lipid3 - ChemEd DL
... The hydrated magnesium ion has two functions. First, one of its waters of hydration binds to one of the oxygen atoms of the phosphate group, holding it in the proper orientation. Second, the environment of the active site lowers the pKa of another water of hydration enough that it can lose a proton. ...
... The hydrated magnesium ion has two functions. First, one of its waters of hydration binds to one of the oxygen atoms of the phosphate group, holding it in the proper orientation. Second, the environment of the active site lowers the pKa of another water of hydration enough that it can lose a proton. ...
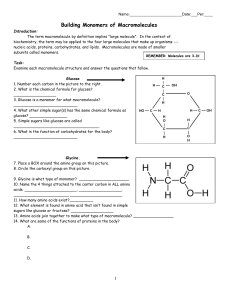
Building Monomers of Macromolecules
... Building Monomers of Macromolecules Introduction: The term macromolecule by definition implies "large molecule". In the context of biochemistry, the term may be applied to the four large molecules that make up organisms --nucleic acids, proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids. Macromolecules are made of ...
... Building Monomers of Macromolecules Introduction: The term macromolecule by definition implies "large molecule". In the context of biochemistry, the term may be applied to the four large molecules that make up organisms --nucleic acids, proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids. Macromolecules are made of ...
Organic Molecule Notes
... --20 different amino acids in proteins. --Polypeptide bonds link amino acids into a polypeptide chain=protein. 4 characteristics of Shape: -primary = -secondary = -tertiary = -quaternary = -the role of a protein is determined by its shape, which is determined by its amino acid sequence. ...
... --20 different amino acids in proteins. --Polypeptide bonds link amino acids into a polypeptide chain=protein. 4 characteristics of Shape: -primary = -secondary = -tertiary = -quaternary = -the role of a protein is determined by its shape, which is determined by its amino acid sequence. ...
word doc
... is mediated by molecular chaperones (e.g. Hsp70) or chaperonins (Hsp60 complexes). Nearly every protein is modified after synthesis on the ribosome. These modifications are essential and dictate the activity, life span or the cellular location of proteins. During modification, various chemical group ...
... is mediated by molecular chaperones (e.g. Hsp70) or chaperonins (Hsp60 complexes). Nearly every protein is modified after synthesis on the ribosome. These modifications are essential and dictate the activity, life span or the cellular location of proteins. During modification, various chemical group ...
Modern Biology: Chapter 3
... – Composed of amino acids (C, H, O, N et al) – 20 essential amino acids, differ in –R groups – Amino acids joined via peptide bond between amino side of 1 & carboxyl side of another – Enzymes are protein catalysts ...
... – Composed of amino acids (C, H, O, N et al) – 20 essential amino acids, differ in –R groups – Amino acids joined via peptide bond between amino side of 1 & carboxyl side of another – Enzymes are protein catalysts ...
Proteins - RHS AP Biology
... RNA and DNA. Amino acids: A group of 20 different kinds of small molecules that link together in long chains to form proteins; building blocks of protein. RNA: a nucleic molecule similar to DNA that delivers DNA's genetic message to the cytoplasm of a cell where proteins are made DNA: a nucleic acid ...
... RNA and DNA. Amino acids: A group of 20 different kinds of small molecules that link together in long chains to form proteins; building blocks of protein. RNA: a nucleic molecule similar to DNA that delivers DNA's genetic message to the cytoplasm of a cell where proteins are made DNA: a nucleic acid ...
Score: ______/18 Biology – Exploring Life - Ms. Faulkner
... Online Activity 5.4 – Build amino acid chains 10) What process is used to build amino acid chains? _____________________________________________________ 11) Each 3 letter abbreviation represents a different amino acid. There are 20 different amino acids that join in different ways to make all of the ...
... Online Activity 5.4 – Build amino acid chains 10) What process is used to build amino acid chains? _____________________________________________________ 11) Each 3 letter abbreviation represents a different amino acid. There are 20 different amino acids that join in different ways to make all of the ...
What_I_need_to_know_about_Protein_Synthesis_2013
... Describe the effect of mutations on the process of protein synthesis. 24. A mutation is a _______________ in DNA that results in an altered _____________ performing different functions in the cell. 25. What causes mutations? _____________, ______________ and _________________ 26. Circle the mutation ...
... Describe the effect of mutations on the process of protein synthesis. 24. A mutation is a _______________ in DNA that results in an altered _____________ performing different functions in the cell. 25. What causes mutations? _____________, ______________ and _________________ 26. Circle the mutation ...
Biology Common Assessment Name
... b. They are opposite of one another. c. They each contain one new and one old strand. d. They were both made by a process called protein synthesis. 24. Scientists can use genetic information to identify people because it is unique to each person. Which specific characteristic is unique to an individ ...
... b. They are opposite of one another. c. They each contain one new and one old strand. d. They were both made by a process called protein synthesis. 24. Scientists can use genetic information to identify people because it is unique to each person. Which specific characteristic is unique to an individ ...
amino acid - Humble ISD
... The mRNA molecule slides through the ribosome one codon at a time. The specified amino acids are carried to the ribosome by tRNA. As another tRNA arrives at the ribosome, the tRNA already there is bumped off, but leaves its amino acid behind. This process continues and a chain of amino acids forms u ...
