Macromolecule Flapbook
... 1. Fold a sheet of paper “hot dog style.” (Landscape). 2. Divide one side of the sheet of paper into four equal sections. 3. Label each section as follows: Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids 4. Then cut each segment (top side only to form flaps!) ...
... 1. Fold a sheet of paper “hot dog style.” (Landscape). 2. Divide one side of the sheet of paper into four equal sections. 3. Label each section as follows: Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids 4. Then cut each segment (top side only to form flaps!) ...
Name
... 3. DNA is named for which part of the molecule it contains (hint: RNA contains a different one of these) 4. What two scientists are given credit for determining the structure of DNA? 5. What are the two base-pairing rules for DNA? 6. Build the bottom side of the DNA molecule on the right: 7. The enz ...
... 3. DNA is named for which part of the molecule it contains (hint: RNA contains a different one of these) 4. What two scientists are given credit for determining the structure of DNA? 5. What are the two base-pairing rules for DNA? 6. Build the bottom side of the DNA molecule on the right: 7. The enz ...
Nucleic Acids - cpprashanths Chemistry
... S= 5 Carbon Sugar (ribose or deoxyribose) B= Nitrogen Base ...
... S= 5 Carbon Sugar (ribose or deoxyribose) B= Nitrogen Base ...
Nitrogen 1 - Website of Neelay Gandhi
... Alpha-ketoglutarate and NH4+ A.A. removed from MOST L-amino acids by transamination Liver, kidney and muscle contain aminotransferases that catalyze the reversible transfer from L-amino acids to alpha-keto acids Aminotransferases catalyze reversible reactions Transamination a.a. parent keto acids ...
... Alpha-ketoglutarate and NH4+ A.A. removed from MOST L-amino acids by transamination Liver, kidney and muscle contain aminotransferases that catalyze the reversible transfer from L-amino acids to alpha-keto acids Aminotransferases catalyze reversible reactions Transamination a.a. parent keto acids ...
6-Premedical-From-Gene-to
... Posttranslational modifications: certain amino acid are modified by attachment of sugars, lipids, phosphate groups. Two or more polypeptides may join to become the subunits of a protein. ...
... Posttranslational modifications: certain amino acid are modified by attachment of sugars, lipids, phosphate groups. Two or more polypeptides may join to become the subunits of a protein. ...
What Processes Produce RNA from DNA and Protein from mRNA
... shown here and the codon chart in Figure 17.4 (page 313) in Biology, 7th edition to answer the next questions. Original template strand of DNA: 3 TAC GCA AGC AAT ACC GAC GAA 5 a. If this DNA strand produces an mRNA, what is the sequence of the mRNA? ________________________________________________ ...
... shown here and the codon chart in Figure 17.4 (page 313) in Biology, 7th edition to answer the next questions. Original template strand of DNA: 3 TAC GCA AGC AAT ACC GAC GAA 5 a. If this DNA strand produces an mRNA, what is the sequence of the mRNA? ________________________________________________ ...
RNA and Protein Synthesis
... RNA and Protein Synthesis 1. What does RNA stand for? Ribonucleic Acid 2. What is the sugar in RNA? Ribose 3. What are the three parts of an RNA nucleotide? Nitrogen base, 5-Carbon Sugar, and Phosphate Group 4. What are the three differences between RNA and DNA? The Sugars, (Ribose vs. Deoxyribose,) ...
... RNA and Protein Synthesis 1. What does RNA stand for? Ribonucleic Acid 2. What is the sugar in RNA? Ribose 3. What are the three parts of an RNA nucleotide? Nitrogen base, 5-Carbon Sugar, and Phosphate Group 4. What are the three differences between RNA and DNA? The Sugars, (Ribose vs. Deoxyribose,) ...
3.2.2 DNA - misslongscience / FrontPage
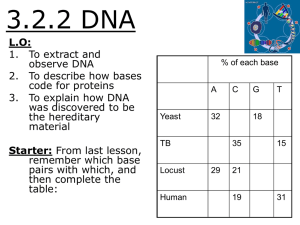
... 3.2.2 DNA L.O: 1. To extract and observe DNA 2. To describe how bases code for proteins 3. To explain how DNA was discovered to be the hereditary material Starter: From last lesson, remember which base pairs with which, and then complete the table: ...
... 3.2.2 DNA L.O: 1. To extract and observe DNA 2. To describe how bases code for proteins 3. To explain how DNA was discovered to be the hereditary material Starter: From last lesson, remember which base pairs with which, and then complete the table: ...
Student worksheet for Proteins
... Student—please print this worksheet and complete it as you interact with the tutorial. The completed worksheet should be turned in to your assigned teacher. Tutorial: Proteins Protein Definition: (PRO-teen) A molecule made up of amino acids that are needed for the body to function properly. 1. Prote ...
... Student—please print this worksheet and complete it as you interact with the tutorial. The completed worksheet should be turned in to your assigned teacher. Tutorial: Proteins Protein Definition: (PRO-teen) A molecule made up of amino acids that are needed for the body to function properly. 1. Prote ...
Lecture 6
... f. DNA replication traps random error in time, for natural selection to work on Origin of LCA a. Problem of improbability before DNA, random mutation traps history b. Two models, not mutually exclusive i. RNA world can from 3-D structures and be catalysts, replicate and carry information ii. Probl ...
