Cellular Respiration:
... Control of metabolism: __________________control the rates of all the metabolic reactions of the cell Enzymes are complex _____________that function to lower the activation energy of a reaction so it may begin and proceed more ______________. Because they do this, enzymes are called ____________. Th ...
... Control of metabolism: __________________control the rates of all the metabolic reactions of the cell Enzymes are complex _____________that function to lower the activation energy of a reaction so it may begin and proceed more ______________. Because they do this, enzymes are called ____________. Th ...
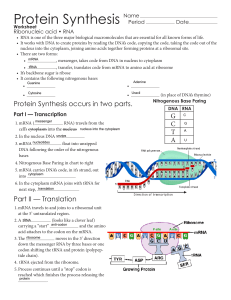
What is translation?
... In contrast to only 4 building blocks in DNA or RNA, there are 20 amino acids that are used to build proteins. This creates diversity in what kinds of proteins that can be made. Future content will be posted to discuss the different amino acids. In this diagram, the green rectangle, labeled ribosome ...
... In contrast to only 4 building blocks in DNA or RNA, there are 20 amino acids that are used to build proteins. This creates diversity in what kinds of proteins that can be made. Future content will be posted to discuss the different amino acids. In this diagram, the green rectangle, labeled ribosome ...
Enzymes/Macromolecules/Bonding
... differing only in the side chain Properties of side chains account for structural and functional differences ...
... differing only in the side chain Properties of side chains account for structural and functional differences ...
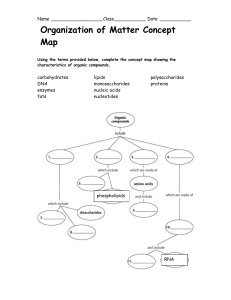
Polymers vs. monomers wkst. and concept map
... Name __________________ Class ___________ Date ___________ 7. Match the POLYmer on the left to the macromolecules on the right. ...
... Name __________________ Class ___________ Date ___________ 7. Match the POLYmer on the left to the macromolecules on the right. ...
Review Problems #2 (Enzyme Review, Phosphatases
... 2) The branchpoint for aromatic amino acid biosynthesis is chorismate. What is the structure of chorismate? What are the three immediate products derived from chorismate that constitute the first unique steps in the synthesis of the three aromatic amino acids? 3) From where are the two carbons of th ...
... 2) The branchpoint for aromatic amino acid biosynthesis is chorismate. What is the structure of chorismate? What are the three immediate products derived from chorismate that constitute the first unique steps in the synthesis of the three aromatic amino acids? 3) From where are the two carbons of th ...
Protein Synthesis Notes
... (the “chefs”) to send these recipes to the ribosomes (“kitchen”) so they can be made. 1. The basic unit of a protein is an amino acid a. we use 20 amino acids to make all of our proteins 2. A chain of amino acids together is a protein 3. Types of proteins include: hormones, enzymes, structural prote ...
... (the “chefs”) to send these recipes to the ribosomes (“kitchen”) so they can be made. 1. The basic unit of a protein is an amino acid a. we use 20 amino acids to make all of our proteins 2. A chain of amino acids together is a protein 3. Types of proteins include: hormones, enzymes, structural prote ...
DNA RNA-Protein Synthesis Homework
... What is a protein? Why are they important? Where are they made in the cell? What makes them? Why are they so different? ...
... What is a protein? Why are they important? Where are they made in the cell? What makes them? Why are they so different? ...
Say It With DNA - District 196 e
... sequence of amino acids on the protein synthesis chart. ! Step 5:! Using the Dictionary of Amino Acids: Abbreviations and Symbols, place the ...
... sequence of amino acids on the protein synthesis chart. ! Step 5:! Using the Dictionary of Amino Acids: Abbreviations and Symbols, place the ...
Chapter 13: RNA and Protein Synthesis
... Each tRNA carries one amino acid – it gets matched with the codon through an anticodon complementary to the mRNA Ribosome helps form a peptide bond between the each amino acid Polypeptide chain continues to grow until the ribosome reaches a “stop” codon It releases both the newly formed polypeptide ...
... Each tRNA carries one amino acid – it gets matched with the codon through an anticodon complementary to the mRNA Ribosome helps form a peptide bond between the each amino acid Polypeptide chain continues to grow until the ribosome reaches a “stop” codon It releases both the newly formed polypeptide ...
Macromolecules Worksheet
... ____________________ 3. This is the name given to an amino acid added to a dipeptide. ____________________ 4. Of what kind of organic compound are oils, waxes, and fats an example? ____________________ 5. These are the individual subunits that make up DNA and RNA. ____________________ 6. What is a l ...
... ____________________ 3. This is the name given to an amino acid added to a dipeptide. ____________________ 4. Of what kind of organic compound are oils, waxes, and fats an example? ____________________ 5. These are the individual subunits that make up DNA and RNA. ____________________ 6. What is a l ...
chapter 3 outline
... Unlike prokaryotes, where there is one principle RNA polymerase, transcription in eukaryotes involves three different RNA polymerases -RNA polymerase I (rRNAs) -RNA polymerase II (mRNAs) -RNA polymerase III (other small functional RNAs) In eukaryotes, RNAs typically undergo processing after being ma ...
