Enzyme Worksheet
... carbohydrates, triglycerides or lipids, polypeptides or proteins, and nucleic acids such as DNA & RNA). Carbohydrates and lipids are made of only carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen (CHO). Proteins are made of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen (CHON). Nucleic acids such as DNA and RNA contain carbon, ...
... carbohydrates, triglycerides or lipids, polypeptides or proteins, and nucleic acids such as DNA & RNA). Carbohydrates and lipids are made of only carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen (CHO). Proteins are made of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen (CHON). Nucleic acids such as DNA and RNA contain carbon, ...
The Origins Of Life
... of the fatty acid and glycerol A long carbon skeleton ending with carboxyl groups The carboxyl group may differ from each other in their functional group, designating the name of the acid Extremely hydrophobic ...
... of the fatty acid and glycerol A long carbon skeleton ending with carboxyl groups The carboxyl group may differ from each other in their functional group, designating the name of the acid Extremely hydrophobic ...
Organic Chemistry - Biology Junction
... Types of fats • Saturated fats have long chains with no double-bonds • Unsaturated fats have double bonds • Polyunsaturated fats have many double bonds – Each time a double bond is encountered, the molecule "Bends" slightly, resulting in a lower density of the lipid. This makes the molecule more li ...
... Types of fats • Saturated fats have long chains with no double-bonds • Unsaturated fats have double bonds • Polyunsaturated fats have many double bonds – Each time a double bond is encountered, the molecule "Bends" slightly, resulting in a lower density of the lipid. This makes the molecule more li ...
Organic Chemistry - Welcome to Cherokee High School
... Types of fats • Saturated fats have long chains with no double-bonds • Unsaturated fats have double bonds • Polyunsaturated fats have many double bonds – Each time a double bond is encountered, the molecule "Bends" slightly, resulting in a lower density of the lipid. This makes the molecule more li ...
... Types of fats • Saturated fats have long chains with no double-bonds • Unsaturated fats have double bonds • Polyunsaturated fats have many double bonds – Each time a double bond is encountered, the molecule "Bends" slightly, resulting in a lower density of the lipid. This makes the molecule more li ...
Honors Biology 11/9
... protein to another. After enough of this bashing and bonding, the solitary egg proteins are solitary no longer. They致e formed a network of interconnected proteins. The water in which the proteins once floated is captured and held in the protein web. If you leave the eggs at a high temperature too lo ...
... protein to another. After enough of this bashing and bonding, the solitary egg proteins are solitary no longer. They致e formed a network of interconnected proteins. The water in which the proteins once floated is captured and held in the protein web. If you leave the eggs at a high temperature too lo ...
Microbial Genetics
... half from the “parent” half newly synthesized. It’s initiated at a replication fork; DNA must be unwound and unbound into two single strands. ...
... half from the “parent” half newly synthesized. It’s initiated at a replication fork; DNA must be unwound and unbound into two single strands. ...
Slide 1
... forms a non-covalent homochiral octamer in a mass spectrometer via electrospray ionization Octamer was found to be chiroselective—formed from enantiopure samples, but not racemic ones! one L-serine selects to bind with 7 more L-enantiomers Also found that they could incorporate more than one type ...
... forms a non-covalent homochiral octamer in a mass spectrometer via electrospray ionization Octamer was found to be chiroselective—formed from enantiopure samples, but not racemic ones! one L-serine selects to bind with 7 more L-enantiomers Also found that they could incorporate more than one type ...
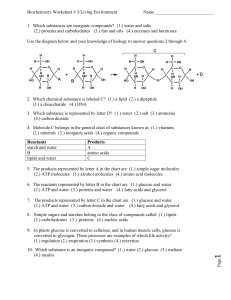
1. Which substances are inorganic compounds?
... (2.) ATP molecules (3.) alcohol molecules (4.) amino acid molecules 6. The reactants represented by letter B in the chart are (1.) glucose and water (2.) ATP and water (3.) proteins and water (4.) fatty acids and glycerol 7. The products represented by letter C in the chart are (1.) glucose and wate ...
... (2.) ATP molecules (3.) alcohol molecules (4.) amino acid molecules 6. The reactants represented by letter B in the chart are (1.) glucose and water (2.) ATP and water (3.) proteins and water (4.) fatty acids and glycerol 7. The products represented by letter C in the chart are (1.) glucose and wate ...
BIo Exam Trashketball Review Questions
... A/An _______________ consists of a central carbon atom bonded to a hydrogen atom, a carboxyl group, an amino group, and a “side group”. ...
... A/An _______________ consists of a central carbon atom bonded to a hydrogen atom, a carboxyl group, an amino group, and a “side group”. ...
