Chemistry of Life
... copy of an organisms information code. These contain all of the codes that give information on how the organism is to operate. RNA – (Ribonucleic Acid) This is a copy of DNA and is used for protein synthesis. There are minor, but important differences between DNA and RNA. ...
... copy of an organisms information code. These contain all of the codes that give information on how the organism is to operate. RNA – (Ribonucleic Acid) This is a copy of DNA and is used for protein synthesis. There are minor, but important differences between DNA and RNA. ...
DNA, etc Good facts to know
... 1. How many chromosomes do prokaryotes have and in what form? 2. How many chromosomes do humans have and in what form? 3. What are small extra-chromosomal double-stranded circular DNA molecules that are found in prokaryotes, viruses, and eukaryotes? 4. Which scientist team used radioactive tags on s ...
... 1. How many chromosomes do prokaryotes have and in what form? 2. How many chromosomes do humans have and in what form? 3. What are small extra-chromosomal double-stranded circular DNA molecules that are found in prokaryotes, viruses, and eukaryotes? 4. Which scientist team used radioactive tags on s ...
Protein Folding Lab with Balloons
... Objective: I can create a protein model based on characteristics of amino acids. DNA codes for RNA which codes for the order of amino acids to make specific proteins. A protein’s structure determines its function. Since different amino acids have different properties, they influence the folding of t ...
... Objective: I can create a protein model based on characteristics of amino acids. DNA codes for RNA which codes for the order of amino acids to make specific proteins. A protein’s structure determines its function. Since different amino acids have different properties, they influence the folding of t ...
Biomolecules Worksheet
... 1). In diagram form, give the general structure of an amino acid, and label any functional groups. Since amino acids have the same general structure, what makes them all different? ...
... 1). In diagram form, give the general structure of an amino acid, and label any functional groups. Since amino acids have the same general structure, what makes them all different? ...
BB350 Lecture 36 Highlights
... 12. ATCase is the primary regulatory enzyme of pyrimidine biosynthesis. It provides balance between purines and pyrimidines, since it is activated by a purine (ATP) and inactivated by a pyrimidine (CTP). 13. Pyrimidine synthesis also includes very simple precursors, such as amino acids. The first py ...
... 12. ATCase is the primary regulatory enzyme of pyrimidine biosynthesis. It provides balance between purines and pyrimidines, since it is activated by a purine (ATP) and inactivated by a pyrimidine (CTP). 13. Pyrimidine synthesis also includes very simple precursors, such as amino acids. The first py ...
Organic Compounds Overview - Kenwood Academy High School
... • Phospholipids (cell membranes)--have 2 fatty acids + phosphate group (PO4) • Cholesterol (animal cell membranes, starting point for other steroids, incl. sex hormones) ...
... • Phospholipids (cell membranes)--have 2 fatty acids + phosphate group (PO4) • Cholesterol (animal cell membranes, starting point for other steroids, incl. sex hormones) ...
MacromoleculeReview
... a) fiber (b) sugar (c) starch (d) cellulose (e) fat 31. Which elements are found in proteins but not in either carbohydrates or lipids. ...
... a) fiber (b) sugar (c) starch (d) cellulose (e) fat 31. Which elements are found in proteins but not in either carbohydrates or lipids. ...
3 " ‡ ‡ ‡ ‡ ‡ ‡ ‡ ‡ ‡ ‡ ‡ - 1 - G 2 ¢ 2 2 – 1. Biological catalysts are (A
... (A) it shuttles NADH across the mitochondrial membrane to yield 2.5 ATP / NADH. (B) it shuttles the electrons from NADH across the mitochondrial membrane to FADH2, yielding 1.5 ATP / NADH. (C) it only operates efficiently at high levels of NADH. (D) malate is a key component in the shuttle process. ...
... (A) it shuttles NADH across the mitochondrial membrane to yield 2.5 ATP / NADH. (B) it shuttles the electrons from NADH across the mitochondrial membrane to FADH2, yielding 1.5 ATP / NADH. (C) it only operates efficiently at high levels of NADH. (D) malate is a key component in the shuttle process. ...