... Unlike prokaryotes, where there is one principle RNA polymerase, transcription in eukaryotes involves three different RNA polymerases -RNA polymerase I (rRNAs) -RNA polymerase II (mRNAs) -RNA polymerase III (other small functional RNAs) In eukaryotes, RNAs typically undergo processing after being ma ...
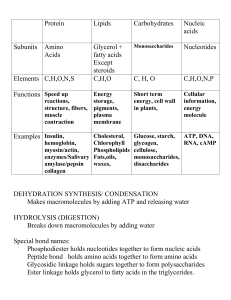
CH 5: Carbs, Lipids, Proteins, and Nucleic Acids – Study Chart I
... Directions: Use your textbook, class notes, and/or internet resources to complete the charts below. In the “box” to the right of each molecule, write a brief description explaining what the molecule is, or does, or is used for, in living things. ...
... Directions: Use your textbook, class notes, and/or internet resources to complete the charts below. In the “box” to the right of each molecule, write a brief description explaining what the molecule is, or does, or is used for, in living things. ...
Translation
... 3. On the opposite side of the tRNA molecule from the amino acid site, there is a sequence of 3 nucleotides that are complement of the nucleotides in the codon. ...
... 3. On the opposite side of the tRNA molecule from the amino acid site, there is a sequence of 3 nucleotides that are complement of the nucleotides in the codon. ...
Protein Synthesis (Translation)
... mRNA is a message that codes for a protein Proteins are made in the cytoplasm and then work to keep the cell alive Translation (protein synthesis): Process of making a protein Proteins are made up of amino acids (small building blocks) There are 20 different types of amino acids ...
... mRNA is a message that codes for a protein Proteins are made in the cytoplasm and then work to keep the cell alive Translation (protein synthesis): Process of making a protein Proteins are made up of amino acids (small building blocks) There are 20 different types of amino acids ...
protein synthesis
... The tRNA will deliver the appropriate amino acid in the cytoplasm that is coded for by the mRNA messenger RNA (mRNA) is decoded to produce a specific protein using specific amino acids ...
... The tRNA will deliver the appropriate amino acid in the cytoplasm that is coded for by the mRNA messenger RNA (mRNA) is decoded to produce a specific protein using specific amino acids ...
Review Problems #2 (Enzyme Review, Phosphatases
... structure of chorismate? What are the three immediate products derived from chorismate that constitute the first unique steps in the synthesis of the three aromatic amino acids? 3) From where are the two carbons of the five-membered ring of tryptophan derived? Be specific. (Show the molecule and hig ...
... structure of chorismate? What are the three immediate products derived from chorismate that constitute the first unique steps in the synthesis of the three aromatic amino acids? 3) From where are the two carbons of the five-membered ring of tryptophan derived? Be specific. (Show the molecule and hig ...
honors Chapter 2.3-2.4 teaching
... Base: a compound that produces OH(hydroxide) ions in solution ...
... Base: a compound that produces OH(hydroxide) ions in solution ...
Protein Synthesis - Issaquah Connect
... nucleus into the cytoplasm, joining amino acids together forming proteins at a ribosomal site. • There are two forms: • mRNA , messenger, takes code from DNA in nucleus to cytoplasm • tRNA , transfer, translates code from mRNA to amino acid at ribosome • It’s backbone sugar is ribose • It conta ...
... nucleus into the cytoplasm, joining amino acids together forming proteins at a ribosomal site. • There are two forms: • mRNA , messenger, takes code from DNA in nucleus to cytoplasm • tRNA , transfer, translates code from mRNA to amino acid at ribosome • It’s backbone sugar is ribose • It conta ...
Competition
... number of amino acids, and their sequence determine the protein. Only 12 of the amino acids can be made by our body, the rest have to come from our food (meat, nuts). These 8 are called Essential Amino Acids. ...
... number of amino acids, and their sequence determine the protein. Only 12 of the amino acids can be made by our body, the rest have to come from our food (meat, nuts). These 8 are called Essential Amino Acids. ...
Biosynthesis

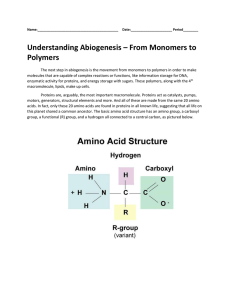
Biosynthesis (also called biogenesis or anabolism) is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined together to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides.The prerequisite elements for biosynthesis include: precursor compounds, chemical energy (e.g. ATP), and catalytic enzymes which may require coenzymes (e.g.NADH, NADPH). These elements create monomers, the building blocks for macromolecules. Some important biological macromolecules include: proteins, which are composed of amino acid monomers joined via peptide bonds, and DNA molecules, which are composed of nucleotides joined via phosphodiester bonds.