Biology Standards Based Benchmark Assessment
... a. It must occur before a cell can divide. b. Two complementary strands are duplicated. c. The double strand unwinds and unzips while it is being duplicated. d. The process is catalyzed by enzymes called DNA mutagens. 36. The enzymes responsible for matching complimentary nucleotides to the exposed ...
... a. It must occur before a cell can divide. b. Two complementary strands are duplicated. c. The double strand unwinds and unzips while it is being duplicated. d. The process is catalyzed by enzymes called DNA mutagens. 36. The enzymes responsible for matching complimentary nucleotides to the exposed ...
What is BIOLOGY?
... What particles are found in atoms? Where are they located? What electric charge does each have? What is an ion? Why is Carbon special? What atoms (carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen, phosphorus, sulfur) and ions (sodium, potassium, calcium, chloride) are important to living things? Be able to give t ...
... What particles are found in atoms? Where are they located? What electric charge does each have? What is an ion? Why is Carbon special? What atoms (carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen, phosphorus, sulfur) and ions (sodium, potassium, calcium, chloride) are important to living things? Be able to give t ...
Protein mteabolism L..
... Folic acid is a member of vitamin B complex. It plays an important role in synthesis of purines and thymidine monophosphate (TMP) and so DNA synthesis. Deficiency of folic acid leads to diminished DNA synthesis and inhibit cell division resulting in meglaoblastic anemia (accumulation of large, immat ...
... Folic acid is a member of vitamin B complex. It plays an important role in synthesis of purines and thymidine monophosphate (TMP) and so DNA synthesis. Deficiency of folic acid leads to diminished DNA synthesis and inhibit cell division resulting in meglaoblastic anemia (accumulation of large, immat ...
Chapter 5: What are the major types of organic molecules?
... Examine the structural formulas for glucose, fructose, and galactose. Note that they are all isomers of each other (i.e. they have the chemical formula C6H12O6). Glucose and galactose are structural isomers of fructose, while glucose and galactose are diastereomers (a type of stereoisomer). ...
... Examine the structural formulas for glucose, fructose, and galactose. Note that they are all isomers of each other (i.e. they have the chemical formula C6H12O6). Glucose and galactose are structural isomers of fructose, while glucose and galactose are diastereomers (a type of stereoisomer). ...
清华大学本科生考试试题专用纸
... A. The ATP molecule is kinetically unstable and is thus consumed within about one minute following its formation in cells. B. ATP provides free energy to a thermodynamically unfavorable reactions by group transfer, always donating a Pi to form a covalent intermediate. C. ATP can be regenerated by co ...
... A. The ATP molecule is kinetically unstable and is thus consumed within about one minute following its formation in cells. B. ATP provides free energy to a thermodynamically unfavorable reactions by group transfer, always donating a Pi to form a covalent intermediate. C. ATP can be regenerated by co ...
Amino Acid Exporter: A Tool for the Next
... of why bacterial cells possess these transporters to export L-amino acids J Biotechnol Biomater ISSN:2155-952X JBTBM an open access journal ...
... of why bacterial cells possess these transporters to export L-amino acids J Biotechnol Biomater ISSN:2155-952X JBTBM an open access journal ...
Organic Chemistry
... Other Lipids • 4 Other types of biologically important Lipids – Phospholipids - Important for membrane structure – Steroids - eg. Cholesterol & testosterone. Provide membrane support / serve as hormones – Terpenes - serve as important components of pigments – Prostaglandins - appear to act like loc ...
... Other Lipids • 4 Other types of biologically important Lipids – Phospholipids - Important for membrane structure – Steroids - eg. Cholesterol & testosterone. Provide membrane support / serve as hormones – Terpenes - serve as important components of pigments – Prostaglandins - appear to act like loc ...
Poster
... Staph infection is caused by the bacteria Staphylococcus aureus, which have become increasingly resistant to a broad spectrum of antibiotics. New ways to combat these bacteria are needed. The Greenfield High School SMART (Students Modeling A Research Topic) Team is modeling the enzyme GatCAB using 3 ...
... Staph infection is caused by the bacteria Staphylococcus aureus, which have become increasingly resistant to a broad spectrum of antibiotics. New ways to combat these bacteria are needed. The Greenfield High School SMART (Students Modeling A Research Topic) Team is modeling the enzyme GatCAB using 3 ...
Building Monomers of Macromolecules
... Atoms join together to form molecules. These molecules are held together by bonds. In this lab you will use toothpicks to represent the bonds. Important note: use one toothpick to represent a single covalent bond, and two toothpicks to represent a double covalent bond. Remember, covalent bonds are b ...
... Atoms join together to form molecules. These molecules are held together by bonds. In this lab you will use toothpicks to represent the bonds. Important note: use one toothpick to represent a single covalent bond, and two toothpicks to represent a double covalent bond. Remember, covalent bonds are b ...
5 questions per round and 9 rounds with 10 team tourney
... 35. What is added to the 3’ end of the premRNA before leaving the nucleus? (poly A tail) 36. What are the pieces that link together to make a protein? (amino acids) 37. What enzyme seals the okazaki fragments? (DNA ligase) 38. What enzyme is responsible for unkinking and uncoiling the DNA? (topoisom ...
... 35. What is added to the 3’ end of the premRNA before leaving the nucleus? (poly A tail) 36. What are the pieces that link together to make a protein? (amino acids) 37. What enzyme seals the okazaki fragments? (DNA ligase) 38. What enzyme is responsible for unkinking and uncoiling the DNA? (topoisom ...
