Protein Synthesis
... stranded molecule, we only need to copy one side of the DNA. The side we use is the 3’ side. (NO lagging strand!!!) • Tell a partner WHY you thing we use the 3’ side of the DNA, be ready to share. • The 3’ side of DNA is called the antisense strand. The 5’ (uncopied) side is called the sense strand. ...
... stranded molecule, we only need to copy one side of the DNA. The side we use is the 3’ side. (NO lagging strand!!!) • Tell a partner WHY you thing we use the 3’ side of the DNA, be ready to share. • The 3’ side of DNA is called the antisense strand. The 5’ (uncopied) side is called the sense strand. ...
amino acid letter codes
... differs from Aspartate by its amide nitrogen (AsN = "N"). [Not used very often are the letters B (either D or N) and Z (either E or Q)]. Q Gln "Q-tamine" ...
... differs from Aspartate by its amide nitrogen (AsN = "N"). [Not used very often are the letters B (either D or N) and Z (either E or Q)]. Q Gln "Q-tamine" ...
Chapter 30
... • Sequence elements in each tRNA are recognized by its specific synthetase including • 1) One or more of 3 bases in acceptor stem • 2) Base at position 73 “Discriminator base” • (3) In many, at least one anticodon base ...
... • Sequence elements in each tRNA are recognized by its specific synthetase including • 1) One or more of 3 bases in acceptor stem • 2) Base at position 73 “Discriminator base” • (3) In many, at least one anticodon base ...
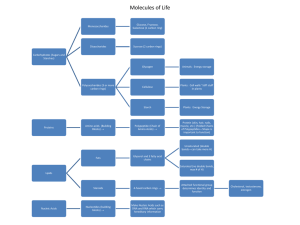
Molecules of Life Review Topics
... Enzymes –What are they? – protein catalysts Why important? – speed reactions in cells Activation energy – needed to start a reaction, enzymes make it lower Active site and substrate – what are they? Modes of enzyme action – lock-and-key, induced fit Conditions that affect enzyme action o Tem ...
... Enzymes –What are they? – protein catalysts Why important? – speed reactions in cells Activation energy – needed to start a reaction, enzymes make it lower Active site and substrate – what are they? Modes of enzyme action – lock-and-key, induced fit Conditions that affect enzyme action o Tem ...
Week 3
... makes is called the “tertiary structure”. And when multiple chains get together to form a polypeptide this overall shape is the “quaternary structure.” Nucleic Acids: DNA and RNA. DNA forms double strands that are exact complements of each other (like an imprint, or a negative copy). RNA is single s ...
... makes is called the “tertiary structure”. And when multiple chains get together to form a polypeptide this overall shape is the “quaternary structure.” Nucleic Acids: DNA and RNA. DNA forms double strands that are exact complements of each other (like an imprint, or a negative copy). RNA is single s ...
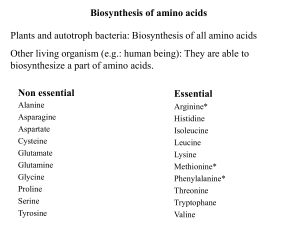
Biosynthesis of the nutritionally nonessential amino acids
... transferases Play Central Roles in Amino Acid Biosynthesis A. Synthesis from α-keto acids Alanine, aspartate, and Glutamate are synthesized by transfer of an amino group to the α-keto acids pyruvate, oxaloacetate, and α-ketoglutarate, respectively. Glutamate is unusual in that it can also be synthes ...
... transferases Play Central Roles in Amino Acid Biosynthesis A. Synthesis from α-keto acids Alanine, aspartate, and Glutamate are synthesized by transfer of an amino group to the α-keto acids pyruvate, oxaloacetate, and α-ketoglutarate, respectively. Glutamate is unusual in that it can also be synthes ...
Amino acid metabolism III. Brake down of amino acids
... • much of the catabolism of amino acids takes place in the liver • branched-chain amino acids are oxidized as fuels primarily in the muscles, adipose, kidney, and brain tissue ...
... • much of the catabolism of amino acids takes place in the liver • branched-chain amino acids are oxidized as fuels primarily in the muscles, adipose, kidney, and brain tissue ...