UNIT 3 Biochem Test Study Guide
... ●Chapter 6 in the book, especially page 167 (take a book home if needed) & 924-928 ●all your notes from Unit 3 Concepts Listed Below: What does organic mean? Indicators used in the lab (Identifying Organic Compound) and what each identifies How to make models of molecules, how to draw them and how t ...
... ●Chapter 6 in the book, especially page 167 (take a book home if needed) & 924-928 ●all your notes from Unit 3 Concepts Listed Below: What does organic mean? Indicators used in the lab (Identifying Organic Compound) and what each identifies How to make models of molecules, how to draw them and how t ...
DNA replication to translation
... mRNA strand (single, linear) – temporary, as needed (5' -> 3') AUGGAAUUCUCGCUC (from template strand) note: by taking information from the template (antisense) strand of DNA, mRNA becomes the coding sequence ...
... mRNA strand (single, linear) – temporary, as needed (5' -> 3') AUGGAAUUCUCGCUC (from template strand) note: by taking information from the template (antisense) strand of DNA, mRNA becomes the coding sequence ...
Principles of BIOCHEMISTRY
... Fumarate formed in urea cycle enters citric acid cycle and is converted to oxaloacetate. Fates of oxaloacetate: (1) transamination to aspartate, ...
... Fumarate formed in urea cycle enters citric acid cycle and is converted to oxaloacetate. Fates of oxaloacetate: (1) transamination to aspartate, ...
No Slide Title
... Golgi apparatus where it is processed and packaged in ________. vesicles 10) Some protein is _________ secreted out of the cell by vesicles moving towards, and fusing with, the plasma membrane. 11) In addition to carbon, hydrogen and oxygen, proteins always contain ________. nitrogen 12) A protein c ...
... Golgi apparatus where it is processed and packaged in ________. vesicles 10) Some protein is _________ secreted out of the cell by vesicles moving towards, and fusing with, the plasma membrane. 11) In addition to carbon, hydrogen and oxygen, proteins always contain ________. nitrogen 12) A protein c ...
CH 3 Notes
... b) phospholipids: two fatty acids joined to glycerol ( cell membrane) c) wax: long fatty acid chain joined to a long alcohol chain 3. Steroids: four fused carbon rings with different functional groups a) Examples: testosterone and cholesterol Lipids ...
... b) phospholipids: two fatty acids joined to glycerol ( cell membrane) c) wax: long fatty acid chain joined to a long alcohol chain 3. Steroids: four fused carbon rings with different functional groups a) Examples: testosterone and cholesterol Lipids ...
Unit 1 – Biochemisty
... I can list the four biological molecule groups and give examples of each. (Including monomers & polymers) ...
... I can list the four biological molecule groups and give examples of each. (Including monomers & polymers) ...
Amino Acids
... hydrophobicity. The side chain of proline and its α-amino group form a ring structure. Proline gives the fibrous structure of collagen, and interrupts the α-helices found in globular proteins. ...
... hydrophobicity. The side chain of proline and its α-amino group form a ring structure. Proline gives the fibrous structure of collagen, and interrupts the α-helices found in globular proteins. ...
activity 2-2. organic chemistry
... “lock-and-key” arrangement in which the enzyme and the substance it reacts with (the substrate) join together to form an enzyme-substrate complex. When the reaction is completed, the enzyme and the newly formed reaction products separate, leaving the enzyme unchanged. Enzymes are highly efficient ca ...
... “lock-and-key” arrangement in which the enzyme and the substance it reacts with (the substrate) join together to form an enzyme-substrate complex. When the reaction is completed, the enzyme and the newly formed reaction products separate, leaving the enzyme unchanged. Enzymes are highly efficient ca ...
Tutorial Kit (Biochemistry-200 L)
... Lipids: Lipids are used to store energy and are an important part of the cell membrane. Nucleic Acids: Nucleic acids store and transmit hereditary or genetic information. There are two kinds of nucleic acids: ribonucleic acid (RNA) and deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). Nucleotides are responsible for mor ...
... Lipids: Lipids are used to store energy and are an important part of the cell membrane. Nucleic Acids: Nucleic acids store and transmit hereditary or genetic information. There are two kinds of nucleic acids: ribonucleic acid (RNA) and deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). Nucleotides are responsible for mor ...
Biosynthesis

Biosynthesis (also called biogenesis or anabolism) is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined together to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides.The prerequisite elements for biosynthesis include: precursor compounds, chemical energy (e.g. ATP), and catalytic enzymes which may require coenzymes (e.g.NADH, NADPH). These elements create monomers, the building blocks for macromolecules. Some important biological macromolecules include: proteins, which are composed of amino acid monomers joined via peptide bonds, and DNA molecules, which are composed of nucleotides joined via phosphodiester bonds.