... f. DNA replication traps random error in time, for natural selection to work on Origin of LCA a. Problem of improbability before DNA, random mutation traps history b. Two models, not mutually exclusive i. RNA world can from 3-D structures and be catalysts, replicate and carry information ii. Probl ...
Molecular_Evolution
... • We now know that most of the DNA does not code for amino acid sequences • Non-coding segments guide translation and are called introns • Coding segments are called exons ...
... • We now know that most of the DNA does not code for amino acid sequences • Non-coding segments guide translation and are called introns • Coding segments are called exons ...
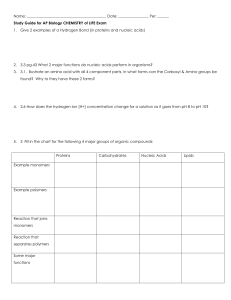
Name: Date: Per: ______ Study Guide for AP Biology CHEMISTRY
... 1. Give 2 examples of a Hydrogen Bond (in proteins and nucleic acids) ...
... 1. Give 2 examples of a Hydrogen Bond (in proteins and nucleic acids) ...
Organic Compounds - West Branch Schools
... Four groups of Organic Cmpds. Found in Living things 1. Carbohydrates - made up of C, H, O 1:2:1 Main source of energy for living things Structural in plants and some animals ...
... Four groups of Organic Cmpds. Found in Living things 1. Carbohydrates - made up of C, H, O 1:2:1 Main source of energy for living things Structural in plants and some animals ...
Nutrients and the structure of macromolecules File
... is partly how fats get their name i.e. C18 or C12 (Lorenzo’s Oil). 2. These chains can also be saturated with Hydrogen molecules so there are only single bonds between carbon atoms Or……… They can be unsaturated and have double bonds between the carbons in the fatty acid chain. 4. The glycerol molecu ...
... is partly how fats get their name i.e. C18 or C12 (Lorenzo’s Oil). 2. These chains can also be saturated with Hydrogen molecules so there are only single bonds between carbon atoms Or……… They can be unsaturated and have double bonds between the carbons in the fatty acid chain. 4. The glycerol molecu ...
Transcription and Translation Work Sheet:
... Abbreviations for the 20 different amino acids: Phenylalanine-Phe, Leucine-Leu, Isoleucine-Ile, Methionine-Met, Valine-Val, Serine-Ser, Proline-Pro, Threonine-Thr, Alanine-Ala, Tyrosine-Tyr, Histidine-His, Glutamine-Gin, Asparagine-Asn, Lysine-Lys, Aspartate-Asp, Glutamate-Glu, Cysteine-Cys, Tryptop ...
... Abbreviations for the 20 different amino acids: Phenylalanine-Phe, Leucine-Leu, Isoleucine-Ile, Methionine-Met, Valine-Val, Serine-Ser, Proline-Pro, Threonine-Thr, Alanine-Ala, Tyrosine-Tyr, Histidine-His, Glutamine-Gin, Asparagine-Asn, Lysine-Lys, Aspartate-Asp, Glutamate-Glu, Cysteine-Cys, Tryptop ...
2- All essential amino acids are glucogenic. False
... 12- Which two non-essential amino acids can be synthesized from glutamate? A. Alanine and arginine B. Arginine and proline √ C. Tyrosine and phenylalanine 13- Amidation of aspartate yields: A. Glutamine B. Asparagine √ C. Glutamate ...
... 12- Which two non-essential amino acids can be synthesized from glutamate? A. Alanine and arginine B. Arginine and proline √ C. Tyrosine and phenylalanine 13- Amidation of aspartate yields: A. Glutamine B. Asparagine √ C. Glutamate ...
chapter 4 pptol
... Delivers genetic information from nucleus to the cytoplasm Single polynucleotide chain Formed beside a strand of DNA RNA nucleotides are complementary to DNA nucleotides (exception – no thymine in RNA; replaced with uracil) How Translation Works -Protein Synthesis The transfer RNA molecule for the l ...
... Delivers genetic information from nucleus to the cytoplasm Single polynucleotide chain Formed beside a strand of DNA RNA nucleotides are complementary to DNA nucleotides (exception – no thymine in RNA; replaced with uracil) How Translation Works -Protein Synthesis The transfer RNA molecule for the l ...
PRACTICE TEST CHAPTER 13 1 ______ 1. Which of the following
... RNA is usually double-stranded and contains the base thymine. RNA is usually single-stranded and contains the base uracil. RNA is longer than DNA and uses five bases to encode information. RNA is made in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells and stays there to carry out its functions. ...
... RNA is usually double-stranded and contains the base thymine. RNA is usually single-stranded and contains the base uracil. RNA is longer than DNA and uses five bases to encode information. RNA is made in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells and stays there to carry out its functions. ...
Biosynthesis

Biosynthesis (also called biogenesis or anabolism) is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined together to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides.The prerequisite elements for biosynthesis include: precursor compounds, chemical energy (e.g. ATP), and catalytic enzymes which may require coenzymes (e.g.NADH, NADPH). These elements create monomers, the building blocks for macromolecules. Some important biological macromolecules include: proteins, which are composed of amino acid monomers joined via peptide bonds, and DNA molecules, which are composed of nucleotides joined via phosphodiester bonds.