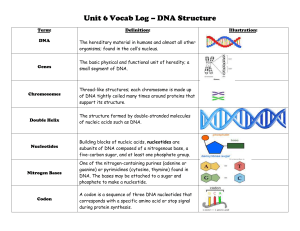
Unit 6 Vocab Log – DNA Structure Term: DNA Definition: The
... of DNA tightly coiled many times around proteins that support its structure. ...
... of DNA tightly coiled many times around proteins that support its structure. ...
Transcription
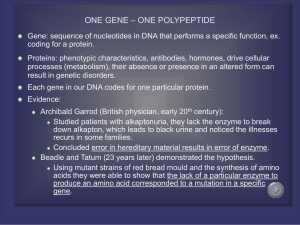
... (each of which is specified by its own gene) Modified to : One gene-one polypeptide hypothesis Transcription: synthesis of RNA under the direction of DNA (mRNA) Translation: actual synthesis of a polypeptide at ribosomes under the direction of mRNA ...
... (each of which is specified by its own gene) Modified to : One gene-one polypeptide hypothesis Transcription: synthesis of RNA under the direction of DNA (mRNA) Translation: actual synthesis of a polypeptide at ribosomes under the direction of mRNA ...
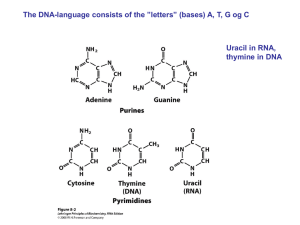
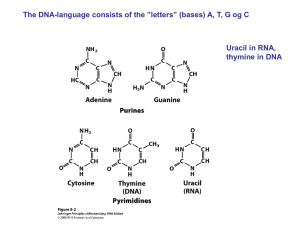
(DNA) and ribose (RNA)
... DNA can replicate itself by the help of numerous proteins. This is perhaps the most important characteristic of life! Life anywhere (in the universe!) without copying is difficult to envision ...
... DNA can replicate itself by the help of numerous proteins. This is perhaps the most important characteristic of life! Life anywhere (in the universe!) without copying is difficult to envision ...
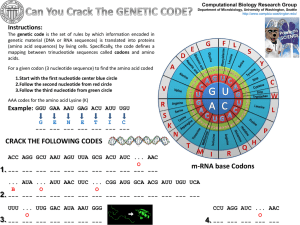
Activating Strategy AP Lesson #51 What is the code? What is
... • DNA to Protein Essay • Can you tell the story? ...
... • DNA to Protein Essay • Can you tell the story? ...
Biomolecules Review Game
... Maltose and Sucrose are isomers. What is an isomer (why do These taste different)? ...
... Maltose and Sucrose are isomers. What is an isomer (why do These taste different)? ...
Reading Guide
... 8. Which amino acid is the precursor for each of these neurotransmitters: GABA, dopamine, serotonin. Skip biosynthesis of essential amino acids and nucloetodes (questions 9-17 below aren’t covered this semester.) 9. Purine bases are synthesize right onto the molecule ____________________. 10. Five s ...
... 8. Which amino acid is the precursor for each of these neurotransmitters: GABA, dopamine, serotonin. Skip biosynthesis of essential amino acids and nucloetodes (questions 9-17 below aren’t covered this semester.) 9. Purine bases are synthesize right onto the molecule ____________________. 10. Five s ...
Slide 1
... • RNA molecule is single-stranded (rather than double stranded in DNA) • Uracil instead of Thymine. So in RNA Adenine binds with Uracil ...
... • RNA molecule is single-stranded (rather than double stranded in DNA) • Uracil instead of Thymine. So in RNA Adenine binds with Uracil ...
Biosynthesis

Biosynthesis (also called biogenesis or anabolism) is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined together to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides.The prerequisite elements for biosynthesis include: precursor compounds, chemical energy (e.g. ATP), and catalytic enzymes which may require coenzymes (e.g.NADH, NADPH). These elements create monomers, the building blocks for macromolecules. Some important biological macromolecules include: proteins, which are composed of amino acid monomers joined via peptide bonds, and DNA molecules, which are composed of nucleotides joined via phosphodiester bonds.