Biochemistry Learning Targets and Essential Vocabulary name describe
... name and describe the functions of the four groups of organic compounds found in living things. (Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins, & Nucleic Acids) describe how polymers are built from monomers (dehydration synthesis) and ...
... name and describe the functions of the four groups of organic compounds found in living things. (Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins, & Nucleic Acids) describe how polymers are built from monomers (dehydration synthesis) and ...
Review Problems #2 (Enzyme Review, Phosphatases
... Review Problems For week 9. We will definitely not get through all of these, but it is useful to have them in one place. ...
... Review Problems For week 9. We will definitely not get through all of these, but it is useful to have them in one place. ...
Tuesday5/10
... to 1/1 billion base pairs. Cells can repair many errors; Humans have 130 known DNA repair enzymes! ...
... to 1/1 billion base pairs. Cells can repair many errors; Humans have 130 known DNA repair enzymes! ...
Transcription and Translation Work Sheet:
... Asparagine-Asn, Lysine-Lys, Aspartate-Asp, Glutamate-Glu, Cysteine-Cys, Tryptophan-Tyr, Arginine-Arg, and GlycineGly. See your notes if you would like to see the structure of each amino acid and to review the structure of the peptide bond that links adjacent amino acids in a protein. --------------- ...
... Asparagine-Asn, Lysine-Lys, Aspartate-Asp, Glutamate-Glu, Cysteine-Cys, Tryptophan-Tyr, Arginine-Arg, and GlycineGly. See your notes if you would like to see the structure of each amino acid and to review the structure of the peptide bond that links adjacent amino acids in a protein. --------------- ...
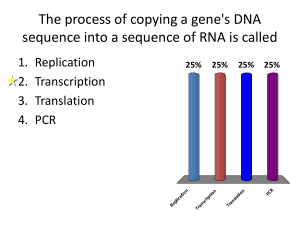
The process of copying a gene`s DNA sequence into a sequence of
... to both DNA replication and transcription? 1. Nucleotides are added to the 3' end of the newly synthesized strand 2. Deoxyribonucleotides are incorporated into the growing sequence 3. Both RNA and DNA polymerase require oligonucleotide priming 4. Both RNA and DNA polymerase initiate at promoter sequ ...
... to both DNA replication and transcription? 1. Nucleotides are added to the 3' end of the newly synthesized strand 2. Deoxyribonucleotides are incorporated into the growing sequence 3. Both RNA and DNA polymerase require oligonucleotide priming 4. Both RNA and DNA polymerase initiate at promoter sequ ...
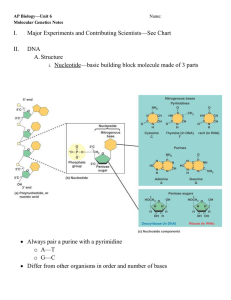
DNA - EPHS Knowles Biology
... 14. What makes up the rungs, which are the steps, of a DNA molecule? 15. Name the four nitrogen bases found in a molecule of DNA. 16. Name the four nitrogen bases found in a molecule of RNA. 17. In what part of the cell does transcription take place? 18. What type of RNA is made from messenger RNA? ...
... 14. What makes up the rungs, which are the steps, of a DNA molecule? 15. Name the four nitrogen bases found in a molecule of DNA. 16. Name the four nitrogen bases found in a molecule of RNA. 17. In what part of the cell does transcription take place? 18. What type of RNA is made from messenger RNA? ...
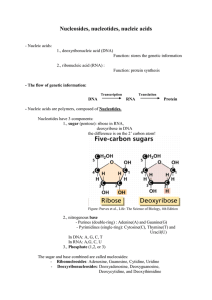
Nucleosides, nucleotides, nucleic acids
... double-stranded regions (in RNA there is Uracil instead of Thymine as a base, it forms double hydrogen bonds with Adenine). - transfer RNA = tRNA : it carries the amino acids to the site of protein synthesis, has an adapter role. Figure: The structure of tRNA. It has self-complementary double-strand ...
... double-stranded regions (in RNA there is Uracil instead of Thymine as a base, it forms double hydrogen bonds with Adenine). - transfer RNA = tRNA : it carries the amino acids to the site of protein synthesis, has an adapter role. Figure: The structure of tRNA. It has self-complementary double-strand ...
9 - Transcription and Translation
... tRNA Structure tRNA is like a “_______________” with a "nucleic acid word" (________________) on one side and a "protein word" (___________________) on the other side Specific amino acids are added to each tRNA molecule with a specific enzyme called ___________________________ _____________________ ...
... tRNA Structure tRNA is like a “_______________” with a "nucleic acid word" (________________) on one side and a "protein word" (___________________) on the other side Specific amino acids are added to each tRNA molecule with a specific enzyme called ___________________________ _____________________ ...
