Practice Questions
... tRNA carrying methionine attaches to mRNA with help of the anticodon __ The stop codon is reached and the polypeptide chain is released __ A new tRNA lands next to the first tRNA and the amino acids form a peptide bond __ The empty tRNA leaves the ribosome and the growing polypeptide chain remains o ...
... tRNA carrying methionine attaches to mRNA with help of the anticodon __ The stop codon is reached and the polypeptide chain is released __ A new tRNA lands next to the first tRNA and the amino acids form a peptide bond __ The empty tRNA leaves the ribosome and the growing polypeptide chain remains o ...
CH2- pt2 student
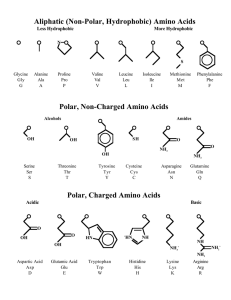
... ◦ Central carbon is attached to hydrogen atom, an amino group (NH2), a carboxyl group (COOH), and a side group. Side group defines the amino acid ...
... ◦ Central carbon is attached to hydrogen atom, an amino group (NH2), a carboxyl group (COOH), and a side group. Side group defines the amino acid ...
Proteins: Amino Acids in Three Dimensions
... 6. Use paper clips to attach the side groups, where appropriate. Use the following key as a guide for which side groups should be attached. -A positive side group can be paper clipped to a negative side group. -A hydrophobic side group can be paper clipped to another hydrophobic side group. -A sulfu ...
... 6. Use paper clips to attach the side groups, where appropriate. Use the following key as a guide for which side groups should be attached. -A positive side group can be paper clipped to a negative side group. -A hydrophobic side group can be paper clipped to another hydrophobic side group. -A sulfu ...
Chapter 10 Section 3 Notes Answer Key
... a. The sides of the ladder are made up of sugarphosphate molecules. b. The rungs of the ladder are made of nitrogen bases. 3. Before a cell divides, its DNA duplicates itself by unwinding and separating its sides, then each side becaomes a pattern on which a new side forms B. Genes- sections of DNA ...
... a. The sides of the ladder are made up of sugarphosphate molecules. b. The rungs of the ladder are made of nitrogen bases. 3. Before a cell divides, its DNA duplicates itself by unwinding and separating its sides, then each side becaomes a pattern on which a new side forms B. Genes- sections of DNA ...
Compounds of Life Chart
... Saturated – solid (no double bonds between carbon atoms), animal fats (like lard and butter) Unsaturated – liquid (like fish and vegetable oils), double or triple bond between carbon atoms Polyunsaturated – many double or triple bonds between carbon atoms Trans fats – unsaturated fatty acids ...
... Saturated – solid (no double bonds between carbon atoms), animal fats (like lard and butter) Unsaturated – liquid (like fish and vegetable oils), double or triple bond between carbon atoms Polyunsaturated – many double or triple bonds between carbon atoms Trans fats – unsaturated fatty acids ...
A mutant defective in enzyme
... 12. Within a layer of phospholipid molecules in a cell, which part of the lipid molecule faces the cytoplasm? (a) the phosphorylated head group (b) the hydrocarbon tails (c) both head and tail because the molecules lie sideways (d) neither; the phospholipids dissolve in water and disperse (e) the fa ...
... 12. Within a layer of phospholipid molecules in a cell, which part of the lipid molecule faces the cytoplasm? (a) the phosphorylated head group (b) the hydrocarbon tails (c) both head and tail because the molecules lie sideways (d) neither; the phospholipids dissolve in water and disperse (e) the fa ...
Chemistry of Life Carbohydrates Lipids Nucleic Acids ATP – The
... and carboxylic acid (COOH),along with a side-chain specific to each amino acid.] The key elements of an amino acid are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen. Proteins are macromolecules made from amino acids (the subunit) binding together. About 500 amino acids are known. ...
... and carboxylic acid (COOH),along with a side-chain specific to each amino acid.] The key elements of an amino acid are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen. Proteins are macromolecules made from amino acids (the subunit) binding together. About 500 amino acids are known. ...
PowerPoint - HRSBSTAFF Home Page
... Different combinations of these 20 amino acids create different proteins. Proteins are made outside the nucleus by organelles called ribosomes. ...
... Different combinations of these 20 amino acids create different proteins. Proteins are made outside the nucleus by organelles called ribosomes. ...
Proteins Multiple choice Proteins can be classified as Polyesters
... maltose. The pH of saliva is about 7, which is close to the optimum temperature of an enzyme. Amylase stops functioning when it enters the stomach which has a pH of 2. What happens to the enzyme on entering the stomach which would cause it to ...
... maltose. The pH of saliva is about 7, which is close to the optimum temperature of an enzyme. Amylase stops functioning when it enters the stomach which has a pH of 2. What happens to the enzyme on entering the stomach which would cause it to ...
Introduction to 9th Grade Biology
... – liquid at room temp – one or more double bonds between carbons in the fatty acids allows for “kinks” in the tails – most plant fats ...
... – liquid at room temp – one or more double bonds between carbons in the fatty acids allows for “kinks” in the tails – most plant fats ...
The Structure and Function of Macromolecules
... • MOST IMPORTANT LIPID IN BIOLOGY = Phospholipid • Phospholipids have 2 fatty acids attached to glycerol. • Fatty acid tails are hydrophobic, phosphate group and attachments form hydrophilic head. ...
... • MOST IMPORTANT LIPID IN BIOLOGY = Phospholipid • Phospholipids have 2 fatty acids attached to glycerol. • Fatty acid tails are hydrophobic, phosphate group and attachments form hydrophilic head. ...
