RNA - Burlington Township School District
... Codons and Amino Acids There are 21 different types of amino acids. AUG is the “start codon” and also signals for the amino acid methionine UAA, UAG, and UGA are “stop codons” and signal the ribosome to release the newly formed protein. ...
... Codons and Amino Acids There are 21 different types of amino acids. AUG is the “start codon” and also signals for the amino acid methionine UAA, UAG, and UGA are “stop codons” and signal the ribosome to release the newly formed protein. ...
Amino Acid Catabolism
... Assimilation into Amino Acids • In microorganisms/plants: assimilation of ammonia is key—synthesis of most amino acids – Glutamine synthetase incorporates amino group • Glutamine serves as nitrogen donor for nucleic acids, etc. ...
... Assimilation into Amino Acids • In microorganisms/plants: assimilation of ammonia is key—synthesis of most amino acids – Glutamine synthetase incorporates amino group • Glutamine serves as nitrogen donor for nucleic acids, etc. ...
Amino Acid Synthesis
... Non‐essential Amino Acid Biosynthesis • Transamination – Pyruvatealanine – Oxaloacetateaspartate – ‐ketoglutarateglutamate ...
... Non‐essential Amino Acid Biosynthesis • Transamination – Pyruvatealanine – Oxaloacetateaspartate – ‐ketoglutarateglutamate ...
Transcription/Translation foldable
... Cut out the steps of protein synthesis, and glue them in order on the back of your ...
... Cut out the steps of protein synthesis, and glue them in order on the back of your ...
Transcrip_Translation
... Note how the tRNA to the left leaves and donates the amino acid to the neighbor on the right ...
... Note how the tRNA to the left leaves and donates the amino acid to the neighbor on the right ...
Proteins and Enzymes - Downtown Magnets High School
... • Proteins! • Speed up rates of reactions w/out being altered (changed). • Lower activation energies of reactions ...
... • Proteins! • Speed up rates of reactions w/out being altered (changed). • Lower activation energies of reactions ...
hwk- pg-331 - WordPress.com
... association an initiator methionine-tRNA with the small ribosomal subunit. The complex binds the mRNA at the 5' cap and scans for the AUG start codon. The large ribosomal subunit then binds, completing the ribosome, and translation proceeds. 2. The role of tRNA in translation is to shuttle the appro ...
... association an initiator methionine-tRNA with the small ribosomal subunit. The complex binds the mRNA at the 5' cap and scans for the AUG start codon. The large ribosomal subunit then binds, completing the ribosome, and translation proceeds. 2. The role of tRNA in translation is to shuttle the appro ...
Protein Synthesis
... Once out of the nucleus a ribosome will bind to the mRNA in two parts, the small sub unit and the large sub unit. The mRNA is initially bound to the aminoacyl site, or site A. At point A the tRNA molecule carrying the correct amino acid binds to the ribosome. The tRNA then binds to site P or peptidy ...
... Once out of the nucleus a ribosome will bind to the mRNA in two parts, the small sub unit and the large sub unit. The mRNA is initially bound to the aminoacyl site, or site A. At point A the tRNA molecule carrying the correct amino acid binds to the ribosome. The tRNA then binds to site P or peptidy ...
Chemistry Review
... Protein Synthesis Notes Protein Synthesis = to make proteins Translation = process of making proteins - decodes RNA to make chain of amino acids - chain of amino acids makes a PROTEIN - Location: cytoplasm ...
... Protein Synthesis Notes Protein Synthesis = to make proteins Translation = process of making proteins - decodes RNA to make chain of amino acids - chain of amino acids makes a PROTEIN - Location: cytoplasm ...
On the Origin of Language
... pairs in biosynthesis • Dashed boxes are hypothetical intermediate stages • Italicised codons do not match coevolution predictions ...
... pairs in biosynthesis • Dashed boxes are hypothetical intermediate stages • Italicised codons do not match coevolution predictions ...