Macromolecules Worksheet
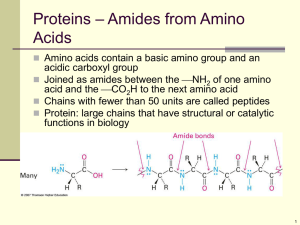
... b. amino acids are held together by a peptide bond (when a peptide bond is formed, a molecule of water is lost) c. Dipeptide - two amino acids joined together by a peptide bond Tripeptide - dipeptide and an amino acid Polypeptide - long chain of amino acids ...
... b. amino acids are held together by a peptide bond (when a peptide bond is formed, a molecule of water is lost) c. Dipeptide - two amino acids joined together by a peptide bond Tripeptide - dipeptide and an amino acid Polypeptide - long chain of amino acids ...
Macromolecules Worksheet
... b. amino acids are held together by a peptide bond (when a peptide bond is formed, a molecule of water is lost) c. Dipeptide - two amino acids joined together by a peptide bond Tripeptide - dipeptide and an amino acid Polypeptide - long chain of amino acids ...
... b. amino acids are held together by a peptide bond (when a peptide bond is formed, a molecule of water is lost) c. Dipeptide - two amino acids joined together by a peptide bond Tripeptide - dipeptide and an amino acid Polypeptide - long chain of amino acids ...
Macromolecules Power Point File
... a) All macromolecules are composed of 40-50 of the same monomers b) All proteins in all organisms are made of the same 20 amino acids. Just as 26 letters make all words ...
... a) All macromolecules are composed of 40-50 of the same monomers b) All proteins in all organisms are made of the same 20 amino acids. Just as 26 letters make all words ...
Chapter 26:Biomolecules: Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins
... their conjugate acid forms, an overall cation In basic solution, the groups are in their base forms, an overall anion In neutral solution cation and anion forms are present This pH where the overall charge is 0 is the isoelectric point, pI ...
... their conjugate acid forms, an overall cation In basic solution, the groups are in their base forms, an overall anion In neutral solution cation and anion forms are present This pH where the overall charge is 0 is the isoelectric point, pI ...
August 31, 2016 - Iowa State University
... b. DNA contains Thymine; RNA contains Uracil c. DNA contains an extra hydroxyl group that RNA does not have d. DNA is much less reactive than RNA ...
... b. DNA contains Thymine; RNA contains Uracil c. DNA contains an extra hydroxyl group that RNA does not have d. DNA is much less reactive than RNA ...
Macromolecules Worksheet - High School Science Help
... b. amino acids are held together by a peptide bond (when a peptide bond is formed, a molecule of water is lost) c. Dipeptide - two amino acids joined together by a peptide bond Tripeptide - dipeptide and an amino acid Polypeptide - long chain of amino acids ...
... b. amino acids are held together by a peptide bond (when a peptide bond is formed, a molecule of water is lost) c. Dipeptide - two amino acids joined together by a peptide bond Tripeptide - dipeptide and an amino acid Polypeptide - long chain of amino acids ...
How Did Life Begin? Unit Objectives Vocabulary: Miller
... By the end of this unit students will be able to: o Describe what it means to be alive using no less than six criteria. o List the two components of cell theory and explain how they apply to the fossil record explored in unit 1 and the origin of life itself. o Explain the origin of organic molecules ...
... By the end of this unit students will be able to: o Describe what it means to be alive using no less than six criteria. o List the two components of cell theory and explain how they apply to the fossil record explored in unit 1 and the origin of life itself. o Explain the origin of organic molecules ...
Biosynthesis

Biosynthesis (also called biogenesis or anabolism) is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined together to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides.The prerequisite elements for biosynthesis include: precursor compounds, chemical energy (e.g. ATP), and catalytic enzymes which may require coenzymes (e.g.NADH, NADPH). These elements create monomers, the building blocks for macromolecules. Some important biological macromolecules include: proteins, which are composed of amino acid monomers joined via peptide bonds, and DNA molecules, which are composed of nucleotides joined via phosphodiester bonds.