Biology Standards (For the Year) *DO NOT LOSE THIS!* CST
... attached to a certain amino acids. The # and order of AA creates that specific protein coded for in the DNA. 4b) DNA has 4 nucleotides adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), and cytosine (C). Within the double stranded DNA, A pairs with T and G with C. However, RNA has Uracil (U) instead of T. There ...
... attached to a certain amino acids. The # and order of AA creates that specific protein coded for in the DNA. 4b) DNA has 4 nucleotides adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), and cytosine (C). Within the double stranded DNA, A pairs with T and G with C. However, RNA has Uracil (U) instead of T. There ...
Transcription: Synthesizing RNA from DNA
... complementary to the template strand of DNA (except T’s are U’s) Does not require a PRIMER to start building (as in replication). Therefore elongation starts as soon as RNA polymerase complex moves to gene and binds to promoter. Promoter does NOT get transcribed As soon as RNA Polymerase compl ...
... complementary to the template strand of DNA (except T’s are U’s) Does not require a PRIMER to start building (as in replication). Therefore elongation starts as soon as RNA polymerase complex moves to gene and binds to promoter. Promoter does NOT get transcribed As soon as RNA Polymerase compl ...
Chalkboard Challenge
... 2 of 21) Which two (of the 3 total) reactants are used during the light reactions of photosynthesis? ...
... 2 of 21) Which two (of the 3 total) reactants are used during the light reactions of photosynthesis? ...
Document
... • The structure of amino acids and their properties (a)Amino acids have both acid and base properties (b)Aromatic amino acids absorb light in the near-ultraviolet (c)All amino acids except glycine show asymmetry ...
... • The structure of amino acids and their properties (a)Amino acids have both acid and base properties (b)Aromatic amino acids absorb light in the near-ultraviolet (c)All amino acids except glycine show asymmetry ...
lecture 5
... the “factories” in which the synthesis of proteins occurs. -The large ribosomal subunit catalyzes formation of the peptide bonds that link amino acid residues in a protein. -The small subunit binds mRNA and is responsible for the accuracy of translation by ensuring correct base-pairing between the c ...
... the “factories” in which the synthesis of proteins occurs. -The large ribosomal subunit catalyzes formation of the peptide bonds that link amino acid residues in a protein. -The small subunit binds mRNA and is responsible for the accuracy of translation by ensuring correct base-pairing between the c ...
Mechanisms of hormonal regulation and pathologies of protein
... •The others are classed as "essential" amino acids and must be obtained in the diet ...
... •The others are classed as "essential" amino acids and must be obtained in the diet ...
Organic Chemistry Answer Key
... quaternary structures of a protein molecule are necessary for the protein to function correctly. Interactions occur between amino and carboxyl groups of amino acids. Carbohydrates are composed of C, H, and O. Monosaccharides are the building blocks of carbohydrates. Two monosaccharides form a disacc ...
... quaternary structures of a protein molecule are necessary for the protein to function correctly. Interactions occur between amino and carboxyl groups of amino acids. Carbohydrates are composed of C, H, and O. Monosaccharides are the building blocks of carbohydrates. Two monosaccharides form a disacc ...
Peptide Structure: The Building Blocks of Life
... Peptides are short polymers of amino acids linked by peptide (amide) bonds. What is an amino acid? o An amino acid is a molecule containing… an amine group a carboxylic acid a side chain (R-varies) ...
... Peptides are short polymers of amino acids linked by peptide (amide) bonds. What is an amino acid? o An amino acid is a molecule containing… an amine group a carboxylic acid a side chain (R-varies) ...
Fill in the blank 12-2 and 12
... ______________________ bonds between base pairs are broken and the two strands of DNA unwind. The principal enzyme involved in DNA replication is _______________________. DNA polymerase joins individual nucleotides to produce a DNA molecule and then “proofreads” each new DNA strand. ...
... ______________________ bonds between base pairs are broken and the two strands of DNA unwind. The principal enzyme involved in DNA replication is _______________________. DNA polymerase joins individual nucleotides to produce a DNA molecule and then “proofreads” each new DNA strand. ...
Unit 4 - University of Colorado Boulder
... expression (What steps are similar? What extra steps do we see in eukaryotes?). 12. List functions that are performed by various RNA molecules during the steps involved in transcription and translation. 13. Recognize the many steps of gene expression in which complementary base pairs play a key role ...
... expression (What steps are similar? What extra steps do we see in eukaryotes?). 12. List functions that are performed by various RNA molecules during the steps involved in transcription and translation. 13. Recognize the many steps of gene expression in which complementary base pairs play a key role ...
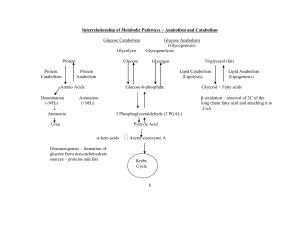
Biosynthesis

Biosynthesis (also called biogenesis or anabolism) is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined together to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides.The prerequisite elements for biosynthesis include: precursor compounds, chemical energy (e.g. ATP), and catalytic enzymes which may require coenzymes (e.g.NADH, NADPH). These elements create monomers, the building blocks for macromolecules. Some important biological macromolecules include: proteins, which are composed of amino acid monomers joined via peptide bonds, and DNA molecules, which are composed of nucleotides joined via phosphodiester bonds.