... 3. Enzymes used for digesAon and other chemical reacAons are proteins (Enzymes speed up the rate of a reacAon) 4. Component of all cell membranes ...
... 3. Enzymes used for digesAon and other chemical reacAons are proteins (Enzymes speed up the rate of a reacAon) 4. Component of all cell membranes ...
Basics of Biology (part 3): transcripCon, translaCon ADN, ARNs
... -> it binds to a specific amino acid! -> it contains the anticodon that binds to the corresponding codon on mRNA! ...
... -> it binds to a specific amino acid! -> it contains the anticodon that binds to the corresponding codon on mRNA! ...
Answers - Shelton State
... 13. An enzyme that will catalyze the reaction of only one molecule has absolute specificity. 14. The sit on the enzyme where reaction occurs is known as the active site. 15. These substances bind to the enzyme and interfere with the reaction. inhibitors 16. Two main categories of nucleic acids. (ful ...
... 13. An enzyme that will catalyze the reaction of only one molecule has absolute specificity. 14. The sit on the enzyme where reaction occurs is known as the active site. 15. These substances bind to the enzyme and interfere with the reaction. inhibitors 16. Two main categories of nucleic acids. (ful ...
Slide 1
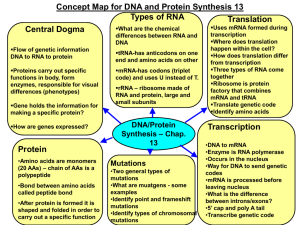
... functions in body, form enzymes, responsible for visual differences (phenotypes) Gene holds the information for making a specific protein? How are genes expressed? ...
... functions in body, form enzymes, responsible for visual differences (phenotypes) Gene holds the information for making a specific protein? How are genes expressed? ...
Amino acids catabolism
... The conversion of serine to cysteine involves some interesting reactions In plants and bacteria: serine is acetylated to form O-acetylserine (by serine acyltransferase, and acetyl-CoA as acyl donor) ...
... The conversion of serine to cysteine involves some interesting reactions In plants and bacteria: serine is acetylated to form O-acetylserine (by serine acyltransferase, and acetyl-CoA as acyl donor) ...
How does DNA control cell activities?
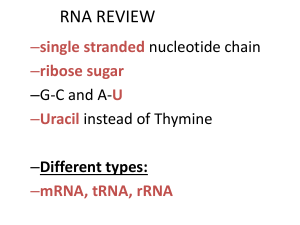
... • Same nitrogenous bases as DNA…EXCEPT thymine is replaced with URACIL • Uracil pairs with Adenine • Takes instructions from DNA and builds proteins amino acid by amino acid. ...
... • Same nitrogenous bases as DNA…EXCEPT thymine is replaced with URACIL • Uracil pairs with Adenine • Takes instructions from DNA and builds proteins amino acid by amino acid. ...
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS - Gull Lake Community Schools / Overview
... holding the nitrogenous bases together (the “steps” of the ladder) at the promoter site. Unattached RNA (free) nucleotides bind to their complimentary bases on the DNA strand to form a molecule of mRNA (messenger RNA); RNA polymerase works like a “train moving down the tracks”. This process repeats ...
... holding the nitrogenous bases together (the “steps” of the ladder) at the promoter site. Unattached RNA (free) nucleotides bind to their complimentary bases on the DNA strand to form a molecule of mRNA (messenger RNA); RNA polymerase works like a “train moving down the tracks”. This process repeats ...
lecture 1
... subunits joined together by phosphodiester bonds - covalent bonds between phosphate group at 5’ carbon and 3’ carbon of next nucleotide – uses oxygens as bridges. ...
... subunits joined together by phosphodiester bonds - covalent bonds between phosphate group at 5’ carbon and 3’ carbon of next nucleotide – uses oxygens as bridges. ...
