Transamination, Deamination,urea cycle
... Glutamate dehydrogenase causes the oxidative deamination of amino acids liberation free ammonia (NH3) • Glutamate ---the only amino acid that undergoes rapid oxidative deamination ...
... Glutamate dehydrogenase causes the oxidative deamination of amino acids liberation free ammonia (NH3) • Glutamate ---the only amino acid that undergoes rapid oxidative deamination ...
Chapter 14 Review
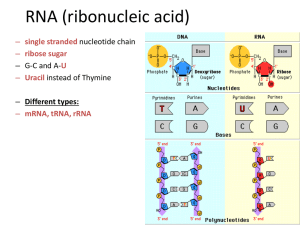
... You must answer in a complete sentence! 1. Write three complete sentences contrasting DNA and RNA. Each sentence must have information about each nucleic acid. Example: Mrs. Tucker has lots and lots of friends, whereas Mr. Stephens has few/no friends. ...
... You must answer in a complete sentence! 1. Write three complete sentences contrasting DNA and RNA. Each sentence must have information about each nucleic acid. Example: Mrs. Tucker has lots and lots of friends, whereas Mr. Stephens has few/no friends. ...
Chapter 3 LEAP Biology practice Test
... Monomers are linked together to form polymers through Dehydration reactions, which remove water Polymers are broken apart by Hydrolysis which is the addition of water Sugar monomers are Monosaccharides which can be hooked together to form more complex structures and polysaccharides What are Monosacc ...
... Monomers are linked together to form polymers through Dehydration reactions, which remove water Polymers are broken apart by Hydrolysis which is the addition of water Sugar monomers are Monosaccharides which can be hooked together to form more complex structures and polysaccharides What are Monosacc ...
Chapter 1 Study Questions
... Please print out your brief, but complete, answers to these questions on separate pages and hand in Monday Aug. 28 in class 1. How are the purine bases chemically different from pyrimidine bases? 2. Distinguish between the following terms: base, nucleoside, nucleotide, and give an example of each. Y ...
... Please print out your brief, but complete, answers to these questions on separate pages and hand in Monday Aug. 28 in class 1. How are the purine bases chemically different from pyrimidine bases? 2. Distinguish between the following terms: base, nucleoside, nucleotide, and give an example of each. Y ...
Transcription - Simone Damiano Ph.D.
... sequence specifies a single amino acid. With few exceptions, the genetic code is universal for all living organisms ...
... sequence specifies a single amino acid. With few exceptions, the genetic code is universal for all living organisms ...
RNA and Protein synthesis
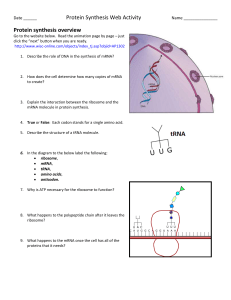
... • mRNA and tRNA have their bases read in 3’s, a sequence of 3 bases in a row is called a “Codon.” • If the tRNA’s “Anti-codon,” and mRNA’s “codon” are able to base pair together, the tRNA transfers it’s amino acid to a pocket of the ribosome. • These amino acids are then combined with other amino ac ...
... • mRNA and tRNA have their bases read in 3’s, a sequence of 3 bases in a row is called a “Codon.” • If the tRNA’s “Anti-codon,” and mRNA’s “codon” are able to base pair together, the tRNA transfers it’s amino acid to a pocket of the ribosome. • These amino acids are then combined with other amino ac ...
Organic Compounds
... • Phospholipids are important structural components of cell membranes. Structure: • a phosphate group (PO4-) is added to a glycerol body. • Next are 2 non-polar tails. ...
... • Phospholipids are important structural components of cell membranes. Structure: • a phosphate group (PO4-) is added to a glycerol body. • Next are 2 non-polar tails. ...
Translation
... 1. Use Figure 22.3 to determine which template strand DNA sequence (written in the 5' → 3' direction) specifies the tripeptide with the sequence gly-ala-leu. A) GGGGCTCTC B) CTCTCGGGG C) CCCCGAGAG D) GAGAGCCCC 2. Which is not true about the genetic code? A) Some amino acids share the same codon. B) ...
