energy currency for cell - Hermantown Community Schools
... to a phosphate group (PO4) •The phosphate group is attracted to water (hydrophilic), Why? •The fatty acid chains are hydrophobic. •Make up all cell membranes ...
... to a phosphate group (PO4) •The phosphate group is attracted to water (hydrophilic), Why? •The fatty acid chains are hydrophobic. •Make up all cell membranes ...
Central Dogma of Molecular Biology
... Is in a clover shaped structure Brings the amino acids to the mRNA Has an anticodon loop to recognise the codons in the mRNA (by WatsonCrick base pairing) Is responsible for the specificity of the codon recognition ...
... Is in a clover shaped structure Brings the amino acids to the mRNA Has an anticodon loop to recognise the codons in the mRNA (by WatsonCrick base pairing) Is responsible for the specificity of the codon recognition ...
Create a comic strip to illustrate and explain protein synthesis
... Create a comic strip to illustrate and explain protein synthesis. Explain what happens during transcription, RNA splicing, and translation (Explanations are worth 3 points each). The comic strip should begin with a sequence of DNA and end with a protein, illustrating and explaining the steps in betw ...
... Create a comic strip to illustrate and explain protein synthesis. Explain what happens during transcription, RNA splicing, and translation (Explanations are worth 3 points each). The comic strip should begin with a sequence of DNA and end with a protein, illustrating and explaining the steps in betw ...
Molecular Biology Unit Review Guide
... 19. Draw a diagram in the space below of two amino acids being connected by a peptide bond, include the important elemental symbols and structures where the bond is made and any elements or molecules that are added or subtracted from the final product. What is this reaction called? ...
... 19. Draw a diagram in the space below of two amino acids being connected by a peptide bond, include the important elemental symbols and structures where the bond is made and any elements or molecules that are added or subtracted from the final product. What is this reaction called? ...
DNA Unit Test Corrections
... 30. What is the normal function of the protein you named in questions #29?________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ 31. What are some other functions of proteins in your b ...
... 30. What is the normal function of the protein you named in questions #29?________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ 31. What are some other functions of proteins in your b ...
biochem2
... • FATTY ACID - Long hydrocarbon chain with a carboxyl group on the end • FATS AND OILS - lipids used to store energy ( Formed from the combining of 3 fatty acids + a glycerol) ...
... • FATTY ACID - Long hydrocarbon chain with a carboxyl group on the end • FATS AND OILS - lipids used to store energy ( Formed from the combining of 3 fatty acids + a glycerol) ...
Organic Compounds
... • FATTY ACID - Long hydrocarbon chain with a carboxyl group on the end • FATS AND OILS - lipids used to store energy ( Formed from the combining of 3 fatty acids + a glycerol) ...
... • FATTY ACID - Long hydrocarbon chain with a carboxyl group on the end • FATS AND OILS - lipids used to store energy ( Formed from the combining of 3 fatty acids + a glycerol) ...
Biochemistry File - Northwest ISD Moodle
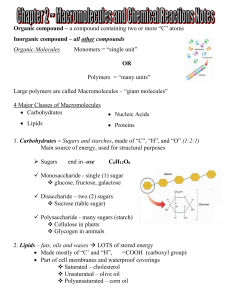
... 4. Proteins – polymers of amino acids joined by peptide bonds Used to build cells, transport molecules, and control the rate of reactions Made of “C”, “H”, “O”, and “N” 20 different amino acids ...
... 4. Proteins – polymers of amino acids joined by peptide bonds Used to build cells, transport molecules, and control the rate of reactions Made of “C”, “H”, “O”, and “N” 20 different amino acids ...
Print Preview - C:\WINDOWS\TEMP\e3temp_6820\.aptcache
... read in order by a cell; 3 different reading frames are possible for each mRNA molecule; Codons must be read in the correct reading frame order for the correct protein to be made. ...
... read in order by a cell; 3 different reading frames are possible for each mRNA molecule; Codons must be read in the correct reading frame order for the correct protein to be made. ...
RNA and Protein Synthesis Notes Organizer
... 8. Following transcription, what would be the complementary mRNA sequence to this strand of DNA? a. DNA: AGC TCC GAT GCA TAC TTG CCA ...
