1.5 Page 4 - csfcbiology
... controls all the activities of a cell. It is able to do this as it carries information, which controls the synthesis of proteins. An important class of proteins is enzymes that control all metabolic reactions. Therefore, by controlling which proteins are made at a particular time in a particular typ ...
... controls all the activities of a cell. It is able to do this as it carries information, which controls the synthesis of proteins. An important class of proteins is enzymes that control all metabolic reactions. Therefore, by controlling which proteins are made at a particular time in a particular typ ...
Origins of Sugars in the Prebiotic World
... • If the nucleophile is the 3’-OH group of another NTP, then a nucleic acid is generated: polymer of nucleotides – Oligomers (“oligos”) short length (DNA/RNA polymers of long ...
... • If the nucleophile is the 3’-OH group of another NTP, then a nucleic acid is generated: polymer of nucleotides – Oligomers (“oligos”) short length (DNA/RNA polymers of long ...
RNA and PROTEIN SYNTHESIS 12-3
... TRANSCRIPTION DNA → RNA ____________ RNA→ Protein TRANSLATION ___________ ...
... TRANSCRIPTION DNA → RNA ____________ RNA→ Protein TRANSLATION ___________ ...
Chapter Outline
... polar (hydrophilic) phosphate group; the phosphate group usually bonds to another organic group (designated by R). 2. The hydrocarbon chains of the fatty acids become the nonpolar (hydrophobic) tails. 3. Phospholipids arrange themselves in a double layer in water, so the polar heads face toward wate ...
... polar (hydrophilic) phosphate group; the phosphate group usually bonds to another organic group (designated by R). 2. The hydrocarbon chains of the fatty acids become the nonpolar (hydrophobic) tails. 3. Phospholipids arrange themselves in a double layer in water, so the polar heads face toward wate ...
Midterm Practice Test
... 53) What products are made specifically in the light dependent reactions of photosynthesis and why are they necessary? 54) What molecule is most responsible for releasing energy for many different cellular process? Where is that energy stored within the molecule? 55) Explain how an antiport works. I ...
... 53) What products are made specifically in the light dependent reactions of photosynthesis and why are they necessary? 54) What molecule is most responsible for releasing energy for many different cellular process? Where is that energy stored within the molecule? 55) Explain how an antiport works. I ...
word - My eCoach
... c. The double strand unwinds and unzips while it is being duplicated. d. The process is catalyzed by enzymes called DNA mutagens. ...
... c. The double strand unwinds and unzips while it is being duplicated. d. The process is catalyzed by enzymes called DNA mutagens. ...
lecture CH21 chem131pikul
... • They increase the rate of a reaction (106 to 1012 times faster), but are unchanged themselves. • Enzymes are very specific; each enzyme catalyzes a certain reaction or type of reaction only. • The names of most enzymes end with the suffix -ase like peptidase, lipase, and hydrolase • A cofactor ...
... • They increase the rate of a reaction (106 to 1012 times faster), but are unchanged themselves. • Enzymes are very specific; each enzyme catalyzes a certain reaction or type of reaction only. • The names of most enzymes end with the suffix -ase like peptidase, lipase, and hydrolase • A cofactor ...
1 - 嘉義大學
... Which of the following statements apply (applies) to the oxidation of fatty acids? 1. The process takes place in the cytosol of mammalian cells. 2. Carbon atoms are removed from the acyl chain one at a time. 3. Before oxidation, fatty acids must be converted to their CoA derivatives. ...
... Which of the following statements apply (applies) to the oxidation of fatty acids? 1. The process takes place in the cytosol of mammalian cells. 2. Carbon atoms are removed from the acyl chain one at a time. 3. Before oxidation, fatty acids must be converted to their CoA derivatives. ...
Document
... Amino acids = More than proteins! Creatine Glutathione Heme Nitric oxide Hormones Neurotransmitters ...
... Amino acids = More than proteins! Creatine Glutathione Heme Nitric oxide Hormones Neurotransmitters ...
Molecules of Life
... monomers with a ribose sugar and the nitrogenous bases adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), and uracil (U); usually single-stranded; functions in protein synthesis and as the genome of some viruses. ...
