DNA Personal Ads
... sequence is really dull, and I’m ready to move on to more exciting things. I’m looking for my true love, mRNA. (transcription) ...
... sequence is really dull, and I’m ready to move on to more exciting things. I’m looking for my true love, mRNA. (transcription) ...
Name___________________________ Date_________________ Period_____
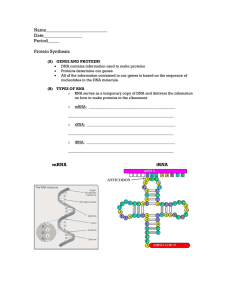
... All of the information contained in our genes is based on the sequence of nucleotides in the DNA molecule. (B) TYPES OF RNA o RNA serves as a temporary copy of DNA and delivers the infomation on how to make proteins to the ribosomes o ...
... All of the information contained in our genes is based on the sequence of nucleotides in the DNA molecule. (B) TYPES OF RNA o RNA serves as a temporary copy of DNA and delivers the infomation on how to make proteins to the ribosomes o ...
CHONPS Creature Creation
... A young scientist gets a copy of this CHONPS DNA code on paper. It is your task to transcribe and translate the DNA. Then use the attached charts to figure out what this CHONPS will actually look like. You then will create your creature on cardstock by drawing, coloring, and clearly illustrating his ...
... A young scientist gets a copy of this CHONPS DNA code on paper. It is your task to transcribe and translate the DNA. Then use the attached charts to figure out what this CHONPS will actually look like. You then will create your creature on cardstock by drawing, coloring, and clearly illustrating his ...
Translation Notes
... – Organisms use 20 different amino acids to build proteins – Your body makes 12, others come from food you eat ...
... – Organisms use 20 different amino acids to build proteins – Your body makes 12, others come from food you eat ...
Worksheet 13.2
... 12. What two mRNA codes corresponds with histidine? ________ ________ 13. How many different mRNA codes correspond to arginine? ______________ 14. How many different mRNA codes correspond with methionine? ____________ 15. What occurs during the process of translation?. ...
... 12. What two mRNA codes corresponds with histidine? ________ ________ 13. How many different mRNA codes correspond to arginine? ______________ 14. How many different mRNA codes correspond with methionine? ____________ 15. What occurs during the process of translation?. ...
Remediation/Corrections Packet
... Lipids are large, nonpolar (won't dissolve in water) molecules. Phospholipids make up cell membranes. Lipids also serve as waxy coverings and steroids. Lipids have more carbon and hydrogen atoms than oxygen atoms. Fats are made of a glycerol (alcohol) and three fatty acid chains. This subunit is ca ...
... Lipids are large, nonpolar (won't dissolve in water) molecules. Phospholipids make up cell membranes. Lipids also serve as waxy coverings and steroids. Lipids have more carbon and hydrogen atoms than oxygen atoms. Fats are made of a glycerol (alcohol) and three fatty acid chains. This subunit is ca ...
Document
... Occurs when chromosomes duplicate An exact copy of the DNA is produced Hydrogen bonds between bases break and the molecule “unzips” with helicases Each old strand of nucleotides serves as a template for each new strand ...
... Occurs when chromosomes duplicate An exact copy of the DNA is produced Hydrogen bonds between bases break and the molecule “unzips” with helicases Each old strand of nucleotides serves as a template for each new strand ...
study guide section 3-1 carbon compounds
... a. the R groups of the amino acids they contain. b. the amino groups of the amino acids they contain. c. the carboxyl groups of the amino acids they contain. d. whether or not they contain any amino acids. 3. ______ Most enzymes a. are changed by the reactions they catalyze. b. increase that activat ...
... a. the R groups of the amino acids they contain. b. the amino groups of the amino acids they contain. c. the carboxyl groups of the amino acids they contain. d. whether or not they contain any amino acids. 3. ______ Most enzymes a. are changed by the reactions they catalyze. b. increase that activat ...
Chapter 17 – Amino Acid Metabolism
... Although the biosynthesis of specific amino acids is diverse, they all share a common feature carbon skeletons come from intermediates of glycolysis, PPP, or citric acid cycle. There are only six biosynthetic families: 1) Derived from oxaloacetate --> Asp, Asn, Met, Thr, Ile, Lys 2) Drived from pyru ...
... Although the biosynthesis of specific amino acids is diverse, they all share a common feature carbon skeletons come from intermediates of glycolysis, PPP, or citric acid cycle. There are only six biosynthetic families: 1) Derived from oxaloacetate --> Asp, Asn, Met, Thr, Ile, Lys 2) Drived from pyru ...
Medical Biochemistry and Molecular Basis of Medical
... 13. A newborn child is eliminating valine in his urine. This suggests the child a. has acaptonuria. b. has a deficiency in the α-ketoacid dehydrogenase needed to metabolize valine. c. cannot metabolize leucine and isoleucine. d. All of the above. 14. You and your study partner are having an argument ...