... 1. Use Figure 22.3 to determine which template strand DNA sequence (written in the 5' → 3' direction) specifies the tripeptide with the sequence gly-ala-leu. A) GGGGCTCTC B) CTCTCGGGG C) CCCCGAGAG D) GAGAGCCCC 2. Which is not true about the genetic code? A) Some amino acids share the same codon. B) ...
Introduction Document
... The three dimensional form of a protein is related to its function. A folded protein has varied nooks and bulges to bind to other molecules to build group or exchange atoms. Proteins are produced in a cell structure called ribosome where the amino acids are assembled one by one from an important mol ...
... The three dimensional form of a protein is related to its function. A folded protein has varied nooks and bulges to bind to other molecules to build group or exchange atoms. Proteins are produced in a cell structure called ribosome where the amino acids are assembled one by one from an important mol ...
amino acids - 11 College Biology
... “KINKS” made in the fatty acid chains allow for space. Liquid at room temperature. Example: olive oil ...
... “KINKS” made in the fatty acid chains allow for space. Liquid at room temperature. Example: olive oil ...
Good Luck and Happy Studying!! Intro to Biochemistry
... Describe saturated and unsaturated fats~ ___________________________________________________________________________________ ...
... Describe saturated and unsaturated fats~ ___________________________________________________________________________________ ...
Chapter 21 Biosynthetic Pathways
... Fatty Acid Biosynthesis ◦ Higher fatty acids, for example C18 (stearic acid), are obtained by addition of one or more additional C2 fragments by a different enzyme system. ◦ Unsaturated fatty acids are synthesized from saturated fatty acids by enzyme-catalyzed oxidation at the appropriate point on ...
... Fatty Acid Biosynthesis ◦ Higher fatty acids, for example C18 (stearic acid), are obtained by addition of one or more additional C2 fragments by a different enzyme system. ◦ Unsaturated fatty acids are synthesized from saturated fatty acids by enzyme-catalyzed oxidation at the appropriate point on ...
C485 Exam I - Chemistry Courses: About
... something about. These are tough questions. If you get either one, it is terrific. If you get them both, you are way over the top….! EC 1 (No partial credit) The biosynthesis of myoinositol phosphate (MIP)catalyzed by MIP synthase starts with the glucose 6-phosphate and gives the indicated product. ...
... something about. These are tough questions. If you get either one, it is terrific. If you get them both, you are way over the top….! EC 1 (No partial credit) The biosynthesis of myoinositol phosphate (MIP)catalyzed by MIP synthase starts with the glucose 6-phosphate and gives the indicated product. ...
Biology Pre-Learning Check
... structure of the subunits (nucleotides) as well as the structure of the RNA molecule itself and comparing/contrasting it with DNA We will also study the process where RNA is used to make proteins. Specifically, we will study each part (transcription and translation), the steps involved and the enzym ...
... structure of the subunits (nucleotides) as well as the structure of the RNA molecule itself and comparing/contrasting it with DNA We will also study the process where RNA is used to make proteins. Specifically, we will study each part (transcription and translation), the steps involved and the enzym ...
Central Dogma PPT
... Protein synthesis occurs in two major parts transcription and translation. 1. Transcription: Process in which DNA serves as a template to produce complementary mRNA 2. Translation: Process in which mRNA is used to link amino acids together to synthesize proteins. DNA ...
... Protein synthesis occurs in two major parts transcription and translation. 1. Transcription: Process in which DNA serves as a template to produce complementary mRNA 2. Translation: Process in which mRNA is used to link amino acids together to synthesize proteins. DNA ...
Biosynthesis

Biosynthesis (also called biogenesis or anabolism) is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined together to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides.The prerequisite elements for biosynthesis include: precursor compounds, chemical energy (e.g. ATP), and catalytic enzymes which may require coenzymes (e.g.NADH, NADPH). These elements create monomers, the building blocks for macromolecules. Some important biological macromolecules include: proteins, which are composed of amino acid monomers joined via peptide bonds, and DNA molecules, which are composed of nucleotides joined via phosphodiester bonds.