... monomers with a ribose sugar and the nitrogenous bases adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), and uracil (U); usually single-stranded; functions in protein synthesis and as the genome of some viruses. ...
Physiology of Cells
... • Remaining portions (exons) are spliced back together • mRNA travels to the nucleus via nuclear pores ...
... • Remaining portions (exons) are spliced back together • mRNA travels to the nucleus via nuclear pores ...
English Version
... (1) The Respiratory Chain Uses Molecular Oxygen to Oxidize NADH and FADH2 (2) Phosphorylation of ADP to ATP is Coupled With Redox Reactions (3) The Efficiency of Glucose of Oxidation is Close to 40% (4) Oxidative Phosphorylation is Regulated (5) Shuttle Systems Indirectly Convey Cytosolic NADH into ...
... (1) The Respiratory Chain Uses Molecular Oxygen to Oxidize NADH and FADH2 (2) Phosphorylation of ADP to ATP is Coupled With Redox Reactions (3) The Efficiency of Glucose of Oxidation is Close to 40% (4) Oxidative Phosphorylation is Regulated (5) Shuttle Systems Indirectly Convey Cytosolic NADH into ...
Essential Amino Acids
... Each day, your body requires 20 to 30 grams of protein to build important molecules, and any excess proteins you eat are broken down into their amino acids and used for energy or converted and stored as fat. Protein breakdown produces the waste urea, which is filtered from the blood by the kidneys. ...
... Each day, your body requires 20 to 30 grams of protein to build important molecules, and any excess proteins you eat are broken down into their amino acids and used for energy or converted and stored as fat. Protein breakdown produces the waste urea, which is filtered from the blood by the kidneys. ...
macromolecules
... The Role of Carbon in Organisms: • Carbon compounds that come from living organisms are called organic compounds. • Two carbon atoms can form various types of covalent bonds—single, double or triple. ...
... The Role of Carbon in Organisms: • Carbon compounds that come from living organisms are called organic compounds. • Two carbon atoms can form various types of covalent bonds—single, double or triple. ...
Section 3.3: Carbon Compounds Building Blocks of Cells • The parts
... In a complex organism, cells recognize neighboring cells by the short, branched chains of varying sugar units on their outer surface. ...
... In a complex organism, cells recognize neighboring cells by the short, branched chains of varying sugar units on their outer surface. ...
1 - VCOMcc
... c. glutamate and glutamine d. all of the above 5. For Hartnup’s disease neutral amino acids such as phenylalanine cannot be imported into intestinal epithelial cells. However, dipeptides that contain phenylalanine can be imported normally. This suggests that patients with Hartup’s disease a. have in ...
... c. glutamate and glutamine d. all of the above 5. For Hartnup’s disease neutral amino acids such as phenylalanine cannot be imported into intestinal epithelial cells. However, dipeptides that contain phenylalanine can be imported normally. This suggests that patients with Hartup’s disease a. have in ...
Conceptual Translation as a part of Gene Expression
... RNA (G, A, U, C) and the nucleotide sequence in DNA (G, A, T, C respectively).The next process of converting that information from nucleotide sequence in RNA to the mRNA. The sequence after skipping the intron part is m-RNA which contains exons only. The next process of converting that information f ...
... RNA (G, A, U, C) and the nucleotide sequence in DNA (G, A, T, C respectively).The next process of converting that information from nucleotide sequence in RNA to the mRNA. The sequence after skipping the intron part is m-RNA which contains exons only. The next process of converting that information f ...
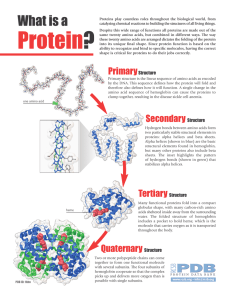
Biosynthesis

Biosynthesis (also called biogenesis or anabolism) is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined together to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides.The prerequisite elements for biosynthesis include: precursor compounds, chemical energy (e.g. ATP), and catalytic enzymes which may require coenzymes (e.g.NADH, NADPH). These elements create monomers, the building blocks for macromolecules. Some important biological macromolecules include: proteins, which are composed of amino acid monomers joined via peptide bonds, and DNA molecules, which are composed of nucleotides joined via phosphodiester bonds.