... The mRNA molecule slides through the ribosome one codon at a time. The specified amino acids are carried to the ribosome by tRNA. As another tRNA arrives at the ribosome, the tRNA already there is bumped off, but leaves its amino acid behind. This process continues and a chain of amino acids forms u ...
Modeling Protein Structure Activity
... b. In a watery environment, nonpolar amino acids want to be near each other _____ from water c. Positively charged amino acids are ________________ to negatively charged amino acids d. Cysteine side chains want to be near each other because they can form stabilizing _______________ bridges e. When ...
... b. In a watery environment, nonpolar amino acids want to be near each other _____ from water c. Positively charged amino acids are ________________ to negatively charged amino acids d. Cysteine side chains want to be near each other because they can form stabilizing _______________ bridges e. When ...
Protein synthesis
... 3. Nutrients include Proteins, Carbohydrates, Lipids (Fats, oils), Nucleic Acids (DNA, RNA), water, oxygen, and minerals (iron, magnesium). 4. Nutrients are catabolized and anabolized to provide cells with building materials and a supply of energy. 5. Materials are needed to replace or add membranes ...
... 3. Nutrients include Proteins, Carbohydrates, Lipids (Fats, oils), Nucleic Acids (DNA, RNA), water, oxygen, and minerals (iron, magnesium). 4. Nutrients are catabolized and anabolized to provide cells with building materials and a supply of energy. 5. Materials are needed to replace or add membranes ...
BIO 6.3 Carbon - Steinbach Science
... The number of amino acids in protein chains determine the kind of protein Proteins are the building blocks of many structural components of organisms, as well as are important in contracting of muscle ...
... The number of amino acids in protein chains determine the kind of protein Proteins are the building blocks of many structural components of organisms, as well as are important in contracting of muscle ...
Ch 2 - Biochemistry
... Cushioning - protective function, i.e. cerebrospinal fluid and amniotic fluid ...
... Cushioning - protective function, i.e. cerebrospinal fluid and amniotic fluid ...
Chapter 16 and 17 Review
... 11. Describe the role of the following enzymes used in DNA replication a) Helicase b) Single stranded binding protein c) Primase d) DNA polymerase III e) DNA polymerase I f) DNA ligase 12. How do the leading strand and lagging strand differ? 13. What is a telomere? Why is the telomere not reduced du ...
... 11. Describe the role of the following enzymes used in DNA replication a) Helicase b) Single stranded binding protein c) Primase d) DNA polymerase III e) DNA polymerase I f) DNA ligase 12. How do the leading strand and lagging strand differ? 13. What is a telomere? Why is the telomere not reduced du ...
summing-up - Zanichelli online per la scuola
... that the information in cells is transferred only in one direction, from DNA to proteins, i.e. from genes to phenotype. This flow takes place in stages, facilitated by RNA ...
... that the information in cells is transferred only in one direction, from DNA to proteins, i.e. from genes to phenotype. This flow takes place in stages, facilitated by RNA ...
the code of translation
... 4. A peptide bond forms between the first two amino acids. 5. The first tRNA leaves, and the ribosome moves along the mRNA to the next codon. 6. The next tRNA brings in the next amino acid, and a peptide bond is formed between this amino acid and the growing amino acid chain. 7. The process continu ...
... 4. A peptide bond forms between the first two amino acids. 5. The first tRNA leaves, and the ribosome moves along the mRNA to the next codon. 6. The next tRNA brings in the next amino acid, and a peptide bond is formed between this amino acid and the growing amino acid chain. 7. The process continu ...
terminal end
... the outer surface (Out) faces the environment. ¾ The matrix of the unit membrane is composed of phospholipids, with the hydrophobic groups directed inward and the hydrophilic groups toward the outside, where they associate with water. ¾ Embedded in the matrix are proteins that have considerable hydr ...
... the outer surface (Out) faces the environment. ¾ The matrix of the unit membrane is composed of phospholipids, with the hydrophobic groups directed inward and the hydrophilic groups toward the outside, where they associate with water. ¾ Embedded in the matrix are proteins that have considerable hydr ...
Chapter 6, Section 3
... Organic: contains carbon ◦ All living things contain carbon (C), hydrogen (H), oxygen (O), nitrogen (N), and phosphorus (P) Monomer: created when C,H,O, N, P bond together to form small molecules Polymer: large compounds that are formed by joining monomers together ...
... Organic: contains carbon ◦ All living things contain carbon (C), hydrogen (H), oxygen (O), nitrogen (N), and phosphorus (P) Monomer: created when C,H,O, N, P bond together to form small molecules Polymer: large compounds that are formed by joining monomers together ...
Biosynthesis

Biosynthesis (also called biogenesis or anabolism) is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined together to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides.The prerequisite elements for biosynthesis include: precursor compounds, chemical energy (e.g. ATP), and catalytic enzymes which may require coenzymes (e.g.NADH, NADPH). These elements create monomers, the building blocks for macromolecules. Some important biological macromolecules include: proteins, which are composed of amino acid monomers joined via peptide bonds, and DNA molecules, which are composed of nucleotides joined via phosphodiester bonds.