CHM 105 - Test 3 Review
... 18. Give the name and type of base shown at right. H2N N N 19. What is the anticodon for the codon UUC? For what amino acid does this code? H 20. DNA is sometimes made from RNA by ________ viruses. This process is called _____________________? 21. Nucleic acids are synthesized from their ____ end to ...
... 18. Give the name and type of base shown at right. H2N N N 19. What is the anticodon for the codon UUC? For what amino acid does this code? H 20. DNA is sometimes made from RNA by ________ viruses. This process is called _____________________? 21. Nucleic acids are synthesized from their ____ end to ...
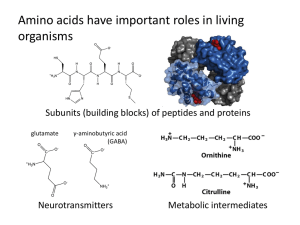
Amino Acid Sidechains have Different Chemical Characteristics
... Amino Acid Sidechains have Different Chemical Characteristics There are 20 amino acids that are the building blocks of all protein structures within our cells. Each amino acid has same backbone (NH2CHR-COOH). It is the R group that makes the amino acids different from one another. 1. Organize the 19 ...
... Amino Acid Sidechains have Different Chemical Characteristics There are 20 amino acids that are the building blocks of all protein structures within our cells. Each amino acid has same backbone (NH2CHR-COOH). It is the R group that makes the amino acids different from one another. 1. Organize the 19 ...
Protein Synthesis and Mutations Review Sheet 2014
... either use them in your answers or separately define or describe their relation to the concepts of protein synthesis or mutations. Protein Synthesis: Chapter 8.4 and 8.5 1. What are three differences between DNA and RNA? 2. Where does transcription take place and describe each step. Use the followin ...
... either use them in your answers or separately define or describe their relation to the concepts of protein synthesis or mutations. Protein Synthesis: Chapter 8.4 and 8.5 1. What are three differences between DNA and RNA? 2. Where does transcription take place and describe each step. Use the followin ...
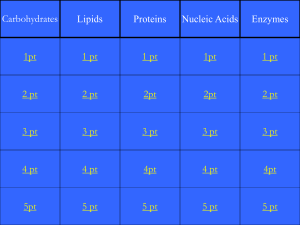
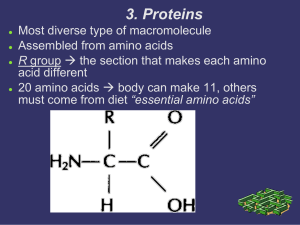
3. Proteins
... Most diverse type of macromolecule Assembled from amino acids R group the section that makes each amino acid different 20 amino acids body can make 11, others must come from diet “essential amino acids” ...
... Most diverse type of macromolecule Assembled from amino acids R group the section that makes each amino acid different 20 amino acids body can make 11, others must come from diet “essential amino acids” ...
Protein Synthesis - Helena High School
... 3. What are the three differences between RNA and DNA? a. b. c. 4. What is the goal of transcription? 5. Where does transcription take place in eukaryotic cells? 6. What RNA molecule copies the DNA code to serve as a template to make proteins? 7. If a section of DNA has the following order of bases, ...
... 3. What are the three differences between RNA and DNA? a. b. c. 4. What is the goal of transcription? 5. Where does transcription take place in eukaryotic cells? 6. What RNA molecule copies the DNA code to serve as a template to make proteins? 7. If a section of DNA has the following order of bases, ...
Biosynthesis

Biosynthesis (also called biogenesis or anabolism) is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined together to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides.The prerequisite elements for biosynthesis include: precursor compounds, chemical energy (e.g. ATP), and catalytic enzymes which may require coenzymes (e.g.NADH, NADPH). These elements create monomers, the building blocks for macromolecules. Some important biological macromolecules include: proteins, which are composed of amino acid monomers joined via peptide bonds, and DNA molecules, which are composed of nucleotides joined via phosphodiester bonds.