... 13. A newborn child is eliminating valine in his urine. This suggests the child a. has acaptonuria. b. has a deficiency in the α-ketoacid dehydrogenase needed to metabolize valine. c. cannot metabolize leucine and isoleucine. d. All of the above. 14. You and your study partner are having an argument ...
ANSWERS TO REVIEW QUESTIONS – CHAPTER 02
... Fibrous and globular proteins can be distinguished by their structures. The primary and secondary structures of proteins refer respectively to (1) the sequence of amino acid monomers and (2) the bending and folding of the amino acid chain. The tertiary structure of a protein refers to the overall sh ...
... Fibrous and globular proteins can be distinguished by their structures. The primary and secondary structures of proteins refer respectively to (1) the sequence of amino acid monomers and (2) the bending and folding of the amino acid chain. The tertiary structure of a protein refers to the overall sh ...
STATE UNIVERSITY OF NEW YORK COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY CANTON, NEW YORK
... enzymes; relate structure to function of proteins; and explain enzyme catalysis and regulation; and apply thermodynamic and kinetic theories to enzyme reactions 3. Describe the physical and chemical properties of lipids, their synthesis and function in membranes and metabolism 4. Describe the centra ...
... enzymes; relate structure to function of proteins; and explain enzyme catalysis and regulation; and apply thermodynamic and kinetic theories to enzyme reactions 3. Describe the physical and chemical properties of lipids, their synthesis and function in membranes and metabolism 4. Describe the centra ...
Protein synthesis
... of certain proteins. - Makes a single stranded compliment of only a segment of DNA and only when it is needed. ...
... of certain proteins. - Makes a single stranded compliment of only a segment of DNA and only when it is needed. ...
No Slide Title
... Polynucleotide chain Nucleosome = DNA + Protein Heritable property Eukaryote: coding sequence non-coding sequence ...
... Polynucleotide chain Nucleosome = DNA + Protein Heritable property Eukaryote: coding sequence non-coding sequence ...
View PDF
... What condition do some people suffer from that by eating breads, potatoes and other starches could be dangerous?diabetes What happens? All carbohydrates that the person eats are turned into sugar. This causes a rise in their blood sugar level. When amino acids are joined together they form what type ...
... What condition do some people suffer from that by eating breads, potatoes and other starches could be dangerous?diabetes What happens? All carbohydrates that the person eats are turned into sugar. This causes a rise in their blood sugar level. When amino acids are joined together they form what type ...
Biochemistry 423 Final Examination
... _____ The link between nucleotides in RNA and DNA is a phosphodiester bond. _____ A highly processive enzyme stays bound to its substrate as it catalyzes a sequence of reactions. _____ Thymine (rather than uracil) is found in DNA in order to ensure that chemical damage to DNA is repaired. _____ Prok ...
... _____ The link between nucleotides in RNA and DNA is a phosphodiester bond. _____ A highly processive enzyme stays bound to its substrate as it catalyzes a sequence of reactions. _____ Thymine (rather than uracil) is found in DNA in order to ensure that chemical damage to DNA is repaired. _____ Prok ...
Chemistry part 2
... functional protein • Polypeptides can be the same (collagen is a homotrimer) or different (hemoglobin is a heterotetramer) ...
... functional protein • Polypeptides can be the same (collagen is a homotrimer) or different (hemoglobin is a heterotetramer) ...
Master Entrance Exam
... 10. 1000 bps DNA coding sequences can make protein roughly (A) 23 (B) 27 (C) 33 (D) 37 (E) 43 kilodalton II. 是非題 (每題 2 分) Yes or No for answer 1. Lipid components of membranes do not readily move from one side of a bilayer to the other. 2. In the Citrate-Pyruvate Cycle, the step that generates NADPH ...
... 10. 1000 bps DNA coding sequences can make protein roughly (A) 23 (B) 27 (C) 33 (D) 37 (E) 43 kilodalton II. 是非題 (每題 2 分) Yes or No for answer 1. Lipid components of membranes do not readily move from one side of a bilayer to the other. 2. In the Citrate-Pyruvate Cycle, the step that generates NADPH ...
Biosynthesis

Biosynthesis (also called biogenesis or anabolism) is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined together to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides.The prerequisite elements for biosynthesis include: precursor compounds, chemical energy (e.g. ATP), and catalytic enzymes which may require coenzymes (e.g.NADH, NADPH). These elements create monomers, the building blocks for macromolecules. Some important biological macromolecules include: proteins, which are composed of amino acid monomers joined via peptide bonds, and DNA molecules, which are composed of nucleotides joined via phosphodiester bonds.