CLINICAL CASE (UREA CYCLE)
... A male child was born into a family with no history of neonatal deaths. He weighed 2.9 kg at birth and appeared to be healthy until 3 days of age when he developed seizures. The mother had a history of aversion to meat, the eating of which was accompanied by episodes of vomiting and lethargy. The pa ...
... A male child was born into a family with no history of neonatal deaths. He weighed 2.9 kg at birth and appeared to be healthy until 3 days of age when he developed seizures. The mother had a history of aversion to meat, the eating of which was accompanied by episodes of vomiting and lethargy. The pa ...
Unit 3: Chemistry of Life
... • Monomer (most): Fatty Acid – hydrophilic head (carboxyl end), hydrophobic tail (hydrocarbon) >Saturated – means all Carbons have 2 hydrogen atoms bonded to it. >Unsaturated – means that some Carbons have double bonds (less H atoms) ...
... • Monomer (most): Fatty Acid – hydrophilic head (carboxyl end), hydrophobic tail (hydrocarbon) >Saturated – means all Carbons have 2 hydrogen atoms bonded to it. >Unsaturated – means that some Carbons have double bonds (less H atoms) ...
Amino Acids - Sehr Gut Web
... —CH—COOH group, the imino nitrogen being depicted as an element in the proline ring. (Imino hydrogen(s) are not depicted.) These are the amino acids in the order in which I memorized them in undergrad. Assuming you can figure out the three-letter abbreviations (since they’re all self-explanatory), I ...
... —CH—COOH group, the imino nitrogen being depicted as an element in the proline ring. (Imino hydrogen(s) are not depicted.) These are the amino acids in the order in which I memorized them in undergrad. Assuming you can figure out the three-letter abbreviations (since they’re all self-explanatory), I ...
Problem Set 9 Key
... 1. Describe the process of delivering amino acids to the liver from: a. Dietary proteins Gastrin Hormone is secreted by gastric mucosal cells which signals the release of HCl and Pepsinogen (pepsin zymogen) by gastric glands. The low pH triggesr Secretin release, which stimulates pancrease to releas ...
... 1. Describe the process of delivering amino acids to the liver from: a. Dietary proteins Gastrin Hormone is secreted by gastric mucosal cells which signals the release of HCl and Pepsinogen (pepsin zymogen) by gastric glands. The low pH triggesr Secretin release, which stimulates pancrease to releas ...
Carbohydrates, Lipids, Nucleic Acids, and Proteins are
... • Building blocks of proteins are amino acids. Amino acids are compounds with an amino group (NH2) and carboxyl group (COOH) on each end. • 20 different amino groups are found in nature • Proteins control rate of reactions and regulate cell processes. Some proteins build tissue like bone and muscle. ...
... • Building blocks of proteins are amino acids. Amino acids are compounds with an amino group (NH2) and carboxyl group (COOH) on each end. • 20 different amino groups are found in nature • Proteins control rate of reactions and regulate cell processes. Some proteins build tissue like bone and muscle. ...
File
... c. It is the job of transfer RNA to bring the proper amino acid into the ribosome to be attached to the growing peptide chain. d. When the ribosome reaches a stop codon, it releases the newly formed polypeptide and the mRNA molecule. 18. What is an anticodon? ...
... c. It is the job of transfer RNA to bring the proper amino acid into the ribosome to be attached to the growing peptide chain. d. When the ribosome reaches a stop codon, it releases the newly formed polypeptide and the mRNA molecule. 18. What is an anticodon? ...
Organic Molecules
... more C-H bonds than O • That + non-polar = insoluble in water • Provide the most stored energy • Important in membrane which regulate what enter and exit cell ...
... more C-H bonds than O • That + non-polar = insoluble in water • Provide the most stored energy • Important in membrane which regulate what enter and exit cell ...
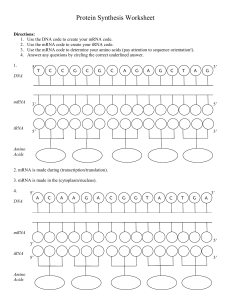
Protein Synthesis Worksheet
... 14. Proteins are made at the (nucleus/ribosome). 15. (tRNA/mRNA) attaches the amino acids into a chain. 16. tRNA is found in the (nucleus/cytoplasm). 17. (Translation/Transcription) converts mRNA into a protein. 18. Translation takes place in the (cytoplasm/nucleus). 19. (DNA/RNA) can leave the nucl ...
... 14. Proteins are made at the (nucleus/ribosome). 15. (tRNA/mRNA) attaches the amino acids into a chain. 16. tRNA is found in the (nucleus/cytoplasm). 17. (Translation/Transcription) converts mRNA into a protein. 18. Translation takes place in the (cytoplasm/nucleus). 19. (DNA/RNA) can leave the nucl ...
4.1_Proteins_Amino_Acids_2011
... chain. The peptide bond is planar (gray shading) and does not permit rotation. By contrast, rotation can occur about the Cα–C bond, whose angle of rotation is called psi (ψ), and about the N–Cα bond, whose angle of rotation is called phi (ϕ). By convention, an R group is often used to denote an amin ...
... chain. The peptide bond is planar (gray shading) and does not permit rotation. By contrast, rotation can occur about the Cα–C bond, whose angle of rotation is called psi (ψ), and about the N–Cα bond, whose angle of rotation is called phi (ϕ). By convention, an R group is often used to denote an amin ...
Biosynthesis

Biosynthesis (also called biogenesis or anabolism) is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined together to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides.The prerequisite elements for biosynthesis include: precursor compounds, chemical energy (e.g. ATP), and catalytic enzymes which may require coenzymes (e.g.NADH, NADPH). These elements create monomers, the building blocks for macromolecules. Some important biological macromolecules include: proteins, which are composed of amino acid monomers joined via peptide bonds, and DNA molecules, which are composed of nucleotides joined via phosphodiester bonds.