... 8. Following transcription, what would be the complementary mRNA sequence to this strand of DNA? a. DNA: AGC TCC GAT GCA TAC TTG CCA ...
Lecture notes 1 - University of Washington
... three phosphate groups. nucleoside = sugar + base. nucleotide = sugar + base + phosphate. 2.1.4. Amino acids 2.1.5. Peptide bond The carboxyle group of one amino acid reacts with the amino group of another forms a peptide bond. Due to a double bond, the peptide has a planar rigid structure. This uni ...
... three phosphate groups. nucleoside = sugar + base. nucleotide = sugar + base + phosphate. 2.1.4. Amino acids 2.1.5. Peptide bond The carboxyle group of one amino acid reacts with the amino group of another forms a peptide bond. Due to a double bond, the peptide has a planar rigid structure. This uni ...
Ch 30 reading guide
... 15. Which two four-carbon amino acids can be converted into oxaloacetate for catabolism? 16. Name four amino acid with 5-carbon backbones that can be transformed into glutamate. Glutamate can be catabolized to the citric acid cycle intermediate __________________ through transamination. 17. Like odd ...
... 15. Which two four-carbon amino acids can be converted into oxaloacetate for catabolism? 16. Name four amino acid with 5-carbon backbones that can be transformed into glutamate. Glutamate can be catabolized to the citric acid cycle intermediate __________________ through transamination. 17. Like odd ...
Carbon compounds - Sonoma Valley High School
... • It can form single, double or triple bonds with other atoms. • Carbon is central to large, organic molecules • It is the ‘backbone’ of the molecule. Left side: what does ‘backbone’ mean in this context? ...
... • It can form single, double or triple bonds with other atoms. • Carbon is central to large, organic molecules • It is the ‘backbone’ of the molecule. Left side: what does ‘backbone’ mean in this context? ...
Biosynthesis of Amino Acids
... acids from their diet. Humans can only synthesize about half of the twenty amino acids. • In general, the more complex amino acids are essential amino acids in humans as they require enzymes that have been lost from the human genome over evolutionary time. • Most animals are much more restricted in ...
... acids from their diet. Humans can only synthesize about half of the twenty amino acids. • In general, the more complex amino acids are essential amino acids in humans as they require enzymes that have been lost from the human genome over evolutionary time. • Most animals are much more restricted in ...
Notes Guide Part 2
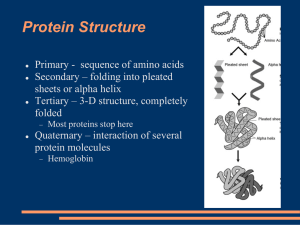
... Primary structure- Form a __________________ of amino acids. Secondary structure- ______________________________ the chain of amino acids. Tertiary Structure- Fold the chain ________________________________. Quaternary Structure- Bring _____ to ________ amino acid subunits together. ...
... Primary structure- Form a __________________ of amino acids. Secondary structure- ______________________________ the chain of amino acids. Tertiary Structure- Fold the chain ________________________________. Quaternary Structure- Bring _____ to ________ amino acid subunits together. ...
Chapter Twenty-Seven: Amino Acids
... o Remove N-protection w dilute base o Rinse solid support o Add second N-protected amino acid via C-terminus ...
... o Remove N-protection w dilute base o Rinse solid support o Add second N-protected amino acid via C-terminus ...
Biomolecules PPT
... of amino acids in the chain. Secondary Structures are either a helix or a pleated sheet formed form hydrogen bonds reacting between the amino acids. ...
... of amino acids in the chain. Secondary Structures are either a helix or a pleated sheet formed form hydrogen bonds reacting between the amino acids. ...
Biosynthesis

Biosynthesis (also called biogenesis or anabolism) is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined together to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides.The prerequisite elements for biosynthesis include: precursor compounds, chemical energy (e.g. ATP), and catalytic enzymes which may require coenzymes (e.g.NADH, NADPH). These elements create monomers, the building blocks for macromolecules. Some important biological macromolecules include: proteins, which are composed of amino acid monomers joined via peptide bonds, and DNA molecules, which are composed of nucleotides joined via phosphodiester bonds.