* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Macromolecules College Notes
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Catalytic triad wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Glyceroneogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
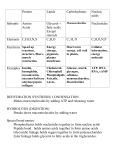
Name: ________________________________________________ Water Covalent bonds- Polarity- Polar- Nonpolar- Hydrogen bond- Properties of Water 1) CohesionExample: surface tension 2) Adhesion- 3) Good Solvent- 4) Expands when it freezes (ice density)- 5) High specific heat (heat capacity)- Period:_____________ Name: ________________________________________________ Period:_____________ Macromolecules Organic CompoundsThe most important element when studying the chemistry of life is ________________. Carbon has four electrons in its valence level, meaning that it needs ___________ more. This gives carbon the ability to form four _____________ bonds with other elements, including oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen, and sulfur. Macromolecules are made from thousands or even hundreds of thousands of smaller molecules. MonomersPolymersExamples: Dehydration Synthesis- (condensation reaction)- Hydrolysis- Ex: When we eat food, it instantly touches water in our saliva. This begins the breakdown of polymers right away. ADP ATP ATP- Energy Adenosine diphosphate (ADP) + Phosphate Partially charged battery Energy Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) Fully charged battery Name: ________________________________________________ Period:_____________ Carbohydrates __________________ are organic compounds composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in a 1:2:1 ratio. (Example: C6H12O6) Purpose: Elements: Monomers: Polymers: Foods: Proteins Purpose: Elements: Monomers: Polymer: General Structure In order to link two amino acids together, a condensation reaction occurs to form a _____________________. Polypeptides can range from a few amino acids to thousands in length. Amino acids Alanine Serine ________________________ determines _______________________ Name: ________________________________________________ Period:_____________ ______________________-determined by the sequence of amino acids (what order the amino acids are hooked together) ______________________- formed by hydrogen bonding between the amino acid R groups. (β-pleated sheets and α helix). ______________________ - formed when the polypeptide chain folds and the R groups of different amino acids form covalent and ionic bonds with each other ______________________ - only in some proteins where there is more than one polypetide chain involved in the structure of the protein _______________________-when anything changes the native conformation, and therefore the proteins structure. Examples: __________________-organic molecules that act as catalysts Enzymes are proteins and their reactions depend on the physical fit between the enzyme molecule and its ___________________, the reactant being catalyzed. And enzyme and its substrate fit together like a __________________________________. The linkage of the substrate to the enzyme allows the protein to change shape, causing bonds in the substrate to weaken (therefore decreasing ___________________________________, which is the amount of energy required for a reaction to start.) Characteristics of Enzymes Reusable- Specific- Sensitive- Name: ________________________________________________ Period:_____________ Lipids Purpose: Elements: Monomers: Polymers: The two ends of fatty acids have very different properties. The head of the fatty acid likes water and is ______________________________ because it is polar. The long fatty acid tails don’t like water and are __________________ because they are nonpolar. The fatty acid is considered to be ____________________ when each carbon atom is covalently bonded to four other atoms. The fatty acid is considered to be ____________________ when the carbons are not bonded to the maximum number of atoms they can bond to. Instead, they form double bonds within the carbon chain. Your body can break down unsaturated fats easier then saturated fats. Three classes of lipids: -___________________ -___________________ -___________________ ___________________________ are formed when three fatty acid molecules join to one molecules of glycerol. Saturated triglycerides (composed of saturated fatty acids) tend to be solid at room temperature (shortening and animal fat). Unsaturated triglycerides (composed of unsaturated fatty acids) tend to be liquids at room temp (vegetable oil). ____________________________-are made of two fatty acids tails and a hydrophilic head region made up of a phosphate group. The phosphate group makes the “heads” ________________, whereas the fatty acids are _______________________. Name: ________________________________________________ Cell membranes are composed of ___________________________ so that when exposed to water on either side (like in a cell) the phospholipids become a bilayer where they hydrophilic heads project outward where there is water and the hydrophobic tails project inward ____________________-composed of four fused carbon rings with various functional groups attached to them. Ex: Cholesterol Testosterone is a male hormone that is a steroid Testosterone is used by males to produce muscle fibers and sex characteristics Cholesterol is a steroid that is needed for nerve cells to function properly Nucleic Acids Purpose: Elements: Monomers: Nucleotides are composed of a phosphate group, 5-carbon ring, and a nitrogen base. Polymers: Period:_____________