Proteins
... for a polypeptide chain are ‘written’ in the DNA as a series of 3-nucleotide ‘words’ Codons ‘U’ (uracil) replaces ‘T’ in RNA ...
... for a polypeptide chain are ‘written’ in the DNA as a series of 3-nucleotide ‘words’ Codons ‘U’ (uracil) replaces ‘T’ in RNA ...
From Gene to Protein Chapter Questions 7) Which of the following
... of nucleotides in the DNA that codes for the amino acids in this protein? A) 3 B) 100 C) 300 D) 900 E) 1,800 20) A codon A) consists of two nucleotides. B) may code for the same amino acid as another codon. C) consists of discrete amino acid regions. D) catalyzes RNA synthesis. E) is found in all eu ...
... of nucleotides in the DNA that codes for the amino acids in this protein? A) 3 B) 100 C) 300 D) 900 E) 1,800 20) A codon A) consists of two nucleotides. B) may code for the same amino acid as another codon. C) consists of discrete amino acid regions. D) catalyzes RNA synthesis. E) is found in all eu ...
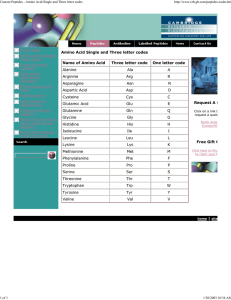
Amino Acid Single and Three letter codes Name of Amino Acid
... buyers guide What length of peptide can be made? Fmoc solid-phase synthesis What level of purification is necessary? What analysis can be done? ...
... buyers guide What length of peptide can be made? Fmoc solid-phase synthesis What level of purification is necessary? What analysis can be done? ...
Name:
... What do you notice about how the letters pair together? 4. Move on to “Protein Synthesis”. After unzipping the DNA, the process of transcription begins. What is the goal of this process? 5. What is different about how the bases pair together when making RNA? 6. After mRNA (messenger RNA) is made, wh ...
... What do you notice about how the letters pair together? 4. Move on to “Protein Synthesis”. After unzipping the DNA, the process of transcription begins. What is the goal of this process? 5. What is different about how the bases pair together when making RNA? 6. After mRNA (messenger RNA) is made, wh ...
Biochemistry Test Review KEY
... 16. Enzymes are what type of macromolecule? Protein 17. What would happen to the human body if enzymes were not available to be used in chemical reactions? It would slow down and eventually stop the breaking down essential nutrients and death would occur. 18. What macromolecule, besides carbohydrate ...
... 16. Enzymes are what type of macromolecule? Protein 17. What would happen to the human body if enzymes were not available to be used in chemical reactions? It would slow down and eventually stop the breaking down essential nutrients and death would occur. 18. What macromolecule, besides carbohydrate ...
Carbon compounds class web14
... • Can form up to 4 bonds. • It can form single, double or triple bonds with other atoms. • Carbon is central to large, organic molecules • It is the ‘backbone’ of the molecule. ...
... • Can form up to 4 bonds. • It can form single, double or triple bonds with other atoms. • Carbon is central to large, organic molecules • It is the ‘backbone’ of the molecule. ...
Gel Electrophoresis
... • Amino acids separate based on their isoelectric point and molar mass • Isoelectric point: – This is the pH where they net charge of amine and carboxylic acid groups cancel out ...
... • Amino acids separate based on their isoelectric point and molar mass • Isoelectric point: – This is the pH where they net charge of amine and carboxylic acid groups cancel out ...
mRNA Codon/Amino Acid Chart
... • Find a codon’s first base in the first column of the chart; stay in this row. • Find the second base in the middle of the chart, stay in this box. • Locate the third base in the far right column, this is the amino acid that matches the mRNA codon. • Warn students against using the tRNA anticodon w ...
... • Find a codon’s first base in the first column of the chart; stay in this row. • Find the second base in the middle of the chart, stay in this box. • Locate the third base in the far right column, this is the amino acid that matches the mRNA codon. • Warn students against using the tRNA anticodon w ...
Translation Worksheet and Key File
... _________________________19. A mutation in which a single base is added or deleted from DNA, throwing off the reading of the rest of the sequence of bases. See pg 125…starts with f. ...
... _________________________19. A mutation in which a single base is added or deleted from DNA, throwing off the reading of the rest of the sequence of bases. See pg 125…starts with f. ...
Biosynthesis

Biosynthesis (also called biogenesis or anabolism) is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined together to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides.The prerequisite elements for biosynthesis include: precursor compounds, chemical energy (e.g. ATP), and catalytic enzymes which may require coenzymes (e.g.NADH, NADPH). These elements create monomers, the building blocks for macromolecules. Some important biological macromolecules include: proteins, which are composed of amino acid monomers joined via peptide bonds, and DNA molecules, which are composed of nucleotides joined via phosphodiester bonds.