Protein Synthesis
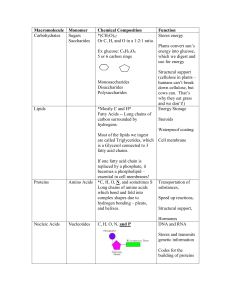
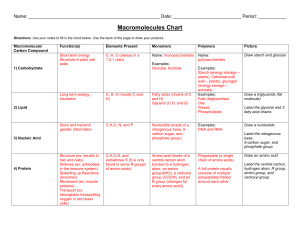
... Importance of Proteins & DNA D. Proteins perform the following important functions: – Enzymes, which speed up chemical reaction sin the body. – Keratin, which makes up our hair and nails. – Collagen, which makes up our skin. – Hemoglobin, which transports O2 in our body E. There are 20 different am ...
... Importance of Proteins & DNA D. Proteins perform the following important functions: – Enzymes, which speed up chemical reaction sin the body. – Keratin, which makes up our hair and nails. – Collagen, which makes up our skin. – Hemoglobin, which transports O2 in our body E. There are 20 different am ...
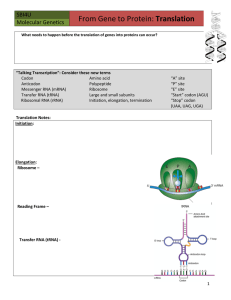
TRANSLATION NOTES - Randolph High School
... Definition of Translation The decoding of mRNA’s message into a protein Happens in the ribosome Also known as Protein Synthesis, which is when proteins are made by stringing amino acids together to form long chains (20+ types of amino acids in humans) ...
... Definition of Translation The decoding of mRNA’s message into a protein Happens in the ribosome Also known as Protein Synthesis, which is when proteins are made by stringing amino acids together to form long chains (20+ types of amino acids in humans) ...
Modelling Protein Synthesis - Jannali
... polypeptides of protein molecule is found on the DNA strand ( code form ). • Genetic code- sequence of the bases along DNA strand. • Codon- 3 bases, the codon codes for one amino acid. • The two processes that use information from the DNA for synthesis of protein: - Transcription - Translation • RNA ...
... polypeptides of protein molecule is found on the DNA strand ( code form ). • Genetic code- sequence of the bases along DNA strand. • Codon- 3 bases, the codon codes for one amino acid. • The two processes that use information from the DNA for synthesis of protein: - Transcription - Translation • RNA ...
Protein Synthesis- Powerpoint
... Protein Synthesis involves two processes: 1. Transcription: the copying of the genetic message (DNA) into a molecule of mRNA 2. Translation: mRNA is used to assemble an amino acid sequence into a polypeptide ...
... Protein Synthesis involves two processes: 1. Transcription: the copying of the genetic message (DNA) into a molecule of mRNA 2. Translation: mRNA is used to assemble an amino acid sequence into a polypeptide ...
DNA, RNA, and Snorks
... • 2. Using the amino acids you wrote below each gene, determine what traits the organism has and record them in the table. • 3. Sketch your two Snorks based on their 10 gene description. ...
... • 2. Using the amino acids you wrote below each gene, determine what traits the organism has and record them in the table. • 3. Sketch your two Snorks based on their 10 gene description. ...
Protein Synthesis Review
... Enzymes, which speed up chemical reactions Build and repair cell structures Determine the structure & function of living organisms ...
... Enzymes, which speed up chemical reactions Build and repair cell structures Determine the structure & function of living organisms ...
Quiz 17 Name: 1. RNA molecules can A) be information carriers B
... Name:_______________________ ...
... Name:_______________________ ...
Biosynthesis

Biosynthesis (also called biogenesis or anabolism) is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined together to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides.The prerequisite elements for biosynthesis include: precursor compounds, chemical energy (e.g. ATP), and catalytic enzymes which may require coenzymes (e.g.NADH, NADPH). These elements create monomers, the building blocks for macromolecules. Some important biological macromolecules include: proteins, which are composed of amino acid monomers joined via peptide bonds, and DNA molecules, which are composed of nucleotides joined